Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy I: Outcomes Therapy
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Immunization against TNF Inhibitors (TNFi) is observed in 30-50% of patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases. With most TNFi, anti-drug antibodies (ADA) lead to rapid decrease of drug concentration that cause relapses. One of the identified factors of prevention of ADA is the co-prescription of methotrexate (MTX). In preliminary data from animal models, MTX is dramatically more efficient in preventing TNFi immunogenicity in B-cell Activating Factor (BAFF) overexpressing mice. The mechanism of interaction between MTX and BAFF could be an increase of the ectoenzyme CD73 expression induced by BAFF which may favor the transformation of AMP (released from the cell by MTX) in adenosine, a powerful immune-regulatory mediator. The goal of this study is to investigate in the clinics a possible interaction between MTX and BAFF to prevent ADA against TNFi.
Methods: Patients from the ABIRISK study, which is designed to prospectively identify risk factors of ADA against TNFi were included in this study. Patient’s underling disease was Rheumatoid Arthritis, (RA) Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) or Juvenile Inflammatory Arthritis (JIA). Patients were considered treated by MTX when this treatment was concomitantly administered with the newly introduced TNFi. Baseline serum was used for BAFF assay. Free BAFF serum levels were quantified using a new highly sensitive Errena immunoassay system based on single molecule counting. ADA were screened at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months post TNFi therapy using a modified Theradiag© assay. Patients with at least one time point with ADA detection were considered immunized (ADA+). Comparisons of BAFF levels among different subsets of patients were performed using Welch’ test.
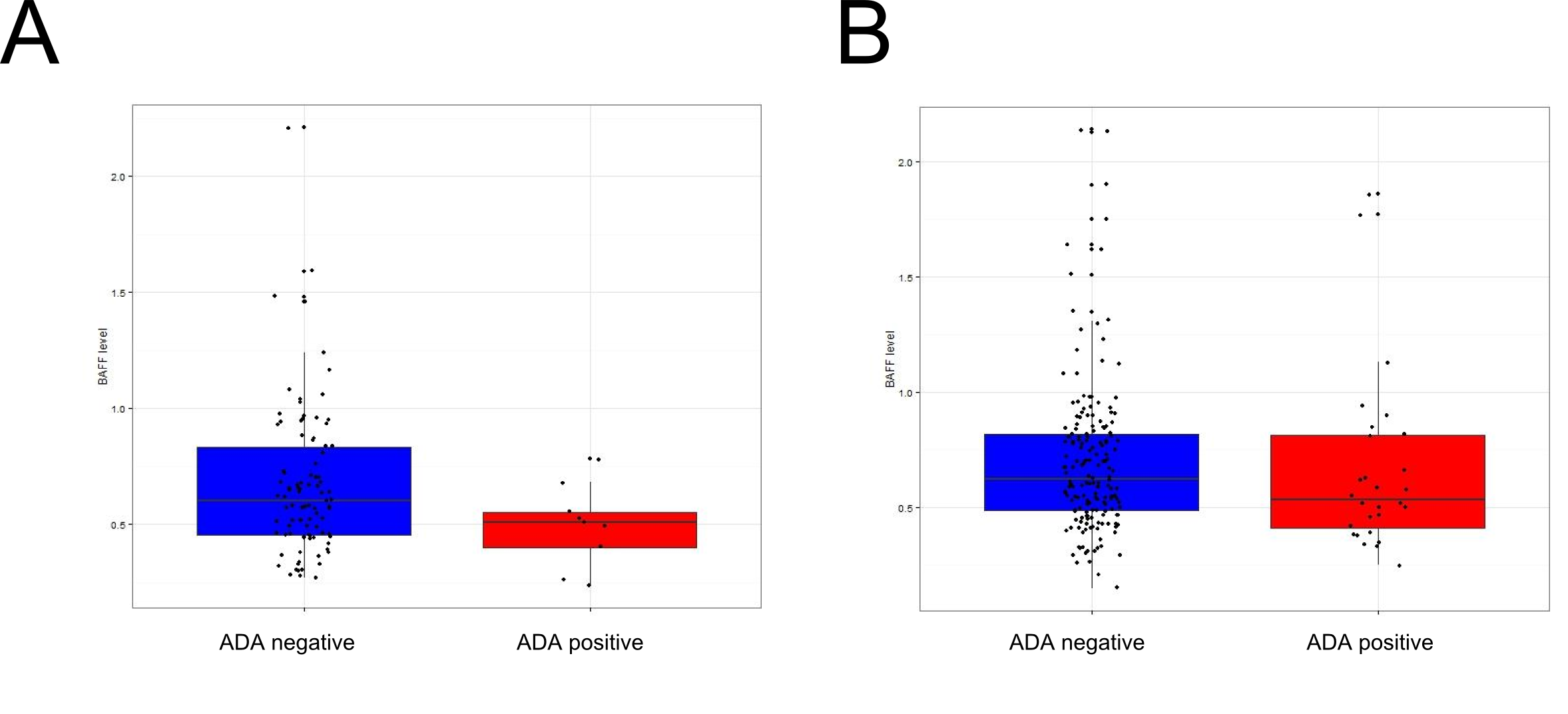
Results: Serum BAFF quantification was performed in 383 patients (191 RA, 173 IBD and 19 JIA) who had undergone at least one dosage of ADA. In the 103 patients (91 RA and 12 IBD) treated with MTX, 9 (8.7%) developed ADA versus 28 (13.5%) in the non-MTX treated patients. In the 103 MTX-treated patients, the level of BAFF was significantly lower ( 0,49ng/mL) in ADA+ patients than in ADA-patients (0,69ng/mL p=0.02,Fig 1A). The removing of 3 patients with a low level of ADA against etanercept reinforces the association between low serum BAFF level and ADA (p=0.006). Conversely, in the 208 non-MTX treated patients, there was no significant difference in the serum level of BAFF between ADA+ and ADA- patients (p=0.65 Fig 1B).
Conclusion: These clinical data support the preliminary findings we have got in mice on an interaction between MTX and BAFF for preventing ADA formation. Patients treated with TNFi and MTX who do not develop ADA have a higher serum BAFF level than patients who develop ADA. Conversely, serum BAFF level has no influence on ADA formation in non MTX-treated patients. Thus, MTX might require high BAFF levels to prevent immunization against TNFi.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Dönnes P, Doublet A, Florence K, Hincelin-Mery A, Nocturne G, Allez M, Ruperto N, Pallardy M, Mariette X. Methotrexate Requires High Serum BAFF Levels to Prevent Immunization Against TNF-α Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-requires-high-serum-baff-levels-to-prevent-immunization-against-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-requires-high-serum-baff-levels-to-prevent-immunization-against-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors/