Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated and Related Disorders Poster I: Giant Cell Arteritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tocilizumab (TCZ) has shown to be useful in the treatment of large-vessel vasculitis, including giant cell arteritis (GCA). There is general agreement on the initial and the standard maintenance dose of TCZ. However, information on duration and optimization of TCZ in GCA is really scarce./
Our aim was to assess the effectiveness and safety of TCZ therapy optimization in an unselected wide series of GCA in real-world clinical practice.
Methods: Multicenter study on 471 patients with GCA who received TCZ therapy. Once complete remission was reached (n=231) TCZ was optimized in 125 patients. We compared patients in whom TCZ was optimized (TCZOPT group) or not (TCZNON-OPT group). Complete remission was defined as normalization of clinical and analytical (CRP and ESR) data. Optimization was done by decreasing the dose and/or prolonging the TCZ dosing interval progressively. We performed a comparison in effectiveness and safety parameters between optimized and non-optimized patients.
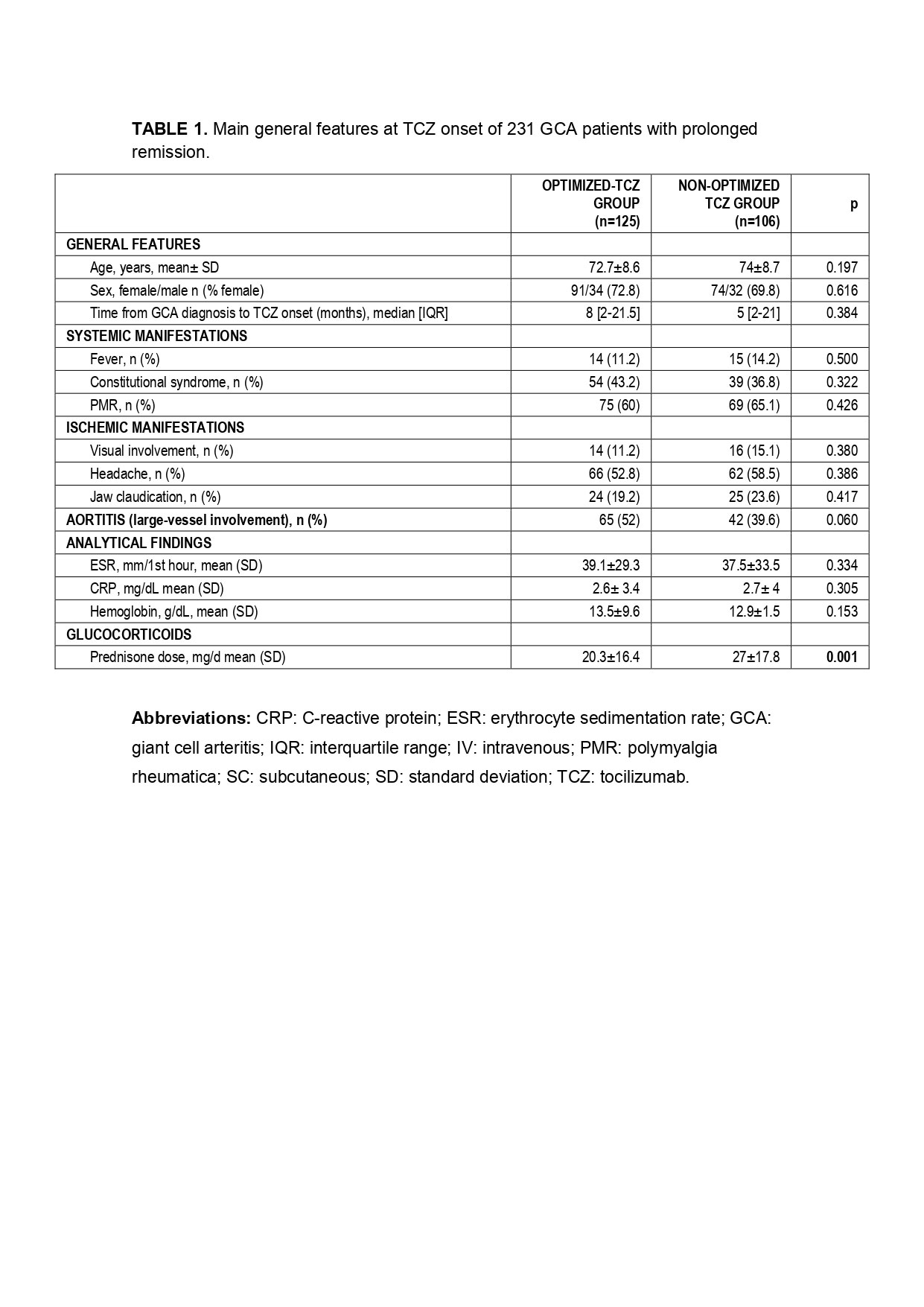
Results: We evaluated 231 GCA patients treated with TCZ with complete remission. No demographic or laboratory data differences was observed at TCZ onset between both groups (TABLE). The mean prednisone dose was higher in the TCZNON-OPT group at TCZ onset. The first TCZ optimization was performed after a median [25-75th] follow-up of 12 [6-17] months.
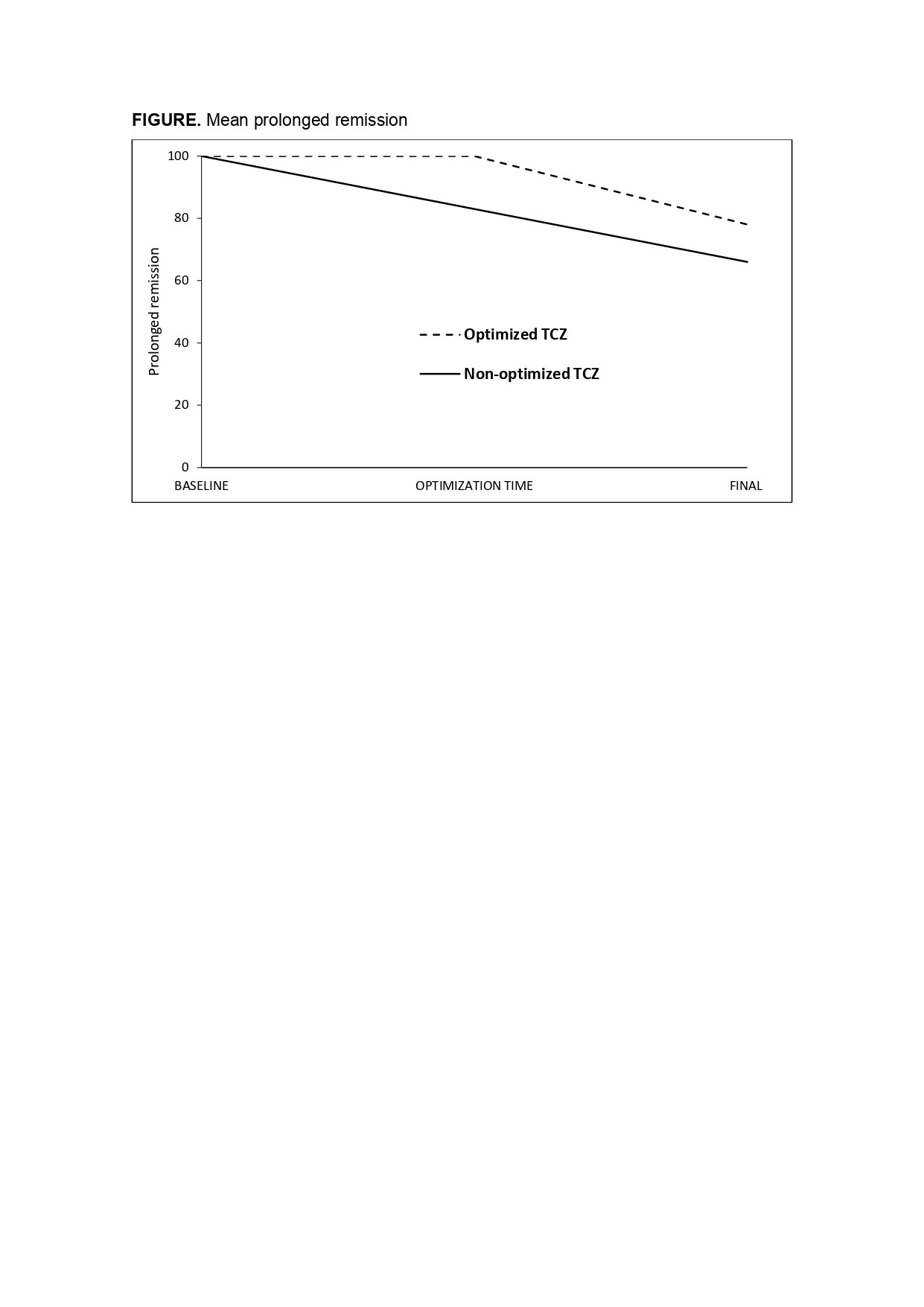
The median prednisone dose at first TCZ optimization was 2.5 [0-5] mg/day. At the end of follow-up prolonged remission was observed in 78.2% of TCZOPT group compared with 66.7% in the TCZNON-OPT group (p= 0.001) (FIGURE). Seven (5.6%) of the 125 optimized cases relapsed. Serious adverse events were similar in both groups, while serious infections were more frequent in the TCZNON-OPT group (p=0.009).
Conclusion: Once complete remission is reached in GCA patients under TCZ treatment, optimization of biologic may be performed. Based on our experience it could be performed by reducing the dose or by prolonging dosing interval of TCZ. It seems to be an effective and safe practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Benavides Villanueva F, Corrales C, Loricera J, Calderón-Goercke M, Moriano C, Castañeda S, NARVAEZ F, Aldasoro V, Maiz O, Melero R, Villa J, Vela-Casampere P, Romero Yuste S, Callejas J, De Miguel E, Galíndez-Agirregoikoa E, Sivera F, Fernández-López J, Galisteo C, Ferraz Amaro I, SANCHEZ MARTIN J, Sánchez-Bilbao L, Hernández J, Gonzalez Gay M, Blanco R. Utility of Optimization of Tocilizumab Therapy in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Multicenter Study of 471 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-optimization-of-tocilizumab-therapy-in-giant-cell-arteritis-a-multicenter-study-of-471-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-optimization-of-tocilizumab-therapy-in-giant-cell-arteritis-a-multicenter-study-of-471-patients/