Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Vasculitis IV
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Behcet’s
Disease (BD) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by recurrent oral
and genital ulcers, skin lesions, uveitis, and arthritis. Although the etiology
of BD still remains to be elucidated, several autoantibodies including
anti-alpha-enolase (ENO1) antibodies (AEA) have been associated with BD. AEA
are directed against endothelial cells and might contribute to vasculitis
leading to subsequent oral ulcer formation. This study was aimed to investigate
the association between AEA and clinical manifestations of BD.
Methods:
In
this study 64 BD patients and 30 age/sex matched healthy controls (HCs) were
enrolled. Western blot with recombinant ENO1 proteins were performed to detect
the presence of AEA in serum from BD patients and HCs. Subsequently, enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to determine the serum levels of AEA.
The association between BD manifestation and AEA levels were examined.
Results:
AEA
were present in 14 (82.4%) of 17 BD patients as compared to 6 (66.7%) of 9 HCs
on Western blot. Serum levels of AEA tended to be increased in BD patients
compared to HCs. (Mean ± SE : 1543 ± 160 vs. 1067 ± 144, p=
0.06). Number of oral ulcers tended to correlate with serum levels of AEA (r = 0.238,
p = 0.06 by Spearmann). BD patients with oral ulcers were grouped into a
mild (number of oral ulcer is less than or equal to 2) and a severe (number of
oral ulcer is greater than 2) disease based on the cumulative number of oral
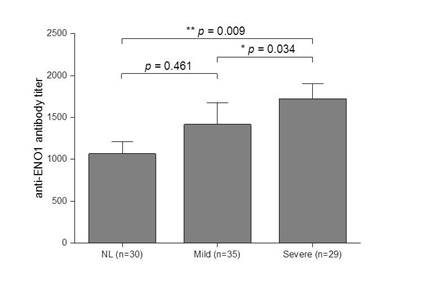
ulcers in the preceding 4 weeks prior to blood sampling. AEA levels differed
between HCs, the BD patients mild and those with extensive oral ulcers (p =
0.04 Kruskal-Wallis). Patients with extensive oral ulcers exhibited significantly
higher levels of AEA than those with mild oral ulcers (1722 ± 178 vs. 1416 ± 257, p =
0.03), and HCs
(1722 ± 178
vs. 1067 ±144, p < 0.01). Skin lesions, uveitis, and arthritis had no association
with serum AEA levels.
Conclusion:
BD
patients with severe oral ulcers have increased serum levels of AEA than those
with mild oral ulcers and HCs, suggesting a possible pathogenic role of AEA in
the oral ulcer formation. A treatment targeting AEA might offer a new
therapeutic option for BD associated severe oral ulcer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kang SE, Lee SJ, Park JK, Lee JY, Lee EY, Lee EB, Song YW. Increased Serum Levels of IgG Antibodies Against to Alpha-Enolase Are Associated with Severity of Oral Ulcers in Patients with Behcet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-igg-antibodies-against-to-alpha-enolase-are-associated-with-severity-of-oral-ulcers-in-patients-with-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-igg-antibodies-against-to-alpha-enolase-are-associated-with-severity-of-oral-ulcers-in-patients-with-behcets-disease/