Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
The American College of Rheumatology treatment guidelines for lupus nephritis (LN) recommend that induction therapy be changed when response to therapy has not occurred within six months. Response is not defined, and renal fibrosis can occur while waiting for this endpoint. Therefore, an early treatment decision support tool is needed. The goal of this project was to create and validate such a tool. Methods .
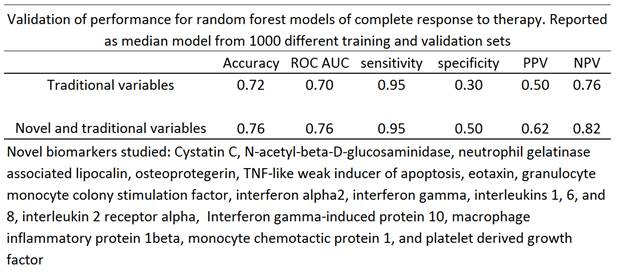
140 patients with active LN were recruited within 12 months of renal biopsy and prospectively evaluated for one year after start of induction therapy. Patients came from two prospective cohorts (the Hopkins cohort and the Medical University of SC) and two randomized controlled trials (the Lupus Nephritis Assessment of Rituximab (LUNAR) and the abatacept lupus nephritis trial). Renal biopsy International Society of Pathology/Renal Pathology Society (ISN/RPS) class, demographics, serum complement, anti-double stranded DNA antibody (dsDNA), and creatinine values, and urine protein/creatinine (traditional biomarkers, per Dall’Era and Wofsy Arthritis Care & Research 2011;63(3):351–357) and novel biomarker values were determined at 0 & 3 months. Seventeen novel biomarkers measured (see table) were based on those in an initial discovery set of 52 candidate biomarkers that were significantly different between groups or that showed promise in the literature. Patients were randomly assigned to training (n=99) and external validation (n=41) sets, stratifying for ISN/RPS class. Baseline and three-month traditional and novel biomarker, ISN/RPS class, treatment regimen, age, sex, and race were used to train random forest models predictive of one-year complete response (CR) to therapy. External validation sets were used to determine the performance of the trained one-year CR model. The process of randomization into training and validation sets and model training/validation was repeated 1000 times, and the median model results were reported. Results .
Several individual biomarkers were different between the two groups (P< 0.001). The resulting test of the LN Decision Support Tool (LNDST) demonstrated the clinically meaningful performance reported in Table I for both models, but the novel biomarker panel had superior specificity for cutpoints giving equal sensitivity.
This study demonstrates the ability of the LNDST to predict CR. Implementation of LNDST may assist clinicians in following the ACR guidelines for treatment of LN.
Disclosure:
B. Wolf,
None;
J. C. Spainhour,
None;
J. Arthur,
None;
M. Janech,
None;
M. Petri,
None;
A. Kiani,
None;
J. Oates,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-machine-learning-lupus-nephritis-decision-support-tool-to-predict-complete-response-to-therapy/