Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The assessment of activity in spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) involves several domains, including enthesitis. Clinical enthesitis has shown low sensitivity, specificity and reliability. The MAdrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index (MASEI) is a feasible and reliable ultrasound score, but its responsiveness to treatment has not yet been evaluated. Our aim was to explore the sensitivity to change of power Doppler (PD) enthesitis in active spondyloarthritis (SpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients.
Methods: Longitudinal study in patients with SpA and PsA with active disease (defined as patients who were going to start or switch biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) therapy). The MAdrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index (MASEI) was performed at baseline, 3- and 6-months visits. MASEI and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) PD enthesitis definitions were checked. A reliability analysis among three readers was performed with ultrasound (US) recorded videos.
Results: US examinations of 25 patients were included, of whom 13(52%) were ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients, 9(36%) PsA and 3(12%) non radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA). Median age was 49 (41-61) years and 13(52%) patients were females. Median DAS28 3.6 (2.3-4.2), median BASDAI 6.7 (6.1-7.4), and CRP values 8.2 (1.6-20), reflect moderate-high disease activity at baseline. Both MASEI and OMERACT PD enthesitis improved significantly at 3- and 6-month follow-up visits (p< 0.05) (Table 1) and showed sensitivity to change with a standard error of measurement (SEM) of 0.47 and 0.61 respectively. Improvement in clinical activity outcomes was significantly associated with a decreased of the MASEI and OMERACT PD enthesitis count (p< 0.05). Reliability of MASEI and OMERACT PD definitions among the three readers was excellent (kappa 0.918 and 0.865 respectively).
Conclusion: PD enthesitis significantly improves at 3- and 6- months of follow up in patients under bDMARD treatment. Both MASEI and OMERACT PD definitions of US active enthesitis reflect treatment response.
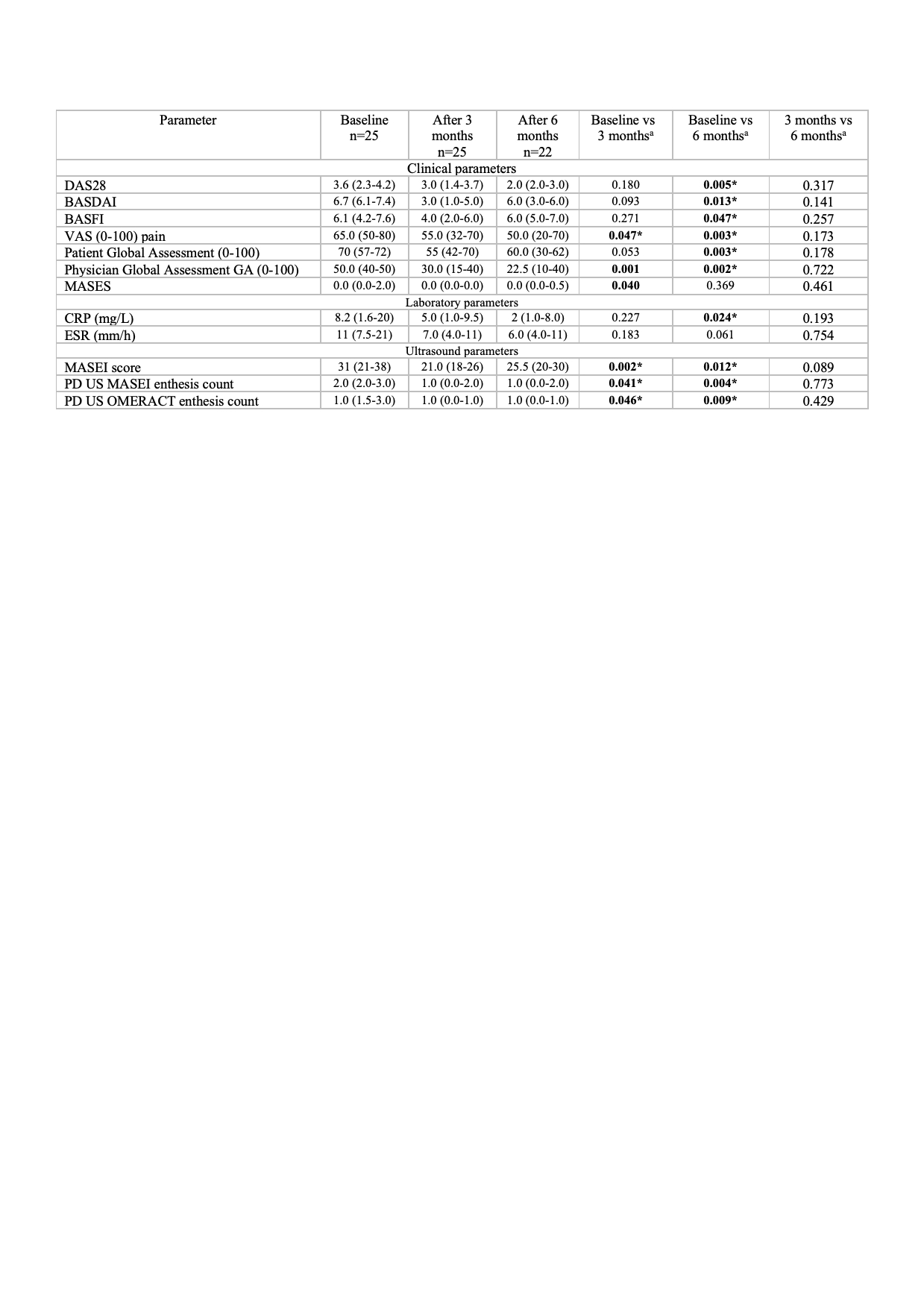 Table 2. Clinical, laboratory and MASEI evaluation at baseline, 3- and 6-month follow-up visits aWilcoxon test between time visits
Table 2. Clinical, laboratory and MASEI evaluation at baseline, 3- and 6-month follow-up visits aWilcoxon test between time visits
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molina Collada J, Macía-Villa C, Plasencia C, Alvaro-Gracia J, De Miguel E. Ultrasound Doppler Enthesitis Shows Sensitivity to Change After Biological Therapy in Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-doppler-enthesitis-shows-sensitivity-to-change-after-biological-therapy-in-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasound-doppler-enthesitis-shows-sensitivity-to-change-after-biological-therapy-in-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/
