Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Clinical imaging modalities in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) such as MRI and ultrasound can detect morphologic changes associated with synovial inflammation. 18F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) can directly assess cellular metabolic activity and has been used to quantify joint inflammation in small studies. We developed a semi-automatic method to evaluate RA disease activity and assessed associations with measures of systemic inflammation.
Methods: Patients with RA underwent static FDG-PET 180 minutes after the intravenous administration of FDG tracer. Regions of interest were drawn around the hips, shoulders, knees, elbows, hands, and feet. An adaptive thresholding algorithm delineated and quantified regions of high tracer uptake in the regions of interest (Figure 1). Of the calculated values, the global partial volume corrected mean standardized uptake value considers all active sites proportional to their active volumes and was considered to best represent overall disease activity as an estimate of total body synovial metabolic activity. Correlations between synovial metabolic activity and systemic inflammation and clinical disease activity were assessed.
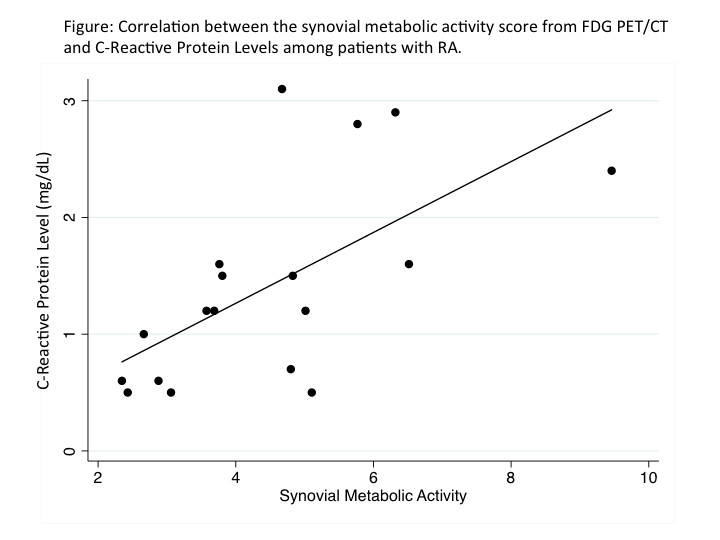
Results: A total of 18 patients (13 men) underwent FDG-PET. The average age was 57.7 (12.1) years with a mean DAS28(CRP) of 3.74 (1.29). The mean synovial metabolic activity score was 4.48 (1.78), with a range of 2.35-9.46 units. A significant correlation was observed between synovial metabolic activity and TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP (Figure 2). In contrast there was poor correlation with other measures of clinical disease such as swollen joints, tender joints, and results of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (Table). Among the 6 subjects with low clinical disease activity [DAS28(CRP) <3.2], there was a strong positive correlation between synovial metabolic activity and CRP (Rho=0.89, p=0.01) and IL-6 (Rho=0.89, p=0.02).
Conclusion: This study describes a novel semi-automated methodology to quantify synovial metabolic activity in RA using FDG-PET. This measure strongly correlates with measures of systemic inflammation, even among those with low disease activity. This methodology may have clinical and research utility in the evaluation of RA-specific systemic inflammation. 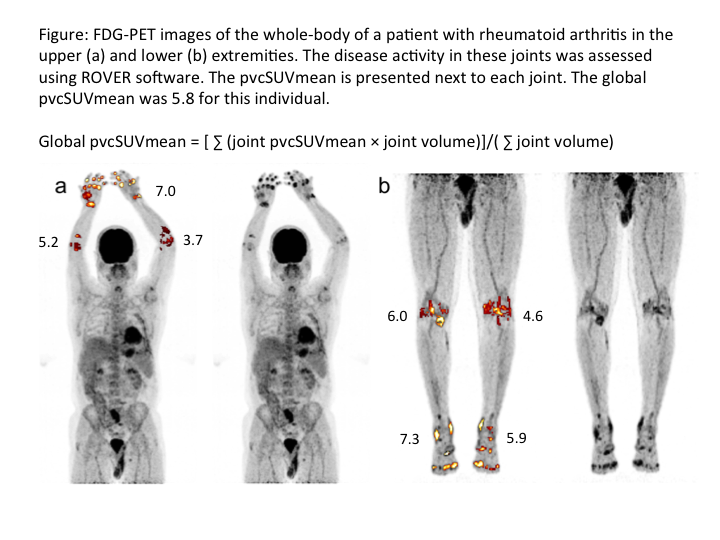
| |
||
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raynor W, Alehashemi S, Houshmand S, Werner TJ, Alavi A, Baker J. Evaluating Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Using Global Assessment of 18f-FDG Uptake in the Joints [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-using-global-assessment-of-18f-fdg-uptake-in-the-joints/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-using-global-assessment-of-18f-fdg-uptake-in-the-joints/