Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Spinal mobility is a major problem for people with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The BASMI has been widely used for measuring spinal mobility but it lacks responsiveness to change and requires clinical expertise to perform. Inertial Motion Unit (IMU) sensors are now available to measure spinal movement without requiring significant operator expertise. Our objective in this study was to test the reliability of these new tools in patients with axSpA and to develop a composite measurement tool analogous to the BASMI.
Methods: The study included 40 patients with axSpA fulfilling ASAS classification criteria (12 females, 28 males) with a mean age of 48 (27-41). Subjects had a wide range of severity of axSpA. ViMove IMU sensors (DorsaVi©) were used to obtain ROM measurements at the cervical and lumbar spine. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of BASMI and IMU tests were assessed by intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) (two-way model, single measure, absolute agreement) with a 95% CI.
Based on these observations we developed a novel scoring system named ‘IMU-ASMI’. It includes four measurements of maximum ROM (degrees) carried out in both lumbar and cervical regions: flexion, extension, averaged L/R values for lateral flexion and rotation. Maximum spinal ROM values in normal subjects taken from an earlier criterion validity study are taken as reference in the composite IMU-ASMI score calculation..
Results:
The mean BASMI was 5.0 (range 0.7 to 8.2, SD 1.9). The mean IMU-ASMI was 5.1 (range 0.4-8.9, SD 2.1). The mean difference between the two scores was 0.04, SD 0.17.
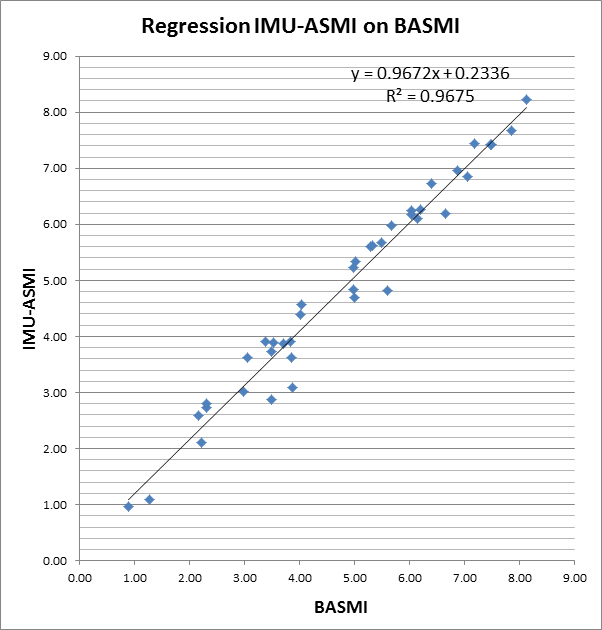
The ICC results demonstrate that a sensor based IMU-ASMI has excellent reliability (table). The R2 on the regression analysis was 0.97, indicating a close relationship between the BASMI and IMU-ASMI (Figure).
|
|
BASMI |
IMU-ASMI |
||
|
ICC (2,1) |
95% CI |
ICC (2,1) |
95% CI |
|
|
Intra-rater |
0.97 |
0.95-0.99 |
0.95 |
0.91-0.96 |
|
Inter-rater |
0.95 |
0.91-0.98 |
0.93 |
0.85-0.98 |
Conclusion: IMU sensors can be used to accurately and reliably measure spinal mobility in patients with axSpA. We present a novel IMU-ASMI score based on combining sensor data on spinal mobility including an assessment of lumbar rotation. The score compares favorably with the BASMI linear scale, and the sensor technology on which it is based on will allow tests of spinal mobility to be carried out by non-experts in the community setting. Further studies are planned to test the sensitivity to change of the IMU-ASMI compared to BASMI.
Acknowledgements: This study was funded by FOREUM (www.foreum.org). Physiotherapist Stephanie Keys also performed spinal mobility tests during this study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gardiner P, Small D, Boyle E, Conlon AM, da Silva JAP, Condell J, Cuesta-Vargas A, Collantes-Estévez E, Garrido-Castro JL. Validation of a New Electronic Spinal Mobility Index for Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Based on Inertial Motion Unit (IMU) Sensors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-new-electronic-spinal-mobility-index-for-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-based-on-inertial-motion-unit-imu-sensors/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-new-electronic-spinal-mobility-index-for-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-based-on-inertial-motion-unit-imu-sensors/