Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To assess the
benefits and harms of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE5) for the
treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP).
Methods: The Cochrane library, MEDLINE,
EMBASE and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched to June 2014 for randomized
controlled trials (RCTs) examining RP with PDE5. Outcomes of interest were: Frequency
of RP attacks, Duration of attacks, Severity of attacks, Pain, Patient global, Withdrawals
and Serious adverse events. Fixed effects models were used to calculate mean
differences (MD) or standardized mean differences (SMD) for continuous outcomes
and pooled risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous outcomes. Heterogeneity was
determined and was considered significant if I2>50%.
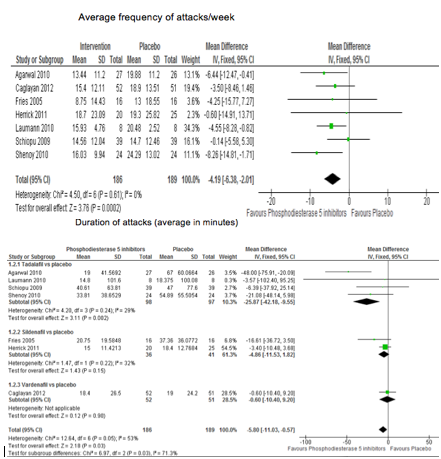
Results: Seven trials (4 with
tadalafil, 2 sildenafil, 1 vardenafil) with an average duration of 5 weeks totaling
255 subjects were included; 97% had RP secondary to systemic sclerosis; SSc).
Trial quality ranged from low to moderate. Many individual trials were not
significantly different from placebo. PDE5 reduced the frequency of attacks by 4.2
attacks/week (95% CI 2.01-6.38) from a baseline of 26 attacks/week, or relative
%change in the frequency of attacks of 22% reduction (95% CI 10-33%). Duration
of attacks decreased by 6 minutes (95% CI 0.5-11); relative %reduction of 24%
(95% CI 2-47%). Severity of RP attacks was assessed in one trial. Raynaud’s
Condition Score (RCS) improved by 0.49 cm (95% CI 0.02-0.95). Pain (VAS
0-10) improved by 1.06 (95% CI 0.09-2.03) with 25% decrease in relative %pain.
The relative %reduction in disability was 39% (95% CI 18-60%). The relative
risk of withdrawals was 4.42 (higher in PDE5 group). The number needed for an
additional harmful outcome (NNTH) was 32 (95% CI 7 to 717). Figure shows the
reduction of RP frequency and duration of attacks. Samples were too small to
detect differences between PDE5 drugs.
Conclusion: PDE5 medications seem to be
effective in treating RP associated with SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pope JE, Rirash F, Tingey P, Harding S, Maxwell LJ, Pardo J, Ghogomu E, Tugwell P, Wells GA. A Meta-Analysis of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Raynaud’s Phenomenon [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-meta-analysis-of-phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitors-for-the-treatment-of-raynauds-phenomenon/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-meta-analysis-of-phosphodiesterase-5-inhibitors-for-the-treatment-of-raynauds-phenomenon/
