Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis
(PsA), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are associated with an increased risk for
cardiovascular disease (CVD). While
management of traditional CVD risk factors improves outcomes, it is unclear to what
degree CVD risk factors are recognized and managed in patients with these
inflammatory diseases. The objectives of this study were the following: 1) to
determine the prevalence and incidence of hypertension (HTN), hyperlipidemia
(HL), and diabetes mellitus (DM) among patients with PsA, psoriasis and RA
compared to the general population, and 2) to examine the treatment of incident
HTN, HL, and DM among patients with RA, PsA, and psoriasis compared to the
general population.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was
performed in The Health Improvement Network (THIN), a medical record database
in the United Kingdom, among patients with PsA, psoriasis, RA and controls from
the general population matched on general practice and start date
(1994-2014). Logistic regression
analysis was used to examine the relative prevalence of HTN, HL, and DM
(defined by diagnosis codes) in RA, PsA, and psoriasis compared to controls
after adjusting for age and sex.
Cohort studies were performed to determine the incidence of HTN, HL, DM,
the hazard ratios for each outcome adjusting for
potential confounders, and the receipt of appropriate therapy within one year
following these diagnoses.
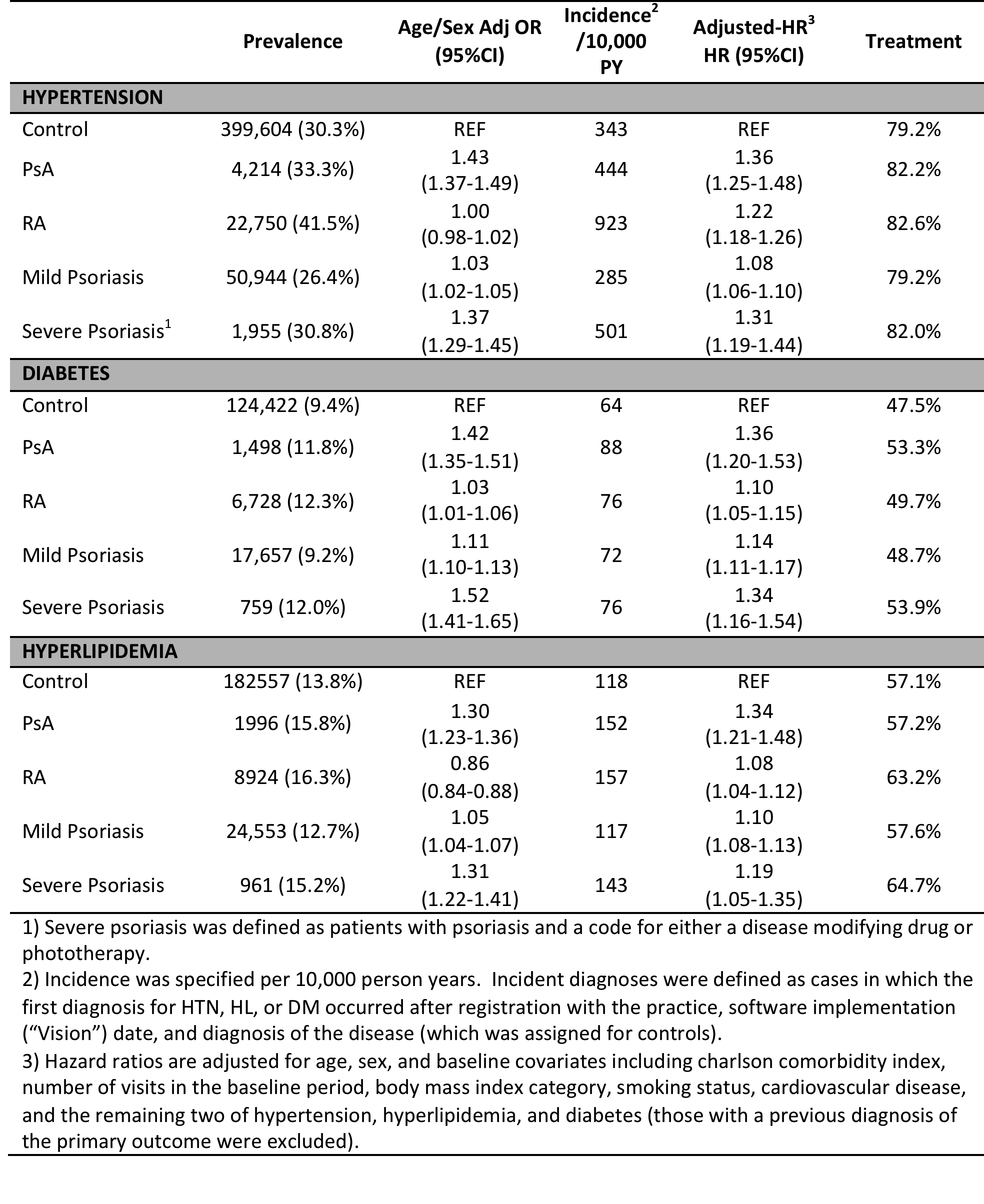
Results: Study subjects included 12,666 patients
with PsA, 193,053 with psoriasis, 54,890 with RA and 1,319,542 matched
controls. In patients with PsA, the
age/sex-adjusted prevalence of HTN (OR 1.43; 95% CI 1.37-1.49), HL (OR 1.30;
95% CI 1.23-1.36), and DM (OR 1.42; 95% CI 1.35-1.51) were significantly
increased compared to controls (see Table). In contrast, in patients with RA, only
the age/sex-adjusted prevalence of DM (OR 1.03; 95% CI 1.01-1.06) was
significantly increased. The
age/sex-adjusted prevalence of HTN, HL, and DM was significantly increased in
both mild and severe psoriasis, although higher among patients with severe
psoriasis compared to mild psoriasis.
The frequency of receipt of therapy among patients with incident
diagnoses of HTN, HL, and DM was not significantly different between the
disease groups and controls; approximately 80%, 50%, and 60% of patients
received prescriptions for HTN, DM, and HL respectively.
Conclusion: In this study, the age-and-sex
adjusted prevalence of diagnosed HTN, HL, and DM was higher in psoriasis and
PsA compared to RA and controls.
Treatment of HTN, DM, and HL was similar between those with inflammatory
diseases and controls. This study examined only “diagnosed” HTN, HL and DM and
did not examine lifestyle modification or potential under-diagnosis of CVD risk
factors. Future work should investigate strategies to manage CVD risk factors
in these inflammatory conditions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jafri K, Bartels CM, Shin D, Ogdie-Beatty A. The Prevalence, Incidence and Management of Hypertension, Diabetes and Hyperlipidemia in Psoriatic Arthritis, Psoriasis and Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-prevalence-incidence-and-management-of-hypertension-diabetes-and-hyperlipidemia-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psoriasis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-prevalence-incidence-and-management-of-hypertension-diabetes-and-hyperlipidemia-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psoriasis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/