Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The
recent advances in metabolomics have allowed the study of the regulatory
processes linked to metabolism. The comprehensive analysis of the
metabolome in biological samples can provide new insights to identify pathological
processes and to develop new biomarkers. The present study represents the
first high-throughput metabolomics analysis of immune-mediated inflammatory
diseases (IMIDs). The objective of the study is the identification and
validation of diagnostic and activity biomarkers through the analysis of the
urine metabolome within two independent cohorts of >2,500 individuals
including healthy controls and IMID patients.
Methods: The metabolomics
analysis was performed using nuclear magnetic resonance on 2 independent
cohorts. The discovery cohort included 100 controls and 200 patients per IMID:
rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), psoriasis (Ps),
ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), and systemic lupus erythematosus
(SLE). The validation cohort included 200 controls and 200 patients per IMID.
The patients of each IMID were selected to define 2 groups: low and high
disease activity patients. A total of N=37 metabolites were accurately
quantified. The association analyses were performed at 3 levels: diagnostic
-comparing each IMID vs controls-, differential
-comparing similar IMIDs between them-, and activity -comparing low and high
activity patients of each IMID-. The statistical analysis was performed using
linear regression adjusted by epidemiological and sample collection variables.
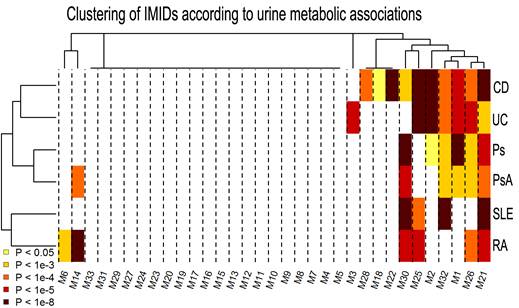
Results: The diagnostic
analysis identified n=28 metabolic associations, from which n=26 were
replicated in the validation cohort. These associations involved n=10 different
metabolites from which n=6 were jointly associated to ≥3 IMIDs. When
analyzing differences between IMIDs, we validated n=3 associations when
comparing CD vs UC. At the nominal level, n=2 further
associations were validated when comparing RA vs
PsA. The analysis of disease activity identified and validated n=3
associations related with disease activity in CD patients. We also validated at
the nominal level n=2 associations in UC and n=1 association in PsA, SLE and
CD.
Conclusion: We have
identified and validated significant differences in metabolite concentrations
when comparing IMID patients vs
healthy controls. CD, UC and RA gathered the largest number of metabolic
associations. Relevantly, n=6 metabolites were associated to ≥3 IMIDs.
These metabolites are then candidate proxies for the physiopathological
processes shared by these diseases. Regarding to the discrimination between
related IMIDs, the urine metabolome has shown significant differences when
comparing CD vs UC and RA vs
PsA. The disease activity analysis also identified significant associations but
with a lower impact than that from the diagnostic analysis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alonso A, Tornero J, Fernandez-Nebro A, Cañete JD, Domènech E, Gisbert JP, Ferrándiz C, Fonseca E, García V, Blanco F, Rodriguez J, Gratacós J, Carreira PE, Julià A, Tortosa R, López-Lasanta M, Correig X, Marsal S. Identification and Validation of Diagnostic and Activity Urinary Metabolomic Biomarkers in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-and-validation-of-diagnostic-and-activity-urinary-metabolomic-biomarkers-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-and-validation-of-diagnostic-and-activity-urinary-metabolomic-biomarkers-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/