Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III: Giant Cell Arteritis
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Assessing cranial artery inflammation plays an important role in the diagnosis of cranial giant cell arteritis (GCA). Although an established tool for assessing large vessel vasculitis, fluorine-18-deoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/CT imaging is not recommended for detecting cranial artery inflammation. Assessing FDG uptake in the cranial arteries may increase the diagnostic value of FDG-PET/CT for GCA and may provide more detailed information regarding involved arteries and extent of the disease. It may thus provide a viable alternative for Duplex ultrasonography (US) and temporal artery biopsy (TAB) as a first line investigation in GCA.
This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of FDG-PET/CT for the detection of cranial artery inflammation in GCA.
Methods: This retrospective case control study included glucocorticoid-naive TAB positive GCA patients who underwent FDG-PET/CT as part of the diagnostic work-up. Controls were age- and sex-matched melanoma patients in remission with FDG-PET/CT after 6 months follow-up.
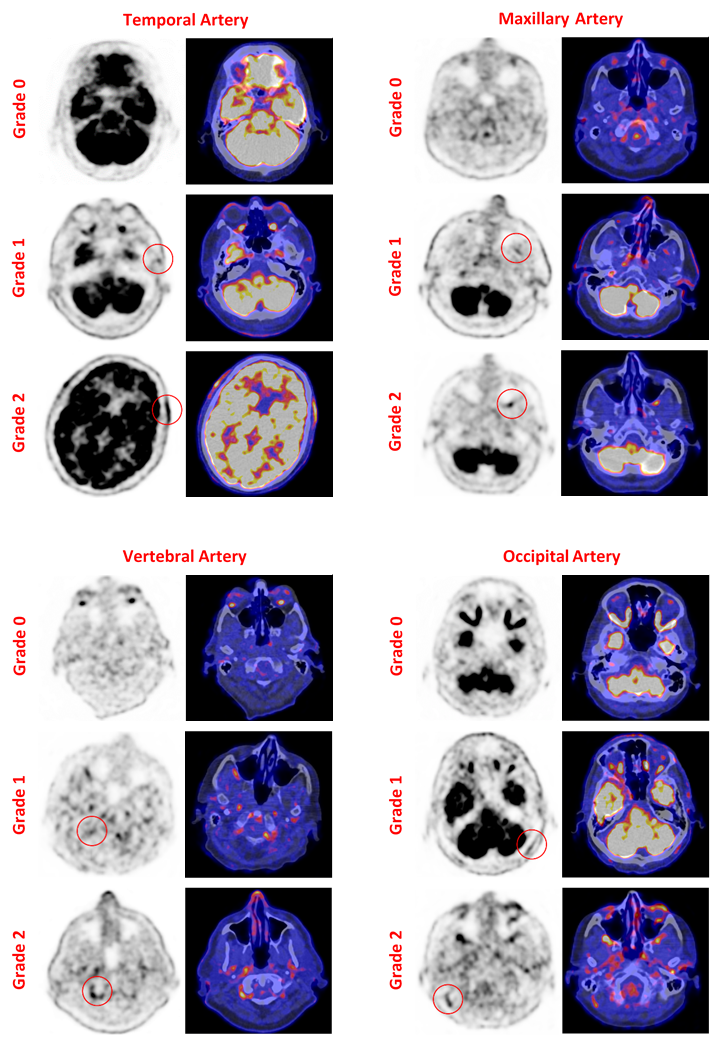
To attain high quality PET images on the Siemens Biograph 64 PET/CT, optimal PET image acquisition and reconstruction parameters were determined and applied to all images. Visual assessment by an experienced nuclear medicine physician was based on uptake intensity compared to surrounding tissue on a 0-2 scale (Figure 1). Additionally, FDG uptake in the cranial arteries was quantified by measuring the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) in the target arteries. The temporal arteries (TA), maxillary arteries (MA), vertebral arteries (VA), and occipital arteries (OA) were assessed bilaterally.
Student t and chi-squared tests were used for evaluation of the visual assessment. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was performed for evaluation of the quantitative assessment. Cohen’s kappa was used to assess agreement of the visual and quantitative assessments.
Results: A total of 24 GCA patients and 24 controls were included. The mean age for both groups was 71 years (SD: 8) and 12/24 were women. Large vessel involvement was seen on PET in 15/24 patients. Duplex US of the temporal artery was performed in 15/24 patients, of which 9 were positive. Median ESR and CRP were 73 (CI95%: 53; 104) mm/h and 73 (CI95%: 37; 110) mg/L, respectively.
Visual assessment revealed a sensitivity of 83% (CI95%: 64; 93) and a specificity of 75% (CI95%: 55; 88) for GCA denoted by a score of ≥1 (uptake higher than background). Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of the quantitative assessment revealed an AUC of 0.88 (CI95%=0.77-0.99) resulting in a sensitivity of 79% (CI95%: 60; 91) and a specificity of 92% (CI95%: 74; 99) for a SUVmax threshold value of 5.00 (Table 1). The agreement between the two assessment methods was 77% (kappa 0.55).
Conclusion: Using optimal scan data reconstruction, visual and quantitative FDG-PET/CT assessment methods can reliably diagnose GCA based on cranial artery inflammation. Extending the use of FDG-PET/CT to the cranial arteries may improve the diagnostic accuracy for GCA. Moderate agreement between visual and quantitative assessment methods suggests that diagnostic accuracy may be improved when combining both methods.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nienhuis P, Slart R, Brouwer E. Visual and Quantitative Assessment of Cranial Arteries on FDG-PET/CT Can Reliably Diagnose Cranial Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/visual-and-quantitative-assessment-of-cranial-arteries-on-fdg-pet-ct-can-reliably-diagnose-cranial-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/visual-and-quantitative-assessment-of-cranial-arteries-on-fdg-pet-ct-can-reliably-diagnose-cranial-giant-cell-arteritis/