Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To account for glomerular filtration rate, urinary creatinine is routinely used for the normalization of urine biomarkers related to disease. Because of the small size of this metabolite, antibodies are difficult and expensive to develop, limiting the applications of disease-specific urine protein biomarkers for antibody-based point of care applications.
Methods: An aptamer-based screening of 1129 proteins in 24 human urine samples (8 active lupus nephritis (LN), 8 inactive LN, 8 healthy controls (HC)) was carried out to identify urine proteins that correlated well with urine creatinine but not disease.
Results: The screen uncovered 18 proteins that correlated well with urinary creatinine but were similar in patients with or without nephritis. Further validation in an independent cohort of 48 subjects (16 active LN, 16 inactive LN, 16 HC) showed a significant positive correlation of urine HVEM, RELT, and Dectin-1 to urinary creatinine. The most promising marker, urine HVEM, was significantly correlated to urinary creatinine in both white (Pearson r = 0.7229, P = 0.0001) and black subjects (Pearson r = 0.6111, P = 0.0009). Finally, normalization of other urinary biomarker proteins against urine HVEM showed comparable fold change and statistical significance as normalization to urinary creatinine.
Conclusion: Instead of the metabolite creatinine, proteins such as HVEM, RELT and Dectin-1 can be used for normalization of urine biomarkers. The use of proteins instead of metabolites for normalization paves the way towards novel diagnostic approaches.
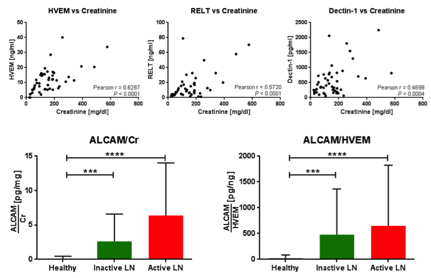
Urine HVEM, RELT, and Dectin-1 were validated by ELISA and found to be significantly correlated with urinary creatinine. HVEM, the most promising marker for GFR normalization, was also used to normalize ALCAM, a biomarker for SLE, to have comparable fold change and statistical significance as normalization to urinary creatinine.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soomro S, Stanley S, Saxena R, Petri M, Mohan C. Unbiased Screening of Urinary Protein Biomarkers for Glomerular Filtration Rate Normalization [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unbiased-screening-of-urinary-protein-biomarkers-for-glomerular-filtration-rate-normalization/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unbiased-screening-of-urinary-protein-biomarkers-for-glomerular-filtration-rate-normalization/
