Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I: Diagnosis and Testing
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sympathetic joint effusion (SJE) is a rarely diagnosed rheumatologic entity characterized by painful yet non-inflammatory range synovial effusion. The condition was originally described in 1978 as a reactive joint effusion associated with adjacent pathology. Literature on the subject has remained scarce due to lack of clinician familiarity and diagnostic criteria, and remains markedly underdiagnosed.1-3 A delay in diagnosis can lead to significant healthcare expenditure, unnecessary treatment and poor outcome.1 A validated diagnostic criteria (Figure 1) would improve diagnostic certainty for clinicians and aid future studies and treatment.
Methods: Retrospective chart review was performed on diagnostic arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis between 1/31/2010 – 2/1/2019. Those with synovial fluid White Blood Cell (WBC) counts (< 2000 cells/mm3), with complete crystal and culture studies were included. A total of 1095 synovial fluid analyses were initially evaluated, with 340 having negative crystal and culture studies.
Results: Using the original SJE description, 125 cases were determined to have SJE with the remaining 215 cases as negative controls. The annualized incidence was 1.268%. Some of the adjacent pathologies found were infections (cellulitis, abscess), vascular manipulation (AV fistula, ECMO, line placement), and DVT.
The sensitivity of monoarticular involvement was 38.1% while specificity was 75.8%. Eight of the SJE patients based on original description with adjacent pathology had complained of >1 joint involved. 65.7% of SJE cases presented with symptoms for greater than 1 day but less than 7, while 14.3% presented after day 7 but within the month. The odds of diagnosis increased 4-fold with erythema (Table 2). On multivariable analysis, erythema and WBC Count < 200 increased the odds of diagnosis 4.9 and 5.7-fold, respectively, after having adjusted for effusion and each other.
With the proposed diagnostic criteria, 59 cases would be considered “Definite” with 58 cases considered “Probable.” Comparing cases on original description with intention to treat all “Definite” or “Probable” cases, the sensitivity of our proposed diagnostic criteria is 93.6% with specificity of 96.7% (PPV=94.4%,NPV=96.3%).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first proposed and validated diagnostic criteria of SJE. The sensitivity and specificity of our criteria are very high, driven by the use of exclusion diagnoses. Strong Odds Ratios for Erythema and WBC Count < 200 indicate the severity of physical symptoms yet minimal synovial inflammation. A weakness of our study is that data was collected retrospectively which is limited by history and exam included in the chart.
References
1. Baker SB, Robinson DR. Sympathetic Joint Effusion in Septic Arthritis. JAMA. 1978; 240(18): 1989.
2. Strickland RW, Raskin RJ, Welton RC. Sympathetic synovial effusions associated with septic arthritis and bursitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):941-3
3. Tan IJ, Barlow JL. Sympathetic Joint Effusion in an Urban Hospital. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 15;1(1):37-42.
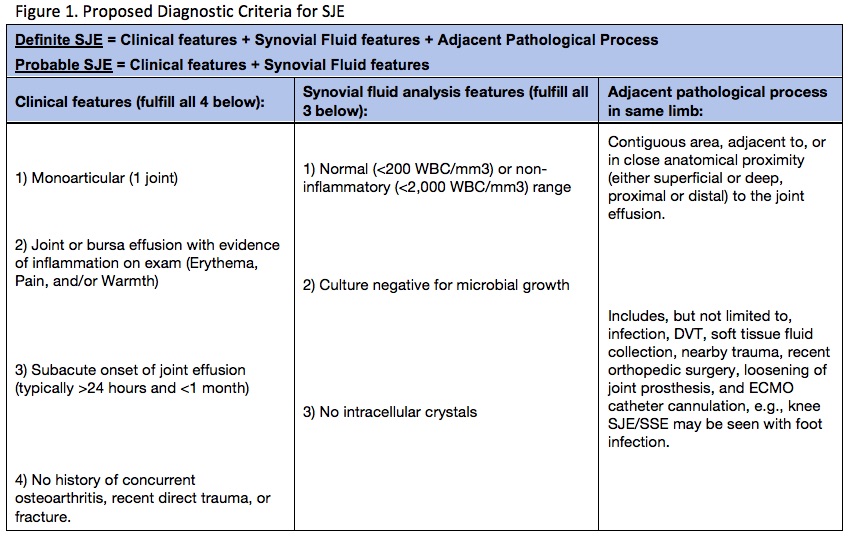 Figure 1. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for SJE
Figure 1. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for SJE
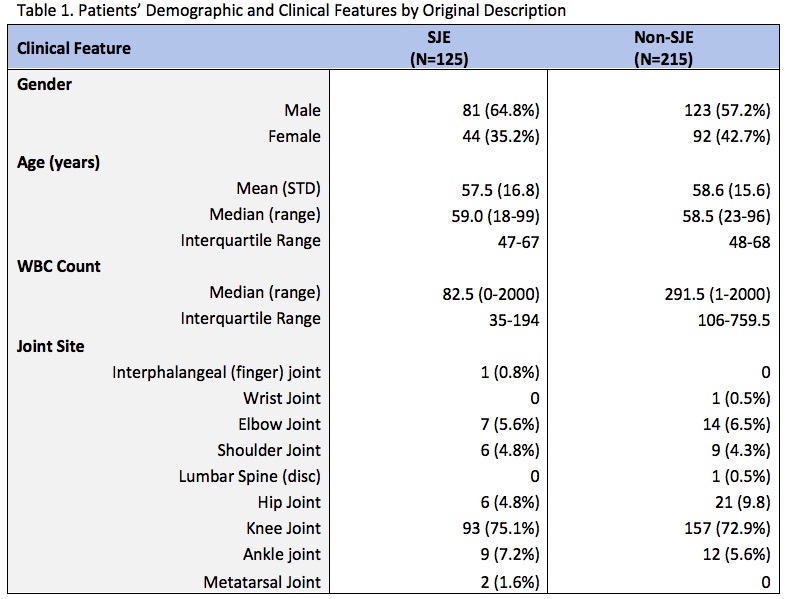 Table 1. Patients’ Demographic and Clinical Features
Table 1. Patients’ Demographic and Clinical Features
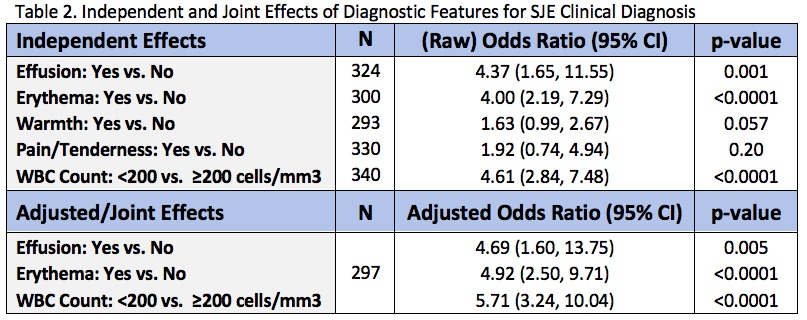 Table 2. Independent and Combined Effects of Diagnostic Features for SJE Clinical Diagnosis
Table 2. Independent and Combined Effects of Diagnostic Features for SJE Clinical Diagnosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Levinson J, Jurkowski M, Kahlon J, Youn H, Yu D, Tan I. Validation Study of Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for Sympathetic Joint Effusion [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-study-of-proposed-diagnostic-criteria-for-sympathetic-joint-effusion/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-study-of-proposed-diagnostic-criteria-for-sympathetic-joint-effusion/
