Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
In Germany, treatment with Tocilizumab (TCZ) is primarily used in rheumatoid
arthritis patients with previous failures of biologic DMARDs. Effectiveness and
adherence of TCZ in patients with multiple bDMARD failures has rarely been investigated.
Methods:
We included 765 RA patients enrolled between 2009 and 2015 in the German
biologics register RABBIT (Rheumatoid arthritis: Observation
of biologic therapy) starting with TCZ. Patients were stratified according
to the number of bDMARD failures prior to the initiation of TCZ: biologic naive
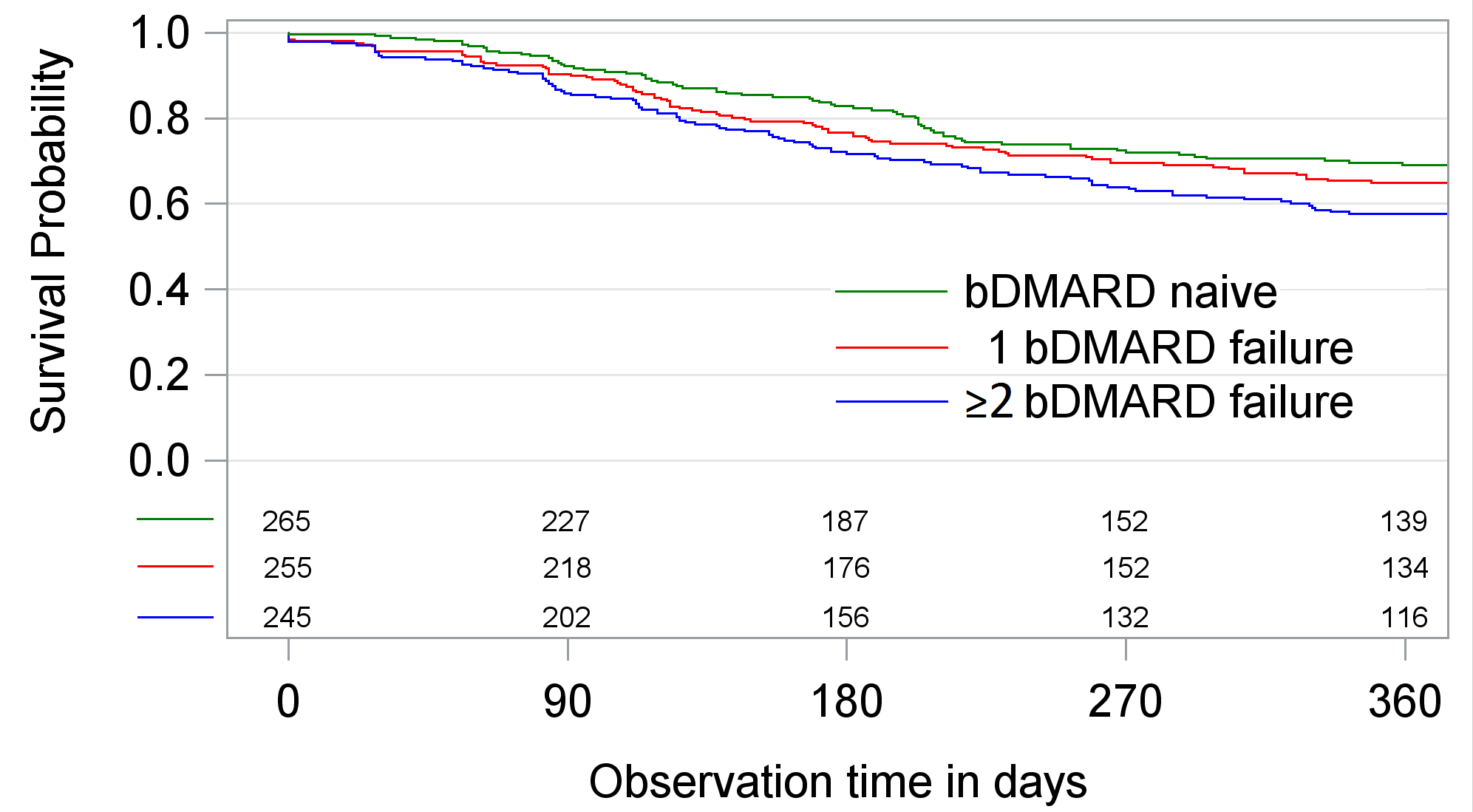
(n=265), 1 bDMARD failure (n=255) and ≥2 bDMARD failures (n=245). Therapy
discontinuation within 12 month after the start of TCZ was investigated using Kaplan-Meier
and Cox-proportional hazard regression. Discontinuation was defined as the stop
of TCZ therapy. Effectiveness regarding control of disease activity (DAS28-ESR)
after 3, 6 and 12 month were examined with linear mixed effects models.
Results: Compared
to biologic naive patients those with prior bDMARD failures at start of TCZ were
younger (1 failure: -1.6y (p=0.09); ≥2 failures: -2.8y (p=0.01)), had
significantly longer disease duration (8.1 vs. 11.4 vs. 14.1 years; p<0.01)
and more csDMARDs failures (p<0.01). Loss of physical function, pain and
fatigue were significantly higher in patients with bDMARD failures (p<0.01).
No differences were found regarding the initial composite score DAS28 (5.2 vs 5.3
vs 5.3), its components: TJC and SJC and the concomitant use of csDMARDs
(p=0.3). During follow-up disease activity (DAS28) was significantly reduced in
all treatment strata. At month 3, 6 and 12 differences between treatment strata
were statistically not significant (Table).
Crude survival on TCZ therapy was significantly lower if
patients had bDMARD failures, unadjusted hazard ratios (HR) compared to bDMARD-naive
patients were 1.17 (p=0.34) and HR=1.50 (p<0.01) (Figure). Adverse events were
the most frequent reason for discontinuation, particularly in patients with
prior bDMARD failures.
Table: Means of DAS28 [95% confidence interval] at month 3,
6 and 12 after enrollment with TCZ. Estimates were adjusted for age, disease
duration, physical function, comorbidities and concomitant use of csDMARDs (yes
vs. no).
|
|
DAS28 at month 3 |
DAS28 at month 6 |
DAS28 at month 12 |
|
bDMARD naive |
3.02 [2.82; 3.22] |
2.84 [2.63; 3.04] |
2.88 [2.66; 3.10] |
|
1 bDMARD failure |
3.19 [3.01; 3.38] |
3.04 [2.84; 3.24] |
3.07 [2.87; 3.28] |
|
≥2 bDMARD failure |
3.37 [3.17; 3.56] |
3.21 [3.00; 3.42] |
3.06 [2.82; 3.29] |
Conclusion: Treatment with TCZ is effective in
patients with and without prior bDMARD failures, the majority of patients
achieves low disease activity (DAS28<3.2) within 6 month and maintains
controlled disease activity throughout month 12. However, the higher
susceptibility of adverse events in patients with prior bDMARD failures needs
further investigation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richter A, Strangfeld A, Kekow J, Bussmann A, Krause A, Stille C, Listing J, Zink A. Tocilizumab Is Effective As 1st, 2nd and 3rd-Line Biologic DMARD in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-is-effective-as-1st-2nd-and-3rd-line-biologic-dmard-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-is-effective-as-1st-2nd-and-3rd-line-biologic-dmard-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/