Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is a key clinical and imaging hallmark in psoriatic arthritis (PsA). ULTIMATE (NCT02662985) demonstrated responsiveness of ultrasound (US) detected synovitis and enthesitis in PsA and confirmed rapid and long-lasting benefits of secukinumab (SEC) through 52 weeks.1,2 Little is known about the relationship between US-detected enthesitis vs clinical enthesitis over time. We evaluated the responsiveness of US enthesitis to SEC over 52 weeks and the correlation with clinical response of enthesitis.
Methods: This was a 52-week study with a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment period, a 12-week open-label (OL) treatment period and a 6-month extension period. Patients with ≥1 clinical enthesitis site, defined by the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) index,were randomized to weekly SEC (300 or 150 mg according to severity of skin psoriasis) or placebo. Placebo patients switched to OL SEC at Week 12 (‘placebo-SEC’). Enthesitis was assessed by Power Doppler (PD) performed bilaterally across 6 sites (enthesitis-level), and at patient level with the novel global Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) enthesitis score, which included 2 definitions of activity: definition 1 combinedB-mode morphological abnormalities (0–1) and PD vascularization abnormalities (0–3); definition 2 focused on PD signal alone (0–3). Clinical response was assessed by SPARCC enthesitis index (0–16). We report observed data on the distribution of US and clinical enthesitis, enthesitis resolution over 52 weeks, and the correlation between US and clinical enthesitis from baseline (BL) to Week 12.
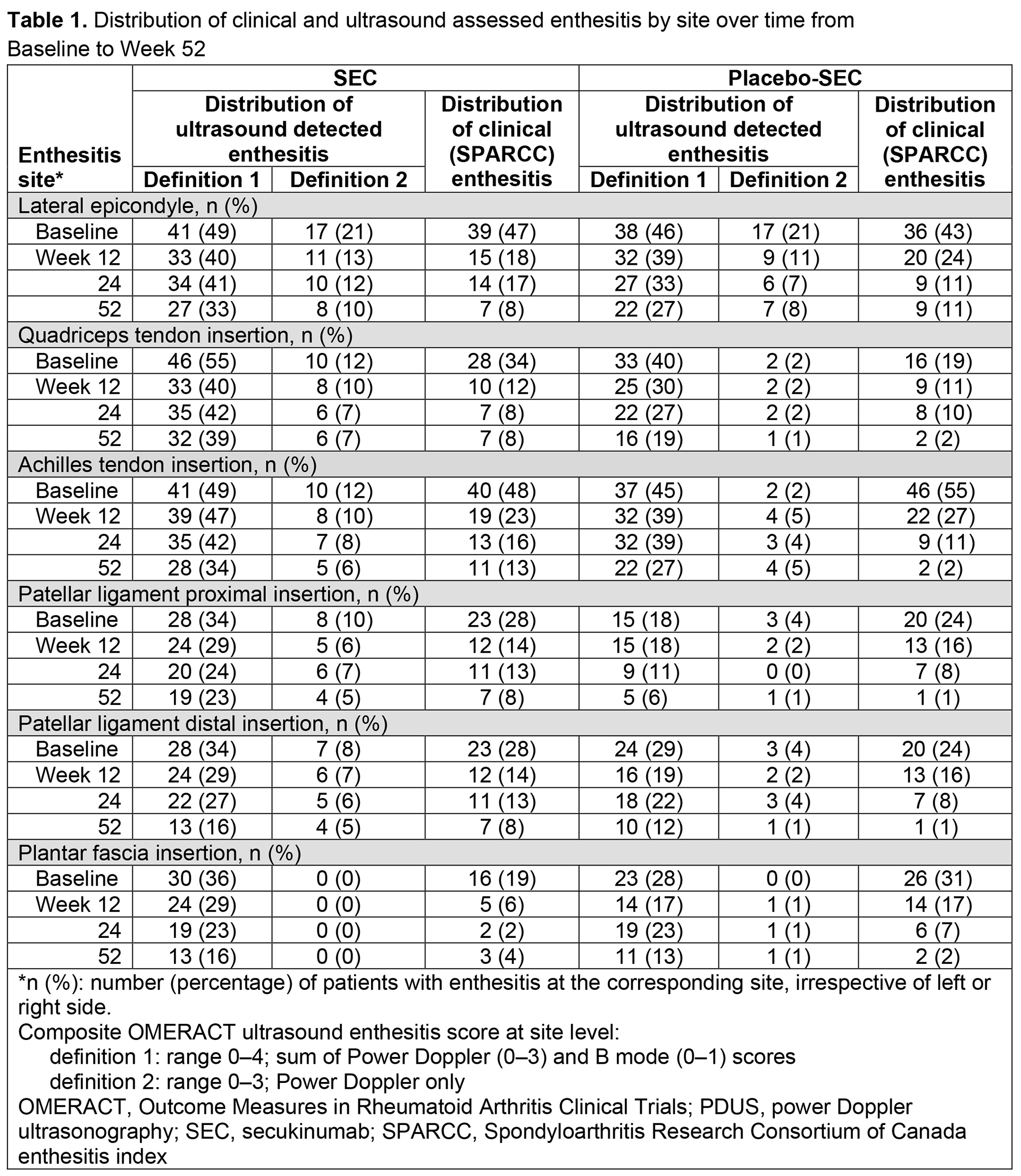
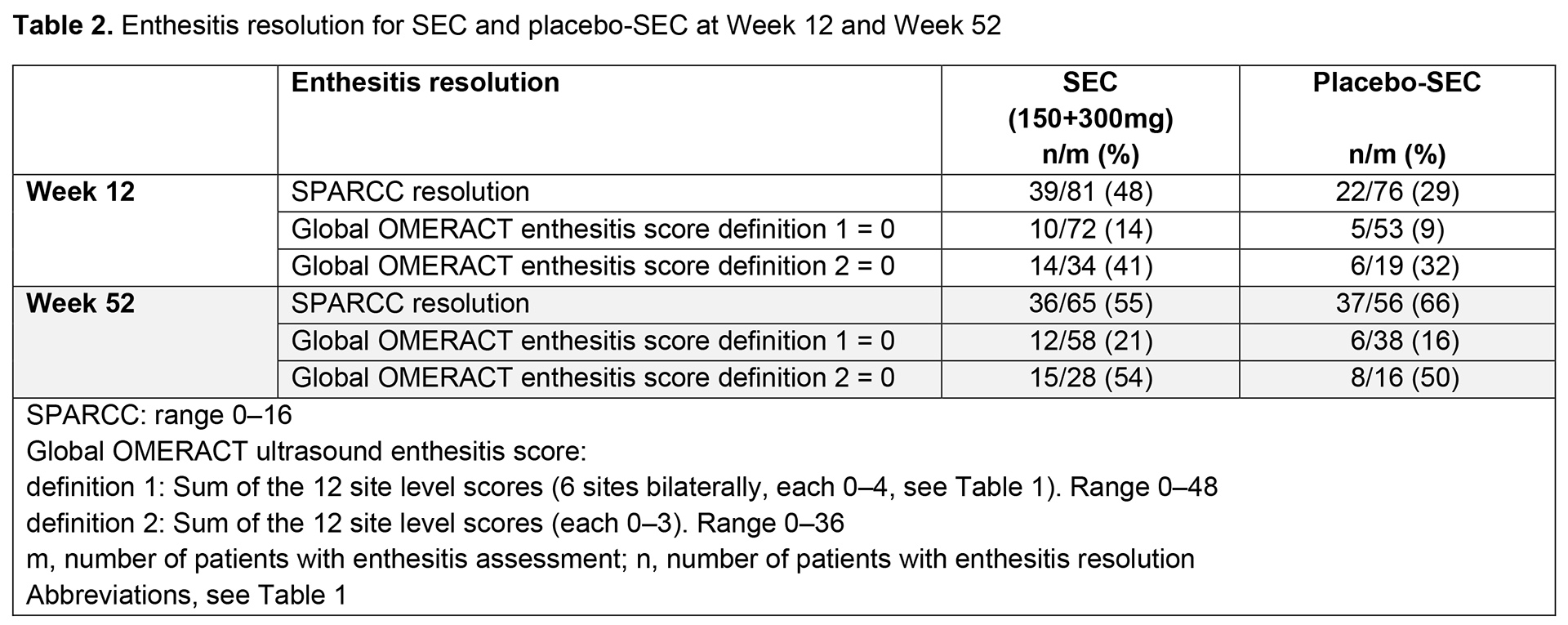
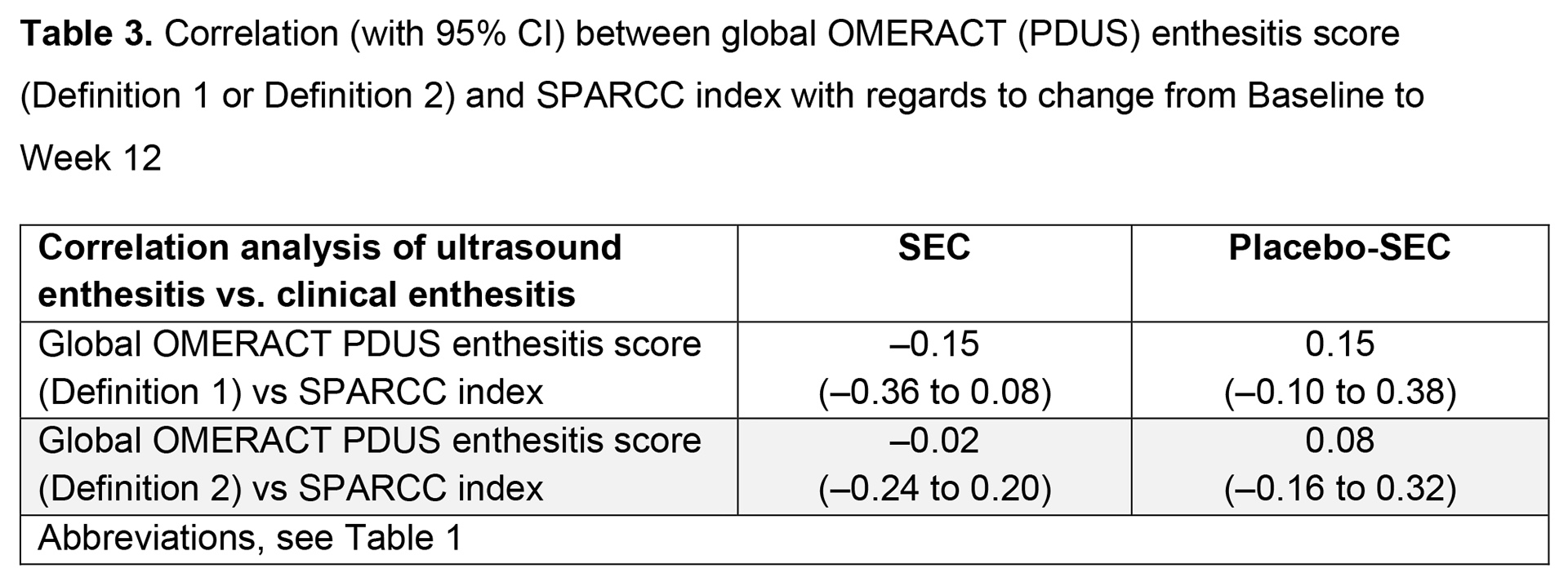
Results: Overall, 166 patients were randomized; 90% (75/83) in the SEC group and 83% (69/83) in the placebo-SEC group completed 52 weeks. The mean number of clinical enthesitis sites at BL was 4 in both the SEC and placebo groups. Mean (SD) global OMERACT enthesitis scores were 6 (4.7) and 5 (3.2) (definition 1) and 3 (3.4) and 3 (1.6) (definition 2), for SEC and placebo-SEC, respectively. The proportion of patients with US-detected and clinical enthesitis decreased for most enthesitis sites in both treatment groups from BL to Week 24 and remained stable up to Week 52; definition 2 generally performed more closely to SPARCC clinical index than definition 1 (Table 1). According to the global OMERACT enthesitis score (definition 1 or 2), resolution of enthesitis was observed in a higher proportion of patients in the SEC vs placebo-SEC group at Week 12; the difference between SEC and placebo-SEC was similar at Week 52 (Table 2). No correlations were observed between the OMERACT score (definition 1 or 2) and SPARCC index regarding change from BL to Week 12 (Table 3).
Conclusion: A long-term stable response was observed with SEC and placebo-SEC in both US and clinical enthesitis up to Week 52. We found no correlation between US and clinically detected enthesitis, likely because the former assesses inflammation based on morphological/functional tissue changes while the SPARCC index evaluates inflammation based on tenderness of the entheseal site.
References:
1. D’Agostino MA, et al [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9).
2. D’Agostino MA, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(5):1867–1876.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
D'Agostino M, Gaillez C, Schett G, Boers M, Carron P, Mandl P, ROSA J, Naredo E, Bakewell C, Bao W, Conaghan P. Ultrasound Enthesitis Responsiveness versus Clinical Enthesitis Responsiveness: Week 52 Results of an Exploratory Analysis from a Phase 3b Study in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-enthesitis-responsiveness-versus-clinical-enthesitis-responsiveness-week-52-results-of-an-exploratory-analysis-from-a-phase-3b-study-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-enthesitis-responsiveness-versus-clinical-enthesitis-responsiveness-week-52-results-of-an-exploratory-analysis-from-a-phase-3b-study-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/