Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Synovial fluid culture
and gram stain offer the most compelling proof of septic arthritis (SA); these
tests are indicated in every suspected case. However, the sensitivity and
specificity of these studies are not well established, especially among patient
who have received antibiotic administration prior to synovial fluid sampling.
The purpose of this study was to define the impact of prior antibiotic use on
synovial fluid gram stain and culture results among patients with septic
arthritis.
Methods:
We conducted a
retrospective cohort study of patients 18 years and older admitted to a single
tertiary care center from 1998 to 2015 with septic monoarthritis. The diagnosis of SA was defined by typical clinical
presentation and positive blood culture, synovial gram stain and/or culture. Patients were stratified by the timing of
antibiotic use with regard to joint aspiration and whether the involved joint
was native or prosthetic.
Results:
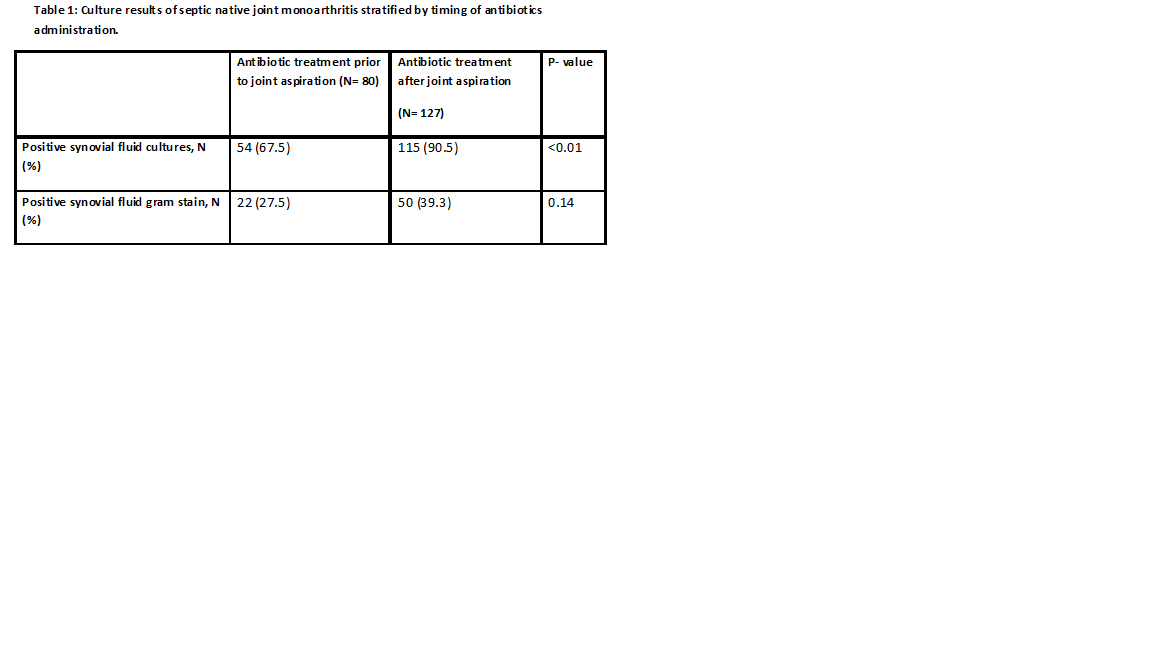
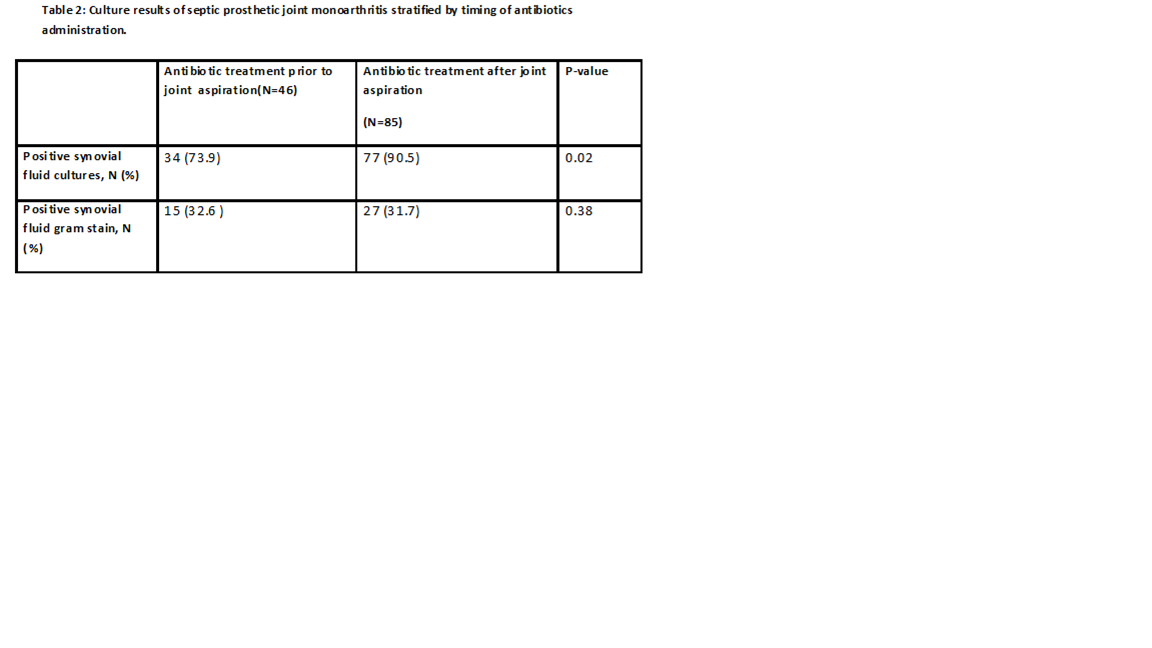
Of 338 patients with SA, 207 had native joint involvement. The synovial fluid cultures were positive in
84.6% of cases while synovial fluid gram stain was positive in only 35%. Prior antibiotic use was associated with a significant
reduction in synovial fluid culture positivity (90.5% without prior antibiotics
vs. 67.5% with prior antibiotics; p<0.01) (Tables 1 and 2). There was no
significant difference in the rate of gram stain positivity based on prior
antibiotic treatment although there was a trend toward fewer positive gram
stain results among those receiving prior antibiotics (Table 1).
Conclusion:
While it is well-known that prior antibiotic administration
may affect the results of synovial fluid culture and gram stain, this is one of
the few large studies that quantitate these effects. We found the most dramatic impact of prior
antibiotic administration is a reduction of synovial fluid culture positivity. Further analysis is ongoing to assess the
timing of prior antibiotic therapy on synovial fluid culture and gram stain
results in SA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paz Z, Lieber SB, Moore A, Zhu C, Fowler ML, Shmerling RH. The Impact of Prior Antibiotic Treatment on Culture Results of Patients with Septic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-prior-antibiotic-treatment-on-culture-results-of-patients-with-septic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-prior-antibiotic-treatment-on-culture-results-of-patients-with-septic-arthritis/