Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There are significant correlations between serum uric acid (sUA) and blood pressure (BP) in individuals with and without gout.1 Limited data suggest that lowering sUA may decrease BP2, but a metaanalysis suggests no consistent effect3. Pegloticase is a recombinant uricase conjugated to polyethylene glycol approved for chronic refractory gout that decreases sUA to <1 mg/dL.4 The results from the pegloticase randomized clinical trials (RCTs) permitted determination of the impact of persistent, very low sUA levels on BP in subjects with chronic refractory gout.
Methods: This analysis used results from 2 6-month RCTs in which subjects were treated with 8 mg pegloticase every 2 or 4 weeks (q2 or q4) or placebo.4 sUA responders maintained sUA <6 mg/dL .4 Sitting BP was measured at each visit and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was determined at baseline and after 3 and 6 months.
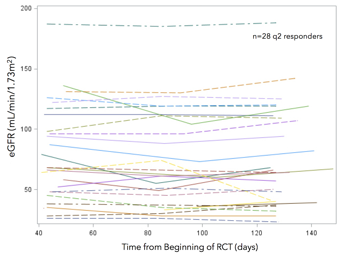
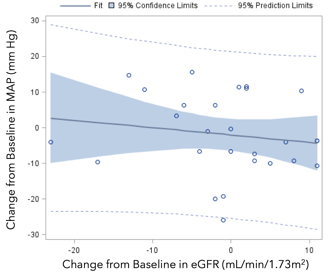
Results: Serial blood pressure measures were obtained in 173 subjects during the course of the RCTs. Significant reductions in mean MAP from baseline to 6 months were noted in q2 responders (P=0.0029) (Figure 1), whereas reductions in mean MAP in other groups were not significant. Notably, 18/29 (62.1%) of q2 sUA responders experienced persistent reductions in MAP (p=0.01 compared to other groups). Of the q2 sUA responders exhibiting persistent decreases in MAP, there were no significant differences in baseline age, gender, race, BMI, history of hypertension, gout duration, MAP, sUA, cholesterol, eGFR or urinary UA /creatinine ratio compared with those who did not lower MAP. There were no significant changes in eGFR in sUA responders to pegloticase treatment over the course of the study (Figure 2) and there was no significant correlation between change from baseline MAP and eGFR in these subjects (r= -0.16, P=0.43) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: sUA responders to pegloticase experienced significant reductions in MAP that were independent of changes in renal function.
1. Lee JJ, et al. J Clin Hyperten.2013;15:435.
2. Agarwal V, et al. J Clin Hyperten. 2013;15:435.
3. Franca GPH, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017, 4:CD008652.
4. Sundy JS, et al. JAMA. 2011;306:711.
Figure 1. MAP over study visits in all treatment groups
Figure 2. eGFR measurements in q2 responders (each line is an individual subject)
Figure 3. Relationship between changes from baseline in MAP and eGFR for q2 responders
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi HK, Johnson R, Yeo A, Lipsky PE. Treatment with Pegloticase Significantly Decreases Mean Arterial Blood Pressure in Patients with Chronic Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-pegloticase-significantly-decreases-mean-arterial-blood-pressure-in-patients-with-chronic-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-pegloticase-significantly-decreases-mean-arterial-blood-pressure-in-patients-with-chronic-gout/