Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) can have a profound negative effect on an individual’s physical functioning, health status and quality of life (QoL), affecting the ability to work (Sieper J et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002). Since interleukin (IL)-17A is implicated in the pathogenesis of AS (Dougados M, Baeten, D. Lancet 2011), inhibition of this cytokine with secukinumab, a fully human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, may help reduce the burden of disease. Here we present the impact of high-dose intravenous (i.v.) loading with secukinumab followed by subcutaneous (s.c.) maintenance dosing on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in a phase 3 trial (MEASURE 1; NCT01358175) over 52 weeks.
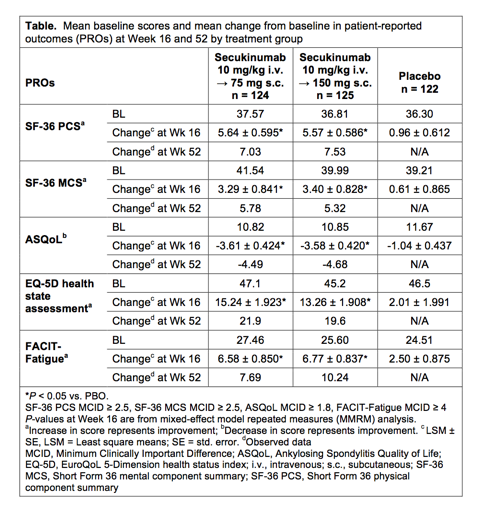
Methods: 371 adults with active AS fulfilling modified New York Criteria and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index ≥ 4 were randomized to receive i.v. secukinumab 10 mg/kg (Week 0, Week 2, Week 4) followed by s.c. secukinumab 75 mg every 4 weeks (10 IV → 75 SC); i.v. secukinumab 10 mg/kg (Week 0, Week 2, Week 4) followed by s.c. secukinumab 150 mg every 4 weeks (10 IV → 150 SC); or i.v. placebo (Week 0, Week 2, Week 4) followed by s.c. placebo every 4 weeks (placebo group; PBO). PBO subjects were re-randomized to either 75 mg or 150 mg s.c. secukinumab based on ASAS20 response at Week 16, with non-responders switched to secukinumab at Week 16 and responders at Week 24. PROs were measured every 4 weeks using the following questionnaires: short form 36 (SF-36), EuroQoL (EQ-5D), AS QoL (ASQoL), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy — Fatigue (FACIT-Fatigue) and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment — General Health (WPAI-GH). PROs to Week 16 are reported using a mixed-effect model repeated measures (MMRM) analysis, except WPAI-GH domains which are observed data.
Results: Demographics and disease severity were comparable among the three groups with subjects experiencing moderate to severe levels of fatigue and impaired health-related QoL at baseline. Secukinumab 10 IV →75 SC and 10 IV → 150 SC significantly improved scores on the SF-36 physical and mental component summaries, ASQoL, EQ-5D and FACIT-Fatigue vs. PBO at Week 16 (Table), with significant differences in these parameters seen with both doses in all assessments starting at Week 4. Mean changes from baseline at Week 16 were greater than the minimum clinically important difference (MCID) for SF-36 PCS, MCS, ASQoL and FACIT-Fatigue (Table). Reductions in the impact of disease on work productivity (WPAI-GH) were observed with secukinumab vs. PBO at Week 16. Improvements in PROs observed with secukinumab were sustained or increased beyond Week 16 through Week 52.
Conclusion: In subjects with active AS, selective inhibition of IL-17A with secukinumab provided rapid and sustained improvements in PROs, including fatigue, general and AS-specific QoL measures, and illness-associated reductions in work productivity.
Disclosure:
A. A. Deodhar,
Research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
2,
Consulting fees from AbbVie, Celgene, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
5;
D. L. Baeten,
Research grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, and Pfizer,
2,
Consulting fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
5;
J. Braun,
Honoraria for talks, advisory boards, paid consultancies and grants for studies from Abbvie (Abbott), Amgen, BMS, Boehringer, Celgene, Celltrion, Centocor, Chugai, EBEWE Pharma, Medac, MSD (Schering-Plough), Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, S,
5;
X. Baraliakos,
Research funds from AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai,
2,
Consulting fees from AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai,
5,
Speakers’ fees from AbbVie, Merck, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, and Chugai,
8;
J. Sieper,
Consulting fees from AbbVie, Pfizer, Merck, UCB and Novartis,
5,
Research grants from AbbVie, Pfizer and Merck,
2,
Speakers’ bureau: AbbVie, Pfizer, Merck and UCB,
8;
M. Dougados,
Research grants from AbbVie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Pfizer,
2,
Consulting fees from Eli Lily,
5;
P. Emery,
Consulting fees from AbbVie, BMS, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
5;
B. Porter,
Novartis stock ownership,
1,
Employee of Novartis,
3;
R. Martin,
Employee of Novartis,
3;
S. Mpofu,
Novartis stock ownership,
1,
Employee of Novartis,
3;
H. Richards,
Employee of Novartis,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-a-monoclonal-antibody-to-interleukin-17a-significantly-improves-physical-function-and-quality-of-life-in-subjects-with-active-ankylosing-spondylitis-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-pla/