Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Given possible increased risk of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune conditions, there is a need to better understand the immunogenicity and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in people living with rheumatic disease. We are currently conducting the Covid VaccinE Response (COVER) trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial to evaluate the response to a SARS-CoV-2 booster in patients with confirmed rheumatic disease on immunomodulatory therapies. In this analysis, we examined response to the primary mRNA vaccine series in relation to the time since vaccination, and therapy.
Methods: COVER randomizes rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients in a large practice-based research network of U.S. rheumatologists to continue their current immunomodulatory therapy regimen or briefly interrupt (ie, hold for 2 weeks) following administration of a 3rd or 4th dose (booster) of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. In this analysis, baseline vaccine response was examined cross-sectionally in relation to time since the primary vaccine series. LabCorp Cov2Quant IgG™ Spike assay was used to measure levels of anti-Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) IgG antibodies in response to vaccination and or/natural infection. Anti-Nucleocapsid antibodies were measured to identify prior SARS-CoV-2 infection and evidence of prior COVID-19 infection was also classified using self-report. Demographic characteristics were reported, and COVID-19 RBD antibody levels examined in relation to time since primary vaccination. Linear regression was used to evaluate determinants of mean log anti-RBD antibody titers and compared by drug categories.
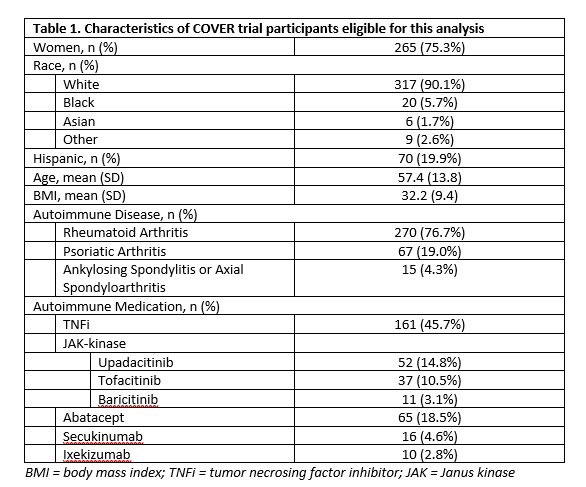
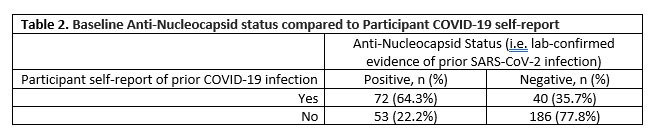
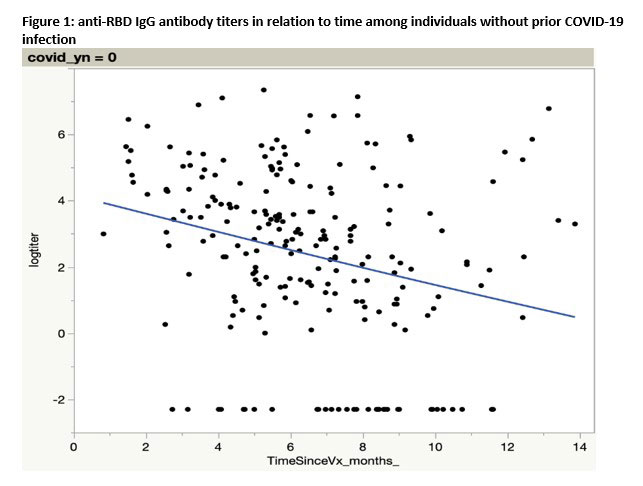
Results: A total of 352 participants completed a baseline visit and were eligible for analysis (Table 1). Participants were 75% women, 90% white, 20% Hispanic. Mean age: 57.4 (13.8), mean BMI 32.2 (9.4). The majority had RA (77%); 46% TNFi use, 28% JAKi, 27% others (abatacept, IL-17i) at primary vaccine series. Among those with no prior COVID-19 infection, anti-RBD IgG antibody titers showed a clear decrease with time since receipt of prior vaccination (Figure 1). In adjusted linear regression, referent to TNFi, JAKi (p=0.02) and abatacept (p=0.05) patients had lower mean titers, even after accounting for time since vaccine, number of vaccine doses and Anti-Nucleocapsid status. Table 2 shows the comparison of anti-Nucleocapsid status at baseline with participant self-report of prior COVID-19 infection, specificity was 78% (95% CI: 72%-83%) and sensitivity was 65% (55%-73%).
Conclusion: A clear decrease of anti-RBD IgG antibody levels in patients with RA or SpA taking immunomodulatory therapy was seen with increasing time following previous vaccine receipt. This effect was more pronounced in those who reported no prior COVID-19 infection, and who were receiving JAKi or abatacept (referent to TNFi). Self-report of prior COVID infection substantially misclassified prior COVID-19 infection and may confound immunogenicity outcomes in vaccine studies. Future analysis of the randomized trial results will look at the effect of holding or continuing immunomodulatory treatment at the time a SARS-CoV-2 booster is given.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mudano A, Cutter G, Mikuls T, Thiele G, Law M, Hamilton B, Zikry M, Chun K, Bastidas M, George M, Williams L, Winthrop K, Busch M, Cohen S, Czubatyj R, Kataria R, Khan R, Mousa S, Pando J, Perkins E, Reddy S, Santos D, Schechtman J, Scott F, Shanmugam S, Singhal A, Tesser J, Tower J, Venuturupalli S, Wollaston S, Ziembinski C, Curtis J. Waning Vaccine Response After Primary Vaccine Series: Results from the Covid19 Vaccine Response in Rheumatology Patients (COVER) Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/waning-vaccine-response-after-primary-vaccine-series-results-from-the-covid19-vaccine-response-in-rheumatology-patients-cover-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/waning-vaccine-response-after-primary-vaccine-series-results-from-the-covid19-vaccine-response-in-rheumatology-patients-cover-study/