Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects IV: Medications and Risk
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
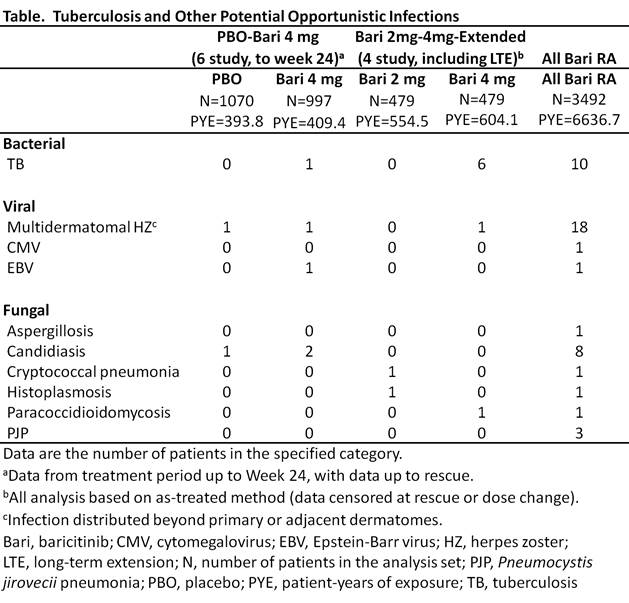
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari) is an oral selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2 inhibitor approved in the EU for the treatment (trt) of moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in adults. Compared to the general population, RA patients (pts) have an increased rate of tuberculosis (TB) and other potential opportunistic infections (OI). This analysis evaluated reported potential OI in RA pts treated with bari across 8 completed studies (4 Phase [Ph] 3, 3 Ph2, 1 Ph1) and 1 ongoing long-term extension (LTE) study, with data up to September 1, 2016.
Methods: The All bari RA analysis set included pts exposed to any bari dose, with exposure up to 5.5 years (yrs) (Ph 1-3 and LTE studies); the comparison with placebo (PBO) was based on 6 studies (Ph 2-3) with bari 4 mg QD and PBO up to week (wk) 24 (PBO-bari 4 mg set); dose-response assessment was based on 4 studies (Ph 2-3) with bari 2 and 4 mg QD, including the LTE (bari 2mg-4mg-extended set); the methotrexate (MTX) and adalimumab (ADA) data were based on the individual studies RA-BEGIN and RA-BEAM, respectively, up to wk 52. Reported potential OI were identified using Lilly-defined preferred terms from the Infections and infestations system organ class of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) and pre-specified pairings of infecting organism and infection site. Sponsor medical review of these events was conducted to identify potential OI.
Results: Forty-five events, including TB, were identified in the All bari RA set (Table). There were 10 reported cases of TB (incidence rate [IR]=0.15/100 pt-yrs [PY]); all occurred in TB-endemic regions and 6 were associated with extra-pulmonary involvement. Bari was associated with an increased risk of trt emergent herpes zoster (HZ) compared to PBO in the PBO-bari 4 mg set (PBO IR=1.0/100PY, bari IR=4.3/100PY). In the All bari RA set, 18 HZ cases had distribution beyond the primary or adjacent dermatomes (considered potential OI), with 194 additional cases (overall IR=3.2/100PY). There were no visceral cases; 4 were associated with facial palsy (3) or other motor nerve palsy (1) and 3 had ocular involvement. Single cases of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infection were reported. Fungal events of candidiasis involving the esophagus (6), lung (1), and soft tissue (1), Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (3, all in Japan) and single cases of histoplasmosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcal lung infections, and aspergillosis skin infection were reported. Few events occurred in the randomized, controlled portion of the studies, or with active comparator trt (MTX: none; ADA: 1 TB). Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy was not seen in the bari RA program.
Conclusion: Trt with bari was associated with an increased risk of HZ. TB and other potential OI, including HZ with distribution of infection beyond the primary or adjacent dermatomes, were uncommon with bari trt.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Lindsey S, Harigai M, Bradley JD, Chen L, Hyslop DL, Issa M, Nishikawa A, Witt S, Dickson CL, Dougados M. Tuberculosis, Potential Opportunistic Infections, and Other Infections of Interest in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Baricitinib Program [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tuberculosis-potential-opportunistic-infections-and-other-infections-of-interest-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-baricitinib-program/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tuberculosis-potential-opportunistic-infections-and-other-infections-of-interest-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-baricitinib-program/