Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develop irreversible organ damage as a consequence of disease activity, chronic inflammation, comorbidities and side effects of medications. Quantifying organ damage is relevant in their assessment. Damage is traditionally evaluated by the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics Damage Index (SLICC-SDI). Two patient-reported damage questionnaires have been validated: Lupus Damage Index Questionnaire (LDIQ) and Brief Index of Lupus Damage (BILD). BILD was developed from the LDIQ. The original English version has better correlation with SLICC-SDI than LDIQ.
Our aim was to perform validation and transcultural adaptation of the BILD questionnaire to Spanish.
Methods: The original BILD questionnaire in English was translated to Spanish independently by two bilingual physicians and a first intermediate Spanish version was produced. A back translation was performed and compared with the original BILD to assess conceptual equivalence and detect possible misunderstandings. On the basis of this comparison, a final Spanish version was created.
The BILD questionnaire was administered to 85 consecutive SLE patients from 2 Hospitals (one public and the other private). All patients fulfilled ACR 1997/ ACR-SLICC 2012 SLE criteria. Sociodemographic data, Charlson comorbidity index, SLICC-SDI, SLEDAI score, global physician visual analogue scale (VAS) were obtained from each patient. Patients also completed the LupusQol questionnaire and global patient VAS.
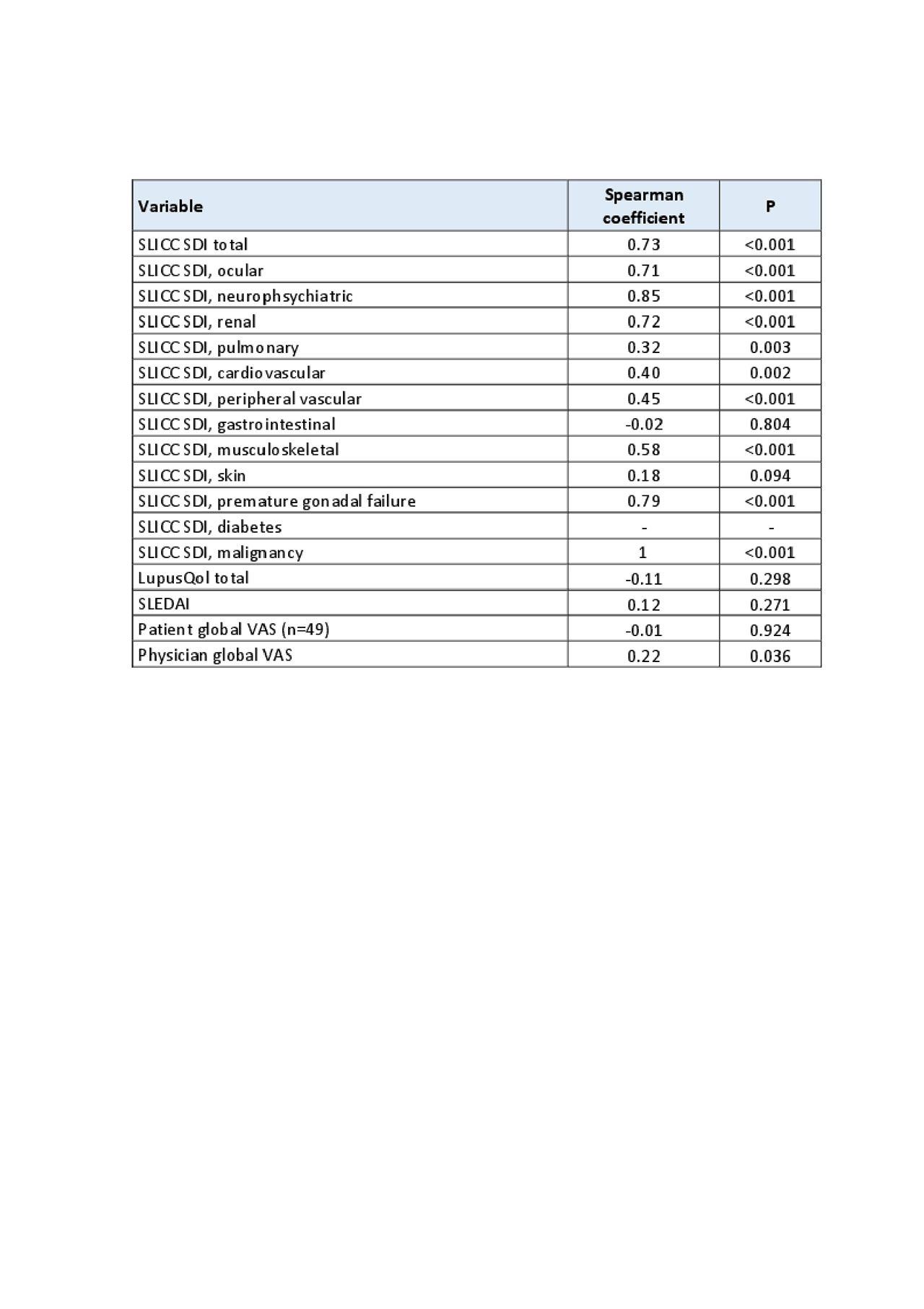
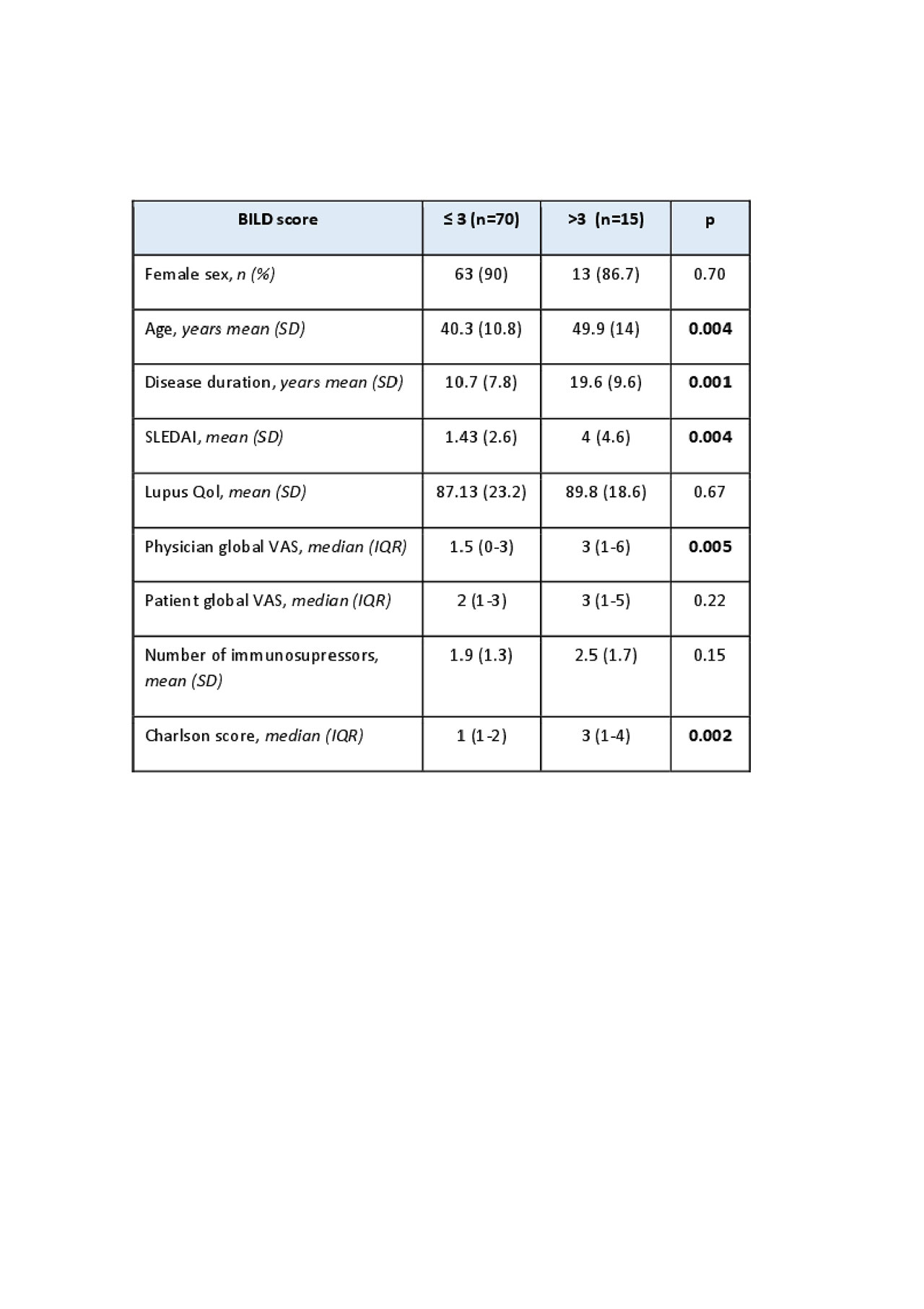
We estimated the stability by a test retest method and a Spearman correlation coefficient. Internal consistency was evaluated with the Cronbach alpha coefficient. To evaluate criterion validity, a Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated for SLICC-SDI and BILD total scores and for item-by-item comparison. To asses construct validity we compared patients characteristics and disease variables in 2 cut off points of the BILD score.
The feasibility was obtained by taking into account the percentage of no answered questions and the time required to answer.
Results: We evaluated 85 patients, 89.4% female, mean age 42 years (SD 11.9) with mean disease duration of 12.3 years (SD 8.8). Eighty percent of patients had more than 12 years of education. Fifty-five patients were white, 20 Amerindian, 9 Mestizo y 1 Asian. The mean SLICC-SDI score was 1.14 (SD 1.44) and the mean BILD score was 1.48 (SD 1.84). The test retest method showed a strong correlation with a Spearman coefficient of 0.91 (p < 0.001). The Cronbach alpha coefficient was 0.66. The correlation between total scores of BILD and SLICC-SDI and each of its domains is shown in Table 1. Table 2 shows the construct validity analysis. In the multivariate analysis patients in the upper half of BILD scores were more likely to have longer disease duration and higher Charlson score. No incomplete answers were obtained and the mean time to answer was 4 minutes and 13 seconds (SD 1.92).
Conclusion: We demonstrated that the self-reported BILD questionnaire has a strong correlation with SLICC-SDI. In the item by item analysis we found that only the domains of gastrointestinal system and skin had a weak or none correlation with the corresponding SLICC-SDI items.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
de la Torre M, Croce M, Alvarez A, Pisoni C. Validation and Transcultural Adaptation of the Spanish Version of Brief Index of Lupus Damage (BILD) Questionnaire [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-and-transcultural-adaptation-of-the-spanish-version-of-brief-index-of-lupus-damage-bild-questionnaire/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-and-transcultural-adaptation-of-the-spanish-version-of-brief-index-of-lupus-damage-bild-questionnaire/