Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: EULAR recommendations highlights ultrasound (US) as the first line imaging investigation for giant cell arteritis (GCA). Traditionally, the halo sign and compression sign have been used to discriminate between GCA and non GCA patients. We propose a novel Halo Score (HS) as a potential marker to diagnose and assess disease activity in follow up GCA patients.
Methods: Preliminary data was collected from the ongoing prospective multicentre HAS GCA study (IRAS# 264294) from referrals of suspected GCA to UK fast track clinics with GCA follow up at months 1,3,6 and 12. Based on the GCA clinical pre-test probability score (PTPS)1, patients were stratified in to Low , Intermediate and High risk categories2. US Halo Score was calculated from the halo thickness and extent in bilateral temporal arteries and branches (TA Halo Score) and bilateral axillary arteries (AA Halo Score) summed up to a Total Halo Score. GCA was diagnosed based on the clinical symptoms and signs, positive US or additional test results with CRP >5 mg/dl. The objective is to recruit 270 patients including 68 patients with GCA.
Mann Whitney U test was used to compare controls and baseline GCA
Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to compared baseline GCA and 1m GCA (only patients that had two measurements)
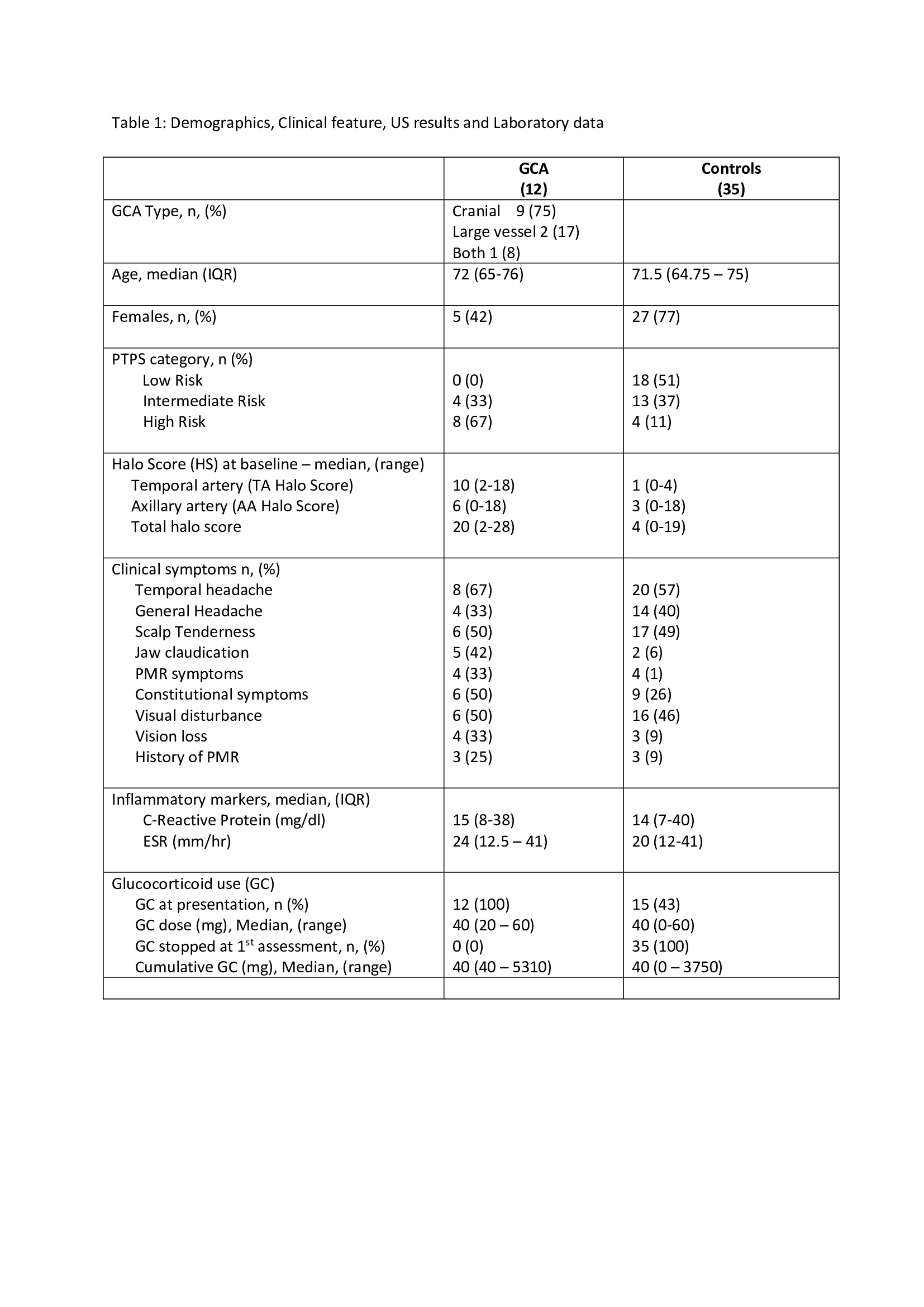
Results: Total of 47 patients have been recruited so far into HAS GCA with 1 month follow up assessments. Demographics, clinical features and US results are shown (Table 1).
Twelve (26%) were confirmed GCA (9 cranial, 2 large vessel and 1 cranial plus large vessel) and 35 (74%) confirmed non-GCA. Median age 72 years in GCA and 71.5 years in controls (42% females in GCA and 77% non GCA). GCA patients stratified by PTPS to Low risk (0%), Intermediate risk (33%) and High risk (66%) whereas the 35 non GCA were categorised by PTPS as Low risk 51%. Intermediate risk 37% and High risk 11%.
In High risk 1 LV GCA patient had negative US and FDG PET/CT confirmed bilateral vertebral arteritis. Another patient with axillary artery US positive LV-GCA had a negative FDG PET/CT without other pathologies. In the Intermediate risk, one patient had negative US and negative MRA.
Jaw claudication (42%) and polymyalgic symptoms (33%) were the dominant features in GCA patients contrast to controls. 4 had permanent visual loss prior to the assessment. a Median Total Halo Score in GCA was 20 and control group was 4 (p=0.0001). 9/12 patients with GCA have completed at least 1 month follow up (Table 2). Median TA Halo Score and Total Halo Score was reduced from 8 to 3 and 16 to 11 respectively (Image). AA Halo Score increased from 6 to 9 in 1 month. All the GCA patients were on glucocorticoids (GC) (prednisolone 40-60 mg daily) at presentation compare to 43% (15) in control group (in all GC discontinued after the assessment).
Conclusion: Along with GCA clinical PTPS, US Halo Score successfully discriminates GCA from non GCA mimics. TA Halo Score and Total Halo Score is effective in showing 4-week response and may be a useful marker to monitor GCA disease activity. The ongoing viral pandemic may have an effect on protocol-based US assessments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sebastian A, Kayani A, Innes S, Jackson J, van der Geest K, Dasgupta B. Ultrasonographic Halo Score as a Marker for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Disease Activity in GCA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasonographic-halo-score-as-a-marker-for-diagnosis-and-monitoring-of-disease-activity-in-gca/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ultrasonographic-halo-score-as-a-marker-for-diagnosis-and-monitoring-of-disease-activity-in-gca/