Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases I: Advanced Imaging in RA and Spondyloarthritides
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Plasma cytokines include tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-ƒ¿, interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 play important roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causing not only joint inflammation but also joint destruction. On the other hand, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can visualize fine distinction in the inflamed joint sensitively, and bone erosions on MRI are well relevant with prospective tangible erosions on X-ray. The aim of this study is to examine the relationship of pretreatment plasma inflammatory cytokines with MRI bone erosion progression in patients with RA patients.
Methods: We enrolled 89 newly diagnosed, untreated patients with RA. Contrast MRIs of the dominant hand and X-ray of hands and feet at baseline and 1 year later were performed. MR images were scored according to the latest OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic imaging score (RAMRIS) for synovitis, osteitis, bone erosions. Changes in MRI erosion scores (DRAMRIS erosion) from baseline to 1 year were calculated. X-ray were also assessed using the modified total Sharp score (mTSS). Plasma levels of ten cytokines were measured by electrochemiluminescence assay.
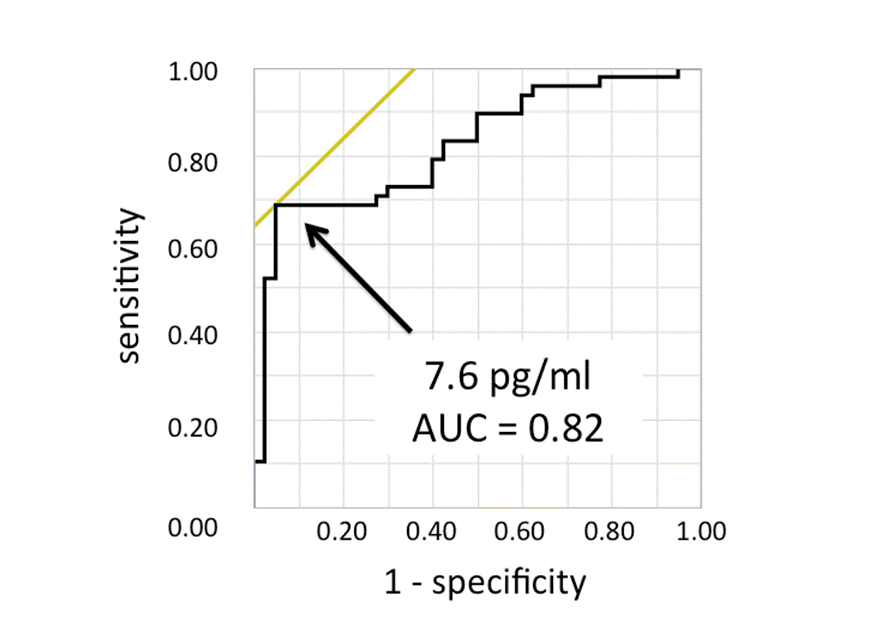
Results: The median age and symptom duration were 58 years and 3.2 months, respectively. The mean DAS28 decreased from 4.8 at baseline to 2.4 at 1 year. Progression in bone erosion were observed more frequently in MRI than in X-ray (54% in MRI vs 21% in X-ray, p = 0.005). Multiple linear regression model with baseline DAS28, seropositivity (positive for anti-CCP or RF), CRP and cytokines including IL-6, VEGF and IL-1ƒÀ as an independent variable revealed that baseline IL-6 levels and seropositivity were independent predictive factors for 1 year DRAMRIS erosion score. Receiver operating characteristic curve found the baseline IL-6 level of 7.6 pg/ml discriminated MRI erosion progression during 1 year with AUC of 0.82 with sensitivity of 69% and specificity of 95% (figure 1). We divided the patients into 4 groups (high, moderate-high, moderate-low and low) according to baseline IL-6 levels. The RAMRIS erosion progression was significantly dependent on baseline IL-6 concentration (p<0.001). While erosions in MRI significantly increased in high and moderate-high IL-6 groups (p < 0.05), mod-low and low IL-6 group showed slight improvement of MRI erosion at 1 year (figure 2)
Conclusion: In newly diagnosed, untreated RA patients, baseline plasma IL-6 levels predict 1-year MRI bone erosion progression in patients with RA. Figure 1
Figure 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kondo Y, Kaneko Y, Sugiura H, Matsumoto S, Nishina N, Jinzaki M, Takeuchi T. Pretreatment Plasma IL-6 Levels Are Responsible for Bone Erosion Progression on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pretreatment-plasma-il-6-levels-are-responsible-for-bone-erosion-progression-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pretreatment-plasma-il-6-levels-are-responsible-for-bone-erosion-progression-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/