Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The CD40L/CD40 co-stimulatory pathway is important for T-cell-dependent antibody production and plays a central role in RA and other autoimmune diseases. VIB4920 (formerly MEDI4920) is an Fc-deficient CD40L antagonist which demonstrated acceptable safety and dose-dependent inhibition of TDAR in a Phase 1a study.
Methods: This Phase 1b, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-ascending dose study enrolled 57 pts with active RA, defined as 28-joint Disease Activity Score–C-reactive protein [DAS28CRP] ≥3.2; and ≥4 tender and swollen joints. Pts were positive for RF and/or anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies and previously had inadequate response to ≥1 DMARDs and/or anti-TNF therapy. Pts were treated with IV VIB4920 (75, 500, 1000 or 1,500 mg) or PBO every other week for 12 weeks. Key endpoints were safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic parameters, anti-drug antibodies (ADAs), change in DAS28–CRP and biomarkers of disease activity (RF, CRP, Vectra-DA) at Day 85.
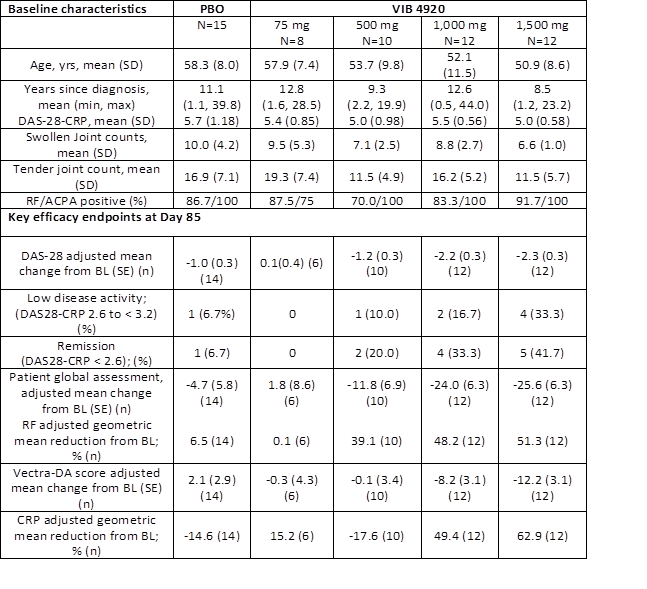
Results: Table 1 summarizes the main baseline demographic and clinical characteristics. Treatment emergent AEs were equally distributed among groups; no thrombotic events or coagulation abnormalities were noted. One grade 4 SAE of encephalitis was reported in the 1500mg VIB4920 dose group. This was considered unrelated to VIB4920. The patient subsequently was diagnosed with metastatic melanoma of the brain after recurrence of similar symptoms. ADAs were observed in over 30% of pts with the lower doses, but no ADAs were observed in the 1000 and 1500 mg dose groups. A significant dose response was demonstrated for the change from baseline in DAS28CRP at Day 85 (P<0.001). A clinically important difference in DAS28CRP improvement versus placebo was observed in the 1000 and 1500 mg VIB4920 groups using mixed model for repeated measures (Figure and Table 1). Low disease activity or DAS28 remission was achieved in 50% of the 1,000 mg and 75% of the 1,500 mg dose groups compared to 13.4% in the PBO group at Day 85. There was a dose dependent decrease from baseline in RF and CRP levels and in Vectra-DA scores (Table) with the greatest effect in the two highest doses.
Conclusion: In this proof of concept study VIB4920 significantly decreased disease activity at Day85 achieving at least low level of disease activity in 50-%70% of patients in the two higher doses. Dose dependent decrease in RF levels and the Vectra DA score provides supportive evidence that VIB4920 effectively blocks the CD40/CD40L pathway. Combined with an acceptable safety profile these data support further development of VIB4920 for autoimmune diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Albulescu M, Müller-Ladner U, Moate R, Middleton K, Wang L, Drappa J, Illei G. VIB4920, a Novel, Engineered CD40L Antagonist Decreased Disease Activity and Improved Biomarkers of Immune Activation in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Phase 1b, Multiple-Ascending Dose Proof-of-Concept Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vib4920-a-novel-engineered-cd40l-antagonist-decreased-disease-activity-and-improved-biomarkers-of-immune-activation-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-phase-1b-multiple-ascending-dos/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vib4920-a-novel-engineered-cd40l-antagonist-decreased-disease-activity-and-improved-biomarkers-of-immune-activation-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-phase-1b-multiple-ascending-dos/