Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Anemia (WHO criteria: Hemoglobin [Hb] levels <12.0 g/dL [females] or <13.0 g/dL [males]) is a common finding associated with increased joint inflammation in patients with RA and changes in Hb levels are associated with changes in disease activity; therefore, the influence of sarilumab on Hb is of clinical interest. This post hoc analysis assessed potential relationships between Hb, disease activity, and physical function in the adalimumab-controlled MONARCH study (NCT02332590).
Methods:
In the MONARCH study, adult patients intolerant of, inappropriate for, or inadequate responders to methotrexate were randomized to SC sarilumab 200 mg q2w or adalimumab 40 mg q2w monotherapy for 24 wks. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in DAS28-ESR at Wk 24. Post hoc analyses were conducted on changes in Hb using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures assuming an unstructured covariance structure: Model = baseline, treatment, region, visit, and treatment-by-visit interaction. Missing data were not imputed. Proportion of anemic patients was summarized by visit. Relationships between Hb and efficacy measures were explored.
Results:
At baseline, mean Hb levels were 13.0 g/dL in sarilumab (n=184) and adalimumab (n=185) groups and 25% of patients had anemia (WHO criteria). For the primary endpoint of change from baseline in DAS28‑ESR, sarilumab was superior to adalimumab (−3.28 vs −2.20; P<0.0001). Compared with adalimumab, at Wks 12 and 24, sarilumab resulted in larger increases in Hb (Wk 24 least squares mean change from baseline 0.591 vs 0.075 g/dL; least squares mean difference 0.516 [95% CI: 0.319, 0.713]; nominal P<0.001 [Figure]). By Wk 24, 16.2% of adalimumab-treated and 10.9% of sarilumab-treated patients were classified with anemia. In the adalimumab group, at Wk 24, correlations between increases in Hb and decreases in markers of disease activity and physical disability were noted (Figure). In the sarilumab group, increases in Hb and decreases in disease activity and physical disability were not correlated. Most common adverse events were neutropenia and injection-site reactions (sarilumab) and headache and worsening RA (adalimumab). There were three adverse event reports of anemia (none were serious or led to treatment discontinuation): 1 report of microcytic anemia (adalimumab) and 2 of worsening of anemia (sarilumab). Decreases from baseline in hepcidin and ferritin were similar for sarilumab and adalimumab at Wk 2, but not measured thereafter.
Conclusion:
Sarilumab treatment was associated with larger increases in Hb and reductions in patients with anemia than adalimumab, unrelated to its better control of RA disease activity. Sarilumab appears to be a good treatment choice in patients with RA and anemia.
Acknowledgements
Study funding and medical writing support (Sarah Feeny, Adelphi Communications) provided by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 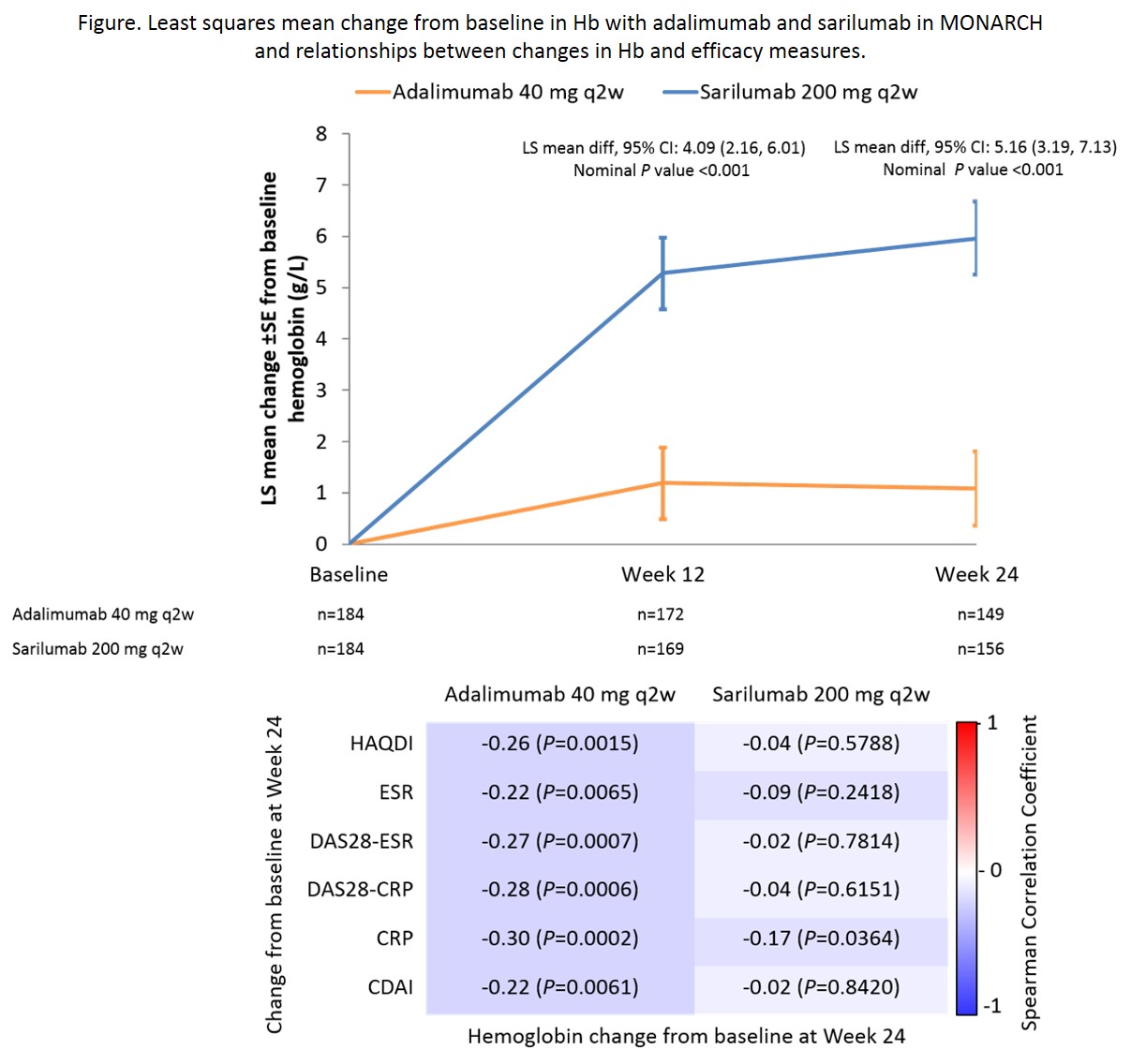
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester GR, Hagino O, Dong Q, Stanislav M, Gomez-Centeno A, Selmi C, Huizinga TWJ, Mangan E, Gabay C, Genovese MC. Unique Changes in Hemoglobin with Sarilumab Versus Adalimumab Are Independent of Better Disease Control in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unique-changes-in-hemoglobin-with-sarilumab-versus-adalimumab-are-independent-of-better-disease-control-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unique-changes-in-hemoglobin-with-sarilumab-versus-adalimumab-are-independent-of-better-disease-control-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/
