Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Heart involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc) includes left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction, right ventricular dysfunction, pericardial disease, and pulmonary hypertension. We recently demonstrated the construct validity for discriminative purposes of 2 new patient-reported outcome instruments: the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System 29-item Health Profile (PROMIS-29) and the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Dyspnea short form (FACIT-Dyspnea) in assessing general health and dyspnea in patients with SSc. No studies to date have assessed the utility of PROMIS-29 and FACIT-Dyspnea in predicting cardiac involvement in SSc as assessed by comprehensive echocardiography. We hypothesized that PROMIS-29 and FACIT-Dyspnea would be comparable to legacy patient-reported outcome instruments such as the Medical Research Council Dyspnea Index (MRC), the Short-Form-36 (SF-36), the Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire (s-HAQ), and the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in predicting cardiac involvement in patients with SSc.
Methods:
Comprehensive 2D/Doppler echocardiography + tissue Doppler imaging was performed to screen for cardiac involvement and pulmonary hypertension at the initial clinic visit to a tertiary referral program. All patients fulfilled ACR criteria for SSc. A battery of legacy patient-reported outcome instruments including the MRC, SF-36, s-HAQ, and SGRQ as well as two novel instruments including the PROMIS-29 and FACIT-Dyspnea were administered.
Results:
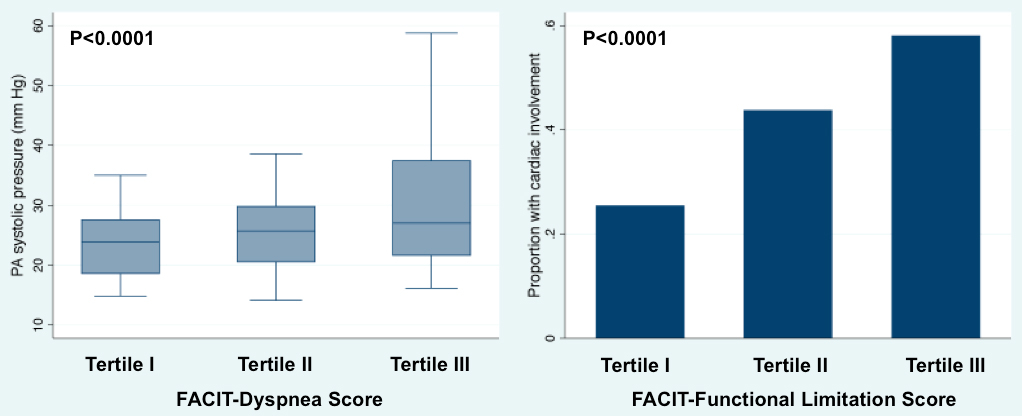
185 patients underwent echocardiography and completed patient-reported outcome questionnaires at the baseline visit. The mean age of subjects was 53±12y, 88% were women, and 60% had limited cutaneous SSc; median modified Rodnan skin score was 6 (interquartile range 4-17). There was echocardiographic evidence for pericardial effusion in 17%, pulmonary artery systolic pressure >40 mmHg in 16%, right ventricular dysfunction in 8%, left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction in in 5%, LV diastolic dysfunction in 26% and any of the above in 43% of subjects. FACIT-Dyspnea and FACIT-Functional Limitation scores were highly associated with PASP on echo and overall cardiac involvement (Figure). Area under the ROC curve for FACIT-Dyspnea (c-statistic > 0.8 for PASP) were comparable to legacy instruments (MRC, s-HAQ, and SGRQ) and superior to SF-36 (P<0.01). For overall cardiac involvement, FACIT-Dyspnea and PROMIS-29 were equivalent to legacy instruments (P=NS).
Conclusion:
PROMIS-29 and FACIT-Dyspnea are comparable to legacy patient-reported outcome instruments in predicting cardiac involvement and pulmonary hypertension in SSc and may be preferable to legacy instruments because they are freely available in many languages, are readily administered electronically, and are simple to score and interpret.
Disclosure:
M. E. Hinchcliff,
None;
M. A. Carns,
None;
S. Podlusky,
None;
J. Varga,
None;
S. J. Shah,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-novel-patient-reported-outcome-instruments-in-predicting-cardiac-involvement-and-pulmonary-hypertension-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/