Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Human Etiology and Pathogenesis - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Arterial thrombosis is a major cause of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA),especially in anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive patients Recent studies suggest that platelet activation is implicated in this pathway1. Platelet activation results in proteolytic cleavage and shedding of platelet specific glycoprotein VI (GPVI) detected in the plasma as soluble GPVI (sGPVI). Shedding of GPVI occurs in response to stimuli, including engagement with the low affinity immunoglobulin G (IgG) receptor (FcγRIIa) on platelets2. ACPA cause platelet activation in vitro, through the FcγRIIa receptor1. We hypothesized that ACPA in patients with RA would cause platelet activation via ligand binding with FcγRIIa causing increased shedding of sGPVI.
Methods: Following ethics approval and informed consent, blood samples were taken from patients with RA (n=111) and OA (n=16). Healthy control samples (n=48) were obtained from volunteers. Demographic and clinical data were collected for all participants. Blood samples were processed as double spun platelet poor plasma. sGPVI levels were measured using a standardized ELISA. Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal – Wallis test was used to compare groups. SpearmanÕs Rank Correlation Coefficient was used to assess for associations between sGPVI levels and demographic and clinical markers. GraphPad Prism Version 6.05 was used for data analysis.
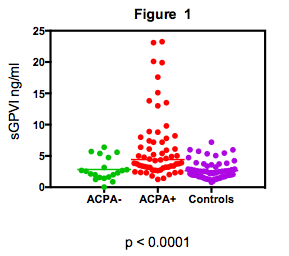
Results: Characteristics of ACPA positive RA vs ACPA negative RA are presented in Table 1. Patients with ACPA positive RA were significantly older, but no signficant correlation was observed between levels of sGPVI and age, CRP, fibrinogen, ESR, platetet count or DAS28 CRP. Patients with ACPA positive RA had significantly higher levels of sGPVI compared to ACPA negative RA and controls (Figure 1). Median (IQR) sGPVI levels were 4.3 ng/ml (3.80, 9.70) in ACPA positive RA , 2.4 ng/ml (31.5,4.3) in ACPA negative RA and 2.1ng/ml (1.6, 3.2) in controls (p<0.0001). ACPA titres correlated with sGPVI levels (r=0.32, p =0.0026).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that ACPA are associated with platelet activation as defined by increased levels of plasma sGPVI. These data could explain, in part, the aggravated cardiovascular risk in ACPA-positive patients . A monoclonal antibody targeting GPVI exists and has been shown to reduce myocardial infarct size in mice. The role of sGPVI as a marker of ACPA mediated platelet activation and therapeutic targeting of GPVI warrants further investigation. 1. Habets KL,Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:209 2. Newman PJ. Blood. 2010 Oct 28;116(17):3124-6.
| Table 1 Characteristics of Patients with ACPA positive RA vs ACPA negative RA | |||
| ACPA + RA | APCA – RA | P value | |
| Total Number | 65 | 21 | |
| Female, n (%) | 50 (76.9) | 18 (85.7) | ns |
| Male, n (%) | 15 (23) | 3 (14) | ns |
| Age, yr (median [IQR]) | 62 [53-71] | 52 [39-64] | 0.01 |
| CRP, mg/l (median [IQR]) | 8 [1-15.7] | 6 [2-20.2] | ns |
| ESR, mm/hr (median [IQR]) | 19 [11-32] | 15 [7-34] | ns |
| Fibrinogen g/l (mean +/- SEM) | 3.37 +/- 1.12 | 3.06 +/- 0.68 | ns |
| Platelet Count x 109(mean +/- SEM) | 282+/- 98 | 285 +/- 80 | ns |
| DAS28-CRP (Mean +/- SEM) | 3.78 +/- 1.51 | 4.37 +/- 2.2 | ns |
| ACPA ant-citrullinated protein antibodies, RA rheumatoid arthritis, CRP c- reactive protein, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate, DAS28 Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, IQR interquartile range, SEM standard error of the mean, ns not significant, sGPVI soluble Glycoprotein VI | |||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stack J, Madigan A, Helbert L, Redmond N, Dunne E, Kenny D, McCarthy GM. Glycoprotein VI: A Potential Target for ACPA-Mediated Platelet Activation? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glycoprotein-vi-a-potential-target-for-acpa-mediated-platelet-activation/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glycoprotein-vi-a-potential-target-for-acpa-mediated-platelet-activation/