Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2257–2325) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We aimed to investigate trends in utilization of hospital palliative care services among hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and analyze its impact on length of hospital stay, hospital charges, and in-hospital mortality.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) 2016-2020 was used to identify hospitalizations for SLE, and these were further stratified based on inpatient palliative care use. Univariate logistic regression analysis was used for yearly trends, with year of admission as the independent variable and palliative care use as the dependent variable. Length of stay and total hospitalization charges were compared using multivariate linear regression, adjusting for potential confounders. A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
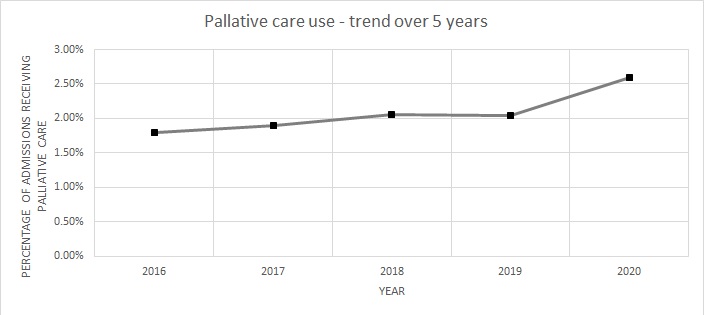
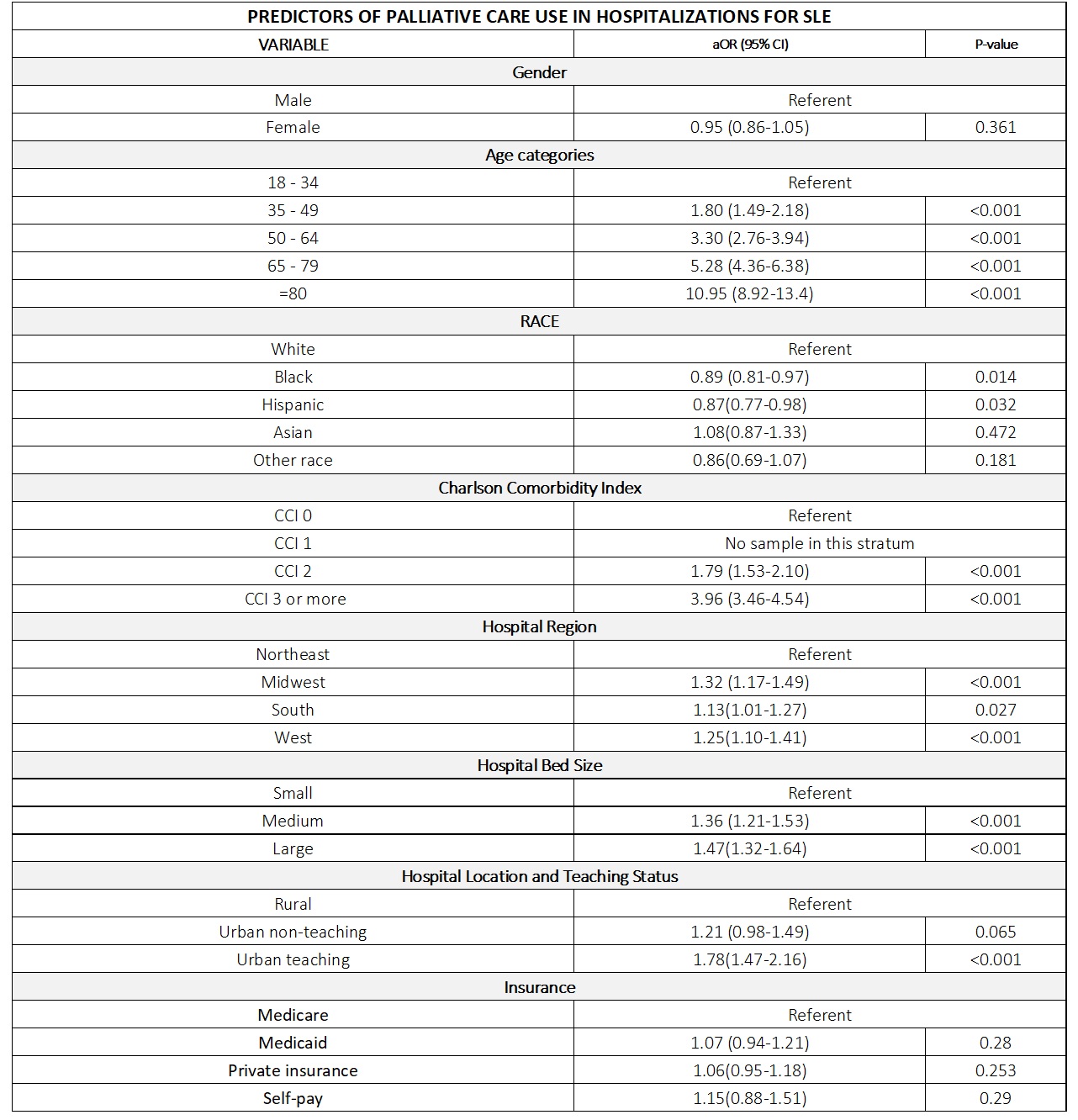
Results: The overall proportion of utilization of hospital palliative care services for patients with SLE over five years, ranging from 2016 to 2020, was 2.07%. There was a rise in the trend of utilization of palliative care services in patients with SLE, increasing from 1.8% in 2016 to 2.60% in 2020 (P-value for trend < 0.001). Older age, higher Charlson comorbidity index, admission in urban teaching hospitals and large-size hospitals were associated with more frequent use of inpatient palliative care. Age less than 35 years, Black and Hispanic race were identified as independent predictors of lower use of inpatient palliative care. Patients with SLE who received palliative care services experienced a longer hospital stay (mean difference [MD]: 4.04 days, 95 % Confidence interval [CI]: 3.62-4.46 days, p < 0.001] as well as higher hospital charges (MD: $61287, 95% CI: $53914-$68660 p < 0.001), compared to SLE admissions that did not receive palliative care.
Conclusion: Utilization for palliative care services has increased over the last five years for hospitalized SLE patients, with a significant rise in utilization during the COVID-19 pandemic. Utilization of palliative care services is associated with increased length of stay in the hospital and increased hospitalization charges. Most importantly, significant disparities exist in palliative care utilization based on racial differences and medical comorbidities. Further efforts are needed for equitable access to palliative care in patients with rheumatological diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tanveer S, Pinnam H, Tanveer F, Ahluwalia D. Utilization of Palliative Care in Hospitalized Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utilization-of-palliative-care-in-hospitalized-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-nationwide-cohort-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utilization-of-palliative-care-in-hospitalized-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-nationwide-cohort-analysis/