Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
We evaluated the relationships between disease activity measures and C4d split products on erythrocytes (EC4d) in SLE subjects from a subset of the Hopkins Lupus cohort treated with methotrexate (MTX) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). We also determined compliance by determining blood levels of these medications.
Methods:
All subjects enrolled in this longitudinal study received MTX and HCQ for at least 6 months. Disease activity was assessed at each visit using the Physician Global Assessment (PGA) and the non-serological SELENA-SLEDAI (without low complement and anti-dsDNA components). Whole blood HCQ levels and red blood cells (RBC) methotrexate polyglutamate (MTXPG3) levels were determined using liquid chromatography and communicated to the clinicians within 4 days of blood collection. Serum C3 and C4 levels were determined using standard immunochemistry techniques while EC4d was measured by quantitative flow cytometry (expressed as net mean fluorescence intensity [MFI] and log normalized for the analysis). Clinicians were blinded to EC4d levels throughout the study. Statistical analysis consisted of a linear mixed effects model with random intercept and fixed slope. Kruskall Wallis ANOVA was used as appropriate. Estimates are shown as average ± SEM.
Results:
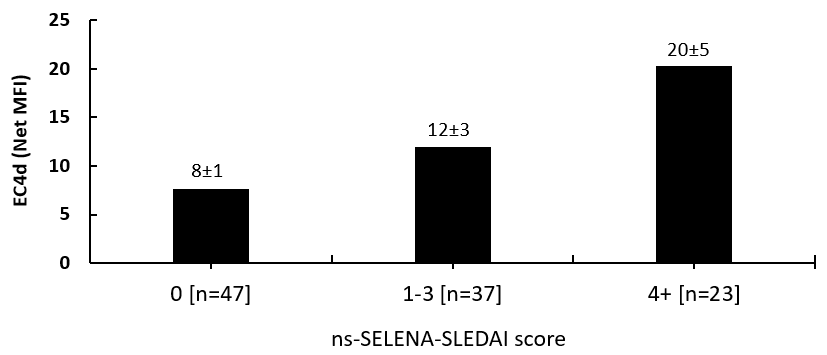
Twenty-three subjects (all females, 56±3 years, average [SEM]) were enrolled and followed prospectively for at least two consecutive visits (average 4.5 visits per subject, total of 107 study visits). At baseline, whole blood HCQ levels were 1245±115 ng/ml (average dose 379±10 mg/day) and average RBC MTXPG3 levels were 35±5 nmol/L (average dose 13.5±1.1 mg/week). Serum complement C3 was 105±6 mg/dl, C4 was 22±2 mg/dl, and EC4d density was 14±6 net MFI. Average ns-SELENA-SLEDAI and PGA were low in this population of SLE (1.3±0.3 and 0.6±0.1 points, respectively). Complete non-compliance to HCQ treatment (HCQ<50 ng/ml) was detected in one subject who was also not compliant to MTX therapy (RBC MTXPG<5 nmol/L). Following consultation, compliance to treatment improved as demonstrated by HCQ and MTXPG3 levels rising to 539 ng/mL and 22 nmol/L at subsequent visits, respectively. Changes in C3, C4, EC4d were not associated with the change in PGA (p>0.15). In contrast, the change in EC4d was associated with the change in ns-SELENA-SLEDAI (intercept: 0.2±0.6, slope estimate [Log net MFI]: 0.7±0.2, p=0.007). Of the 107 study visits, 23 presented with active disease (ns-SELENA-SLEDAI score of 4 points or above), and 47 presented with inactive disease (ns-SELENA-SLEDAI score of 0 point). As presented in the Figure, heightened EC4d expression was associated with higher disease activity (p<0.01).
Conclusion:
This pilot study indicates that complement C4d split products deposited on erythrocytes are associated with the ns-SELENA-SLEDAI. Further investigations are required to establish the utility of this marker in the management of SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Petri M, Qu Y, Conklin J, Brady K, Apilado R, Dervieux T. Complement C4d Split Products on Erythrocytes Are Associated with Composite Measure of Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Subjects Receiving Methotrexate and Hydroxychloroquine [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-c4d-split-products-on-erythrocytes-are-associated-with-composite-measure-of-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-subjects-receiving-methotrexate-and-hydroxychloroquine/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-c4d-split-products-on-erythrocytes-are-associated-with-composite-measure-of-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-subjects-receiving-methotrexate-and-hydroxychloroquine/