Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2387–2424) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Visual loss is one of the most feared complications in giant cell arteritis (GCA). Some factors have been previously associated with visual loss, as lower levels of inflammatory markers, jaw claudication or thrombocytosis, although some of these studies showed contradictory results. Our objective was to identify predictive factors of visual involvement in a large cohort of patients with GCA.
Methods: ARTESER is a large Spanish multicenter registry promoted by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology, including patients with GCA diagnosis from June 2013 to March 2019. The following variables were collected at diagnosis per protocol: demographics, symptoms (including all visual manifestations reported by clinicians), laboratory test results, temporal artery biopsy and imaging techniques (ultrasound, PET, MRI, CT).Patients with and without visual involvement were compared in a bivariate analysis. Multivariate logistic regression model was performed to determine potential predictive factors of visual manifestations.
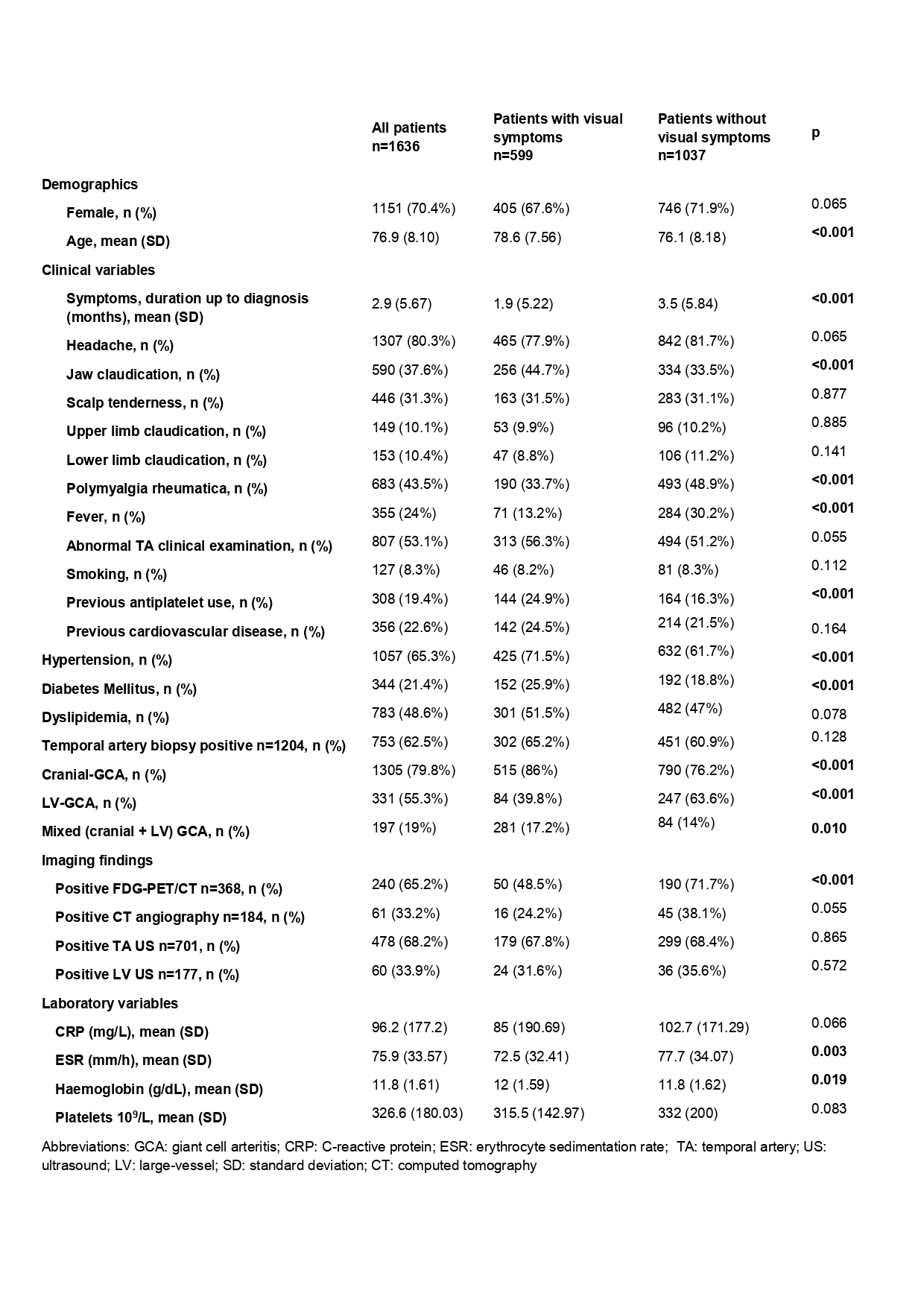
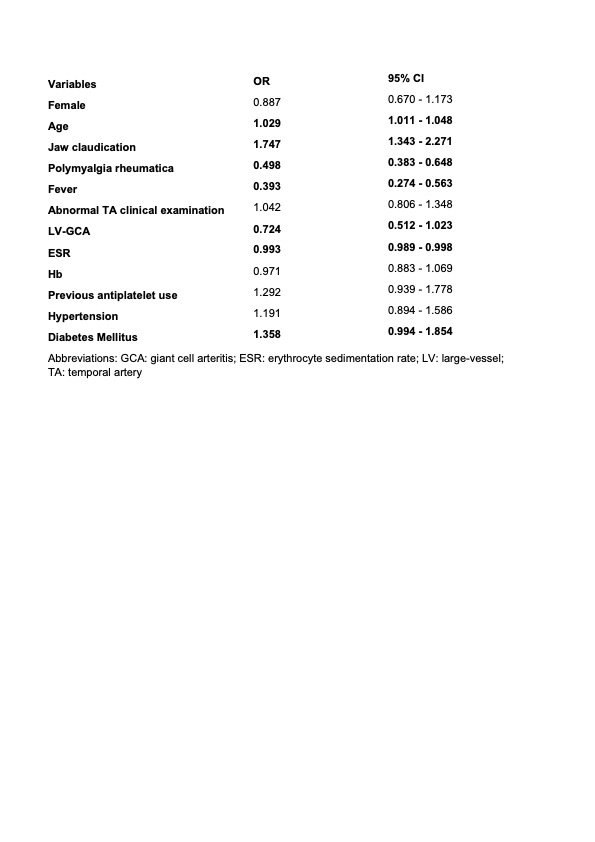
Results: A total of 1636 GCA patients were included for analysis, of whom 599 (36.6%) presented visual involvement. The most frequent visual manifestation was anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (45.7%), followed by transient monocular vision loss (45.1%). Clinical, laboratory and imaging variables of patients with and without visual symptoms are shownin Table 1. Older age (OR 1.029; 95% CI 1.011-1.048), jaw claudication (OR 1.747; 95% CI 1.343-2.271) and diabetes mellitus (OR 1.358; 95% CI 0.994-1.854) were the only independent predictors of visual symptoms in our cohort. The presence of polymyalgia rheumatica (OR 0.498; 95% CI 0.383-0.648), fever (OR 0.393; 95% CI 0.274-0.563) and higher erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (OR 0.993; 95% CI 0.989-0.998) were associated with a reduced risk of developing visual involvement (Table 2).
Conclusion: One out of every three GCA patients present visual manifestations at diagnosis. Older age, jaw claudication and diabetes mellitus are independent predictors of visual manifestations, whereas polymyalgia rheumatica, fever and high ESR reduces the risk of visual involvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molina-Collada J, Domínguez M, Melero-Gonzalez R, Fernandez-Fernandez E, Silva-Diaz M, Belzunegui J, González I, Sanchez Martin J, Narvaez J, Galíndez E, Mendizábal j, Leon Mateos L, Loricera J, Muñoz A, Castañeda S, Castellvi I, Tortosa-Cabañas M, Navarro V, Galisteo C, Casafont-Solé I, Roman Ivorra J, SALMAN MONTE T, Rocha M, Iñiguez C, Hernandez Hernandez M, Campos C, Alcalde M, Mas A, Prado F, Blanco R. Visual Manifestations in Giant Cell Arteritis: Identification of Risk Factors from the ARTESER Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/visual-manifestations-in-giant-cell-arteritis-identification-of-risk-factors-from-the-arteser-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/visual-manifestations-in-giant-cell-arteritis-identification-of-risk-factors-from-the-arteser-registry/