Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Several options exist in the treatment of PsA, but data on long-term persistence are rare. Here, we assess long-term persistence with ustekinumab (UST) or TNF inhibitor (TNFi) in patients treated for PsA in the real world.
Methods: PsABio (NCT02627768) was a multinational, observational study in patients with PsA treated with 1st, 2nd, or 3rd line UST or a TNFi. Here we present drug persistence, one of the primary outcomes. All patients with baseline and post-baseline effectiveness data up to the complete study duration (3 years ± 3 months), including those who switched/stopped initial treatment, were analyzed. Persistence of UST and TNFi is presented as Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves and compared between cohorts using Cox regression analysis, including propensity score (PS) to adjust for baseline imbalanced covariates. Factors including concomitant MTX use and skin involvement were added to the Cox model to investigate their effect on the PS-adjusted treatment effect. Hazard ratios (HR) including 95% confidence intervals (CI) are presented.
Results: Baseline characteristics, treatment data, and comorbidities potentially influencing persistence showed imbalance between treatment groups, especially with treatment line (21% of patients in the UST group were on 3rd-line treatment vs 12% in the TNFi group) and comorbidities (67% in UST vs 57% in the TNFi group) (Table 1). Of 439 and 456 patients who started UST and TNFi, respectively, 42% and 41% stayed on their first treatment up to Month 36. Mean duration of initial treatment line was 24.7 (95% CI: 23.5 ; 25.8) months for UST and 24.1 (95% CI: 22.9 ; 25.3) months for TNFi-treated patients. Reasons for stopping/switching were related to safety and tolerability in 17% (UST) and 24% (TNFi) patients, and effectiveness in 83% (UST) and 76% (TNFi) patients.
Unadjusted KM graphs are shown in Figure 1a–c. Similar to findings from the 1-year persistence analysis (1), the estimates demonstrated similar drug persistence between UST and TNFi (Figure 1a). As expected, 1st-line biologic treatment was associated with longer treatment persistence than other lines. After PS adjustment for baseline imbalances, the risk of stopping/switching was similar for UST vs TNFi; HR 0.94 (0.75 ; 1.16). In patients with severe psoriasis (body surface area >10%), risk of stopping/switching was lower for UST vs TNFi; HR 0.55 (0.32 ; 0.98); a similar effect was seen for treatment with UST monotherapy vs TNFi monotherapy (without MTX); HR 0.75 (0.57 ; 0.98). This points to the importance of treatment persistence, next to concomitant therapy, when there is skin involvement.
Conclusion: In the prospectively followed PsABio study across Europe, slightly more than 40% of PsA patients stayed on UST or TNFi for 3 years or more. After correction for baseline differences, the risk of stopping/switching treatment over 3 years was similar for UST and TNFi, with better persistence for UST vs TNFi in the subgroup of patients with severe psoriasis and in those receiving the biologic DMARD without MTX. Both drug classes offer interesting options for the treatment of PsA.
Reference:
1. Gossec L, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(suppl 1):1145 (Abstract SAT0398).
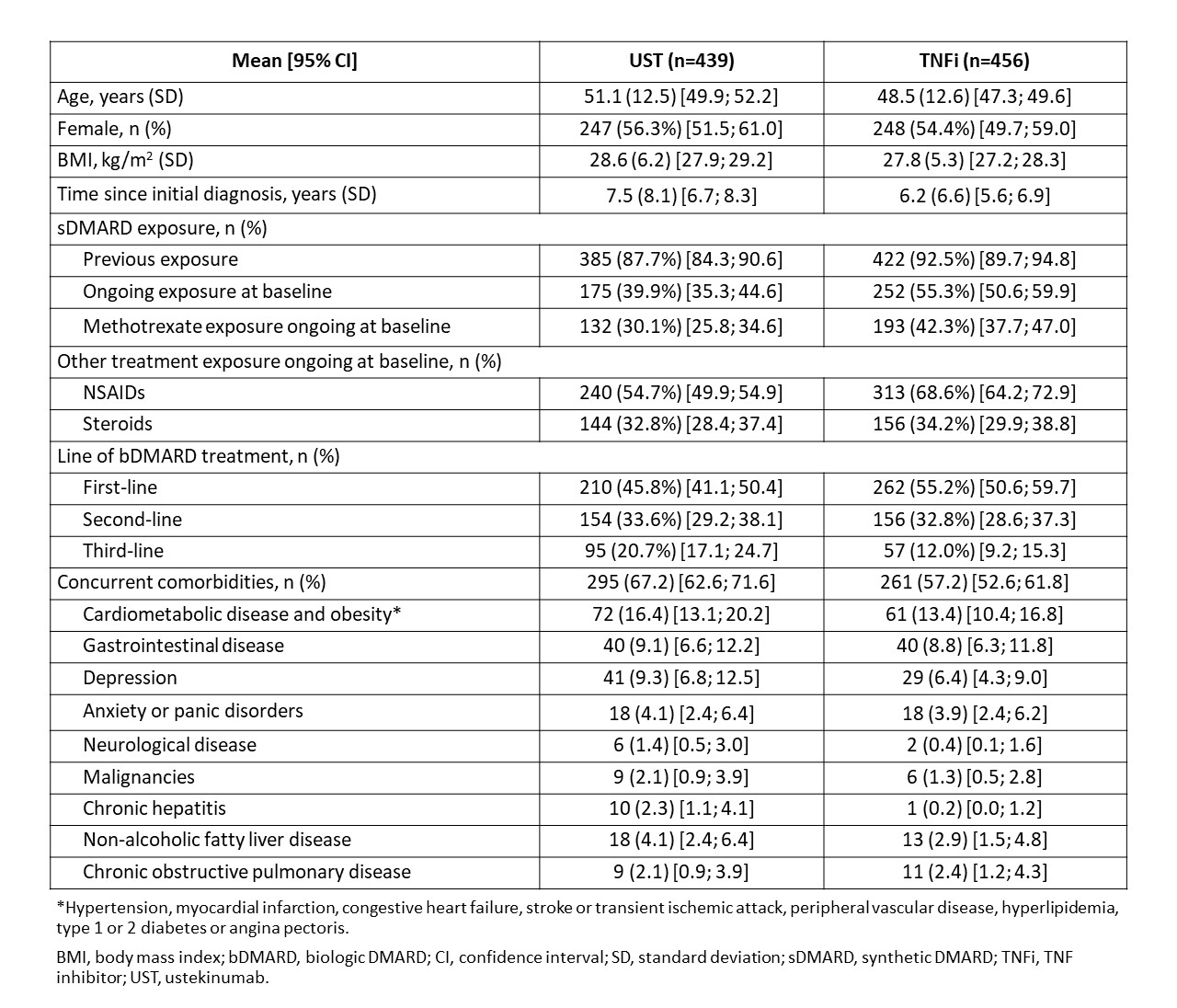 Table 1: Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics and comorbidities of PsA patients treated with ustekinumab and TNFi
Table 1: Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics and comorbidities of PsA patients treated with ustekinumab and TNFi
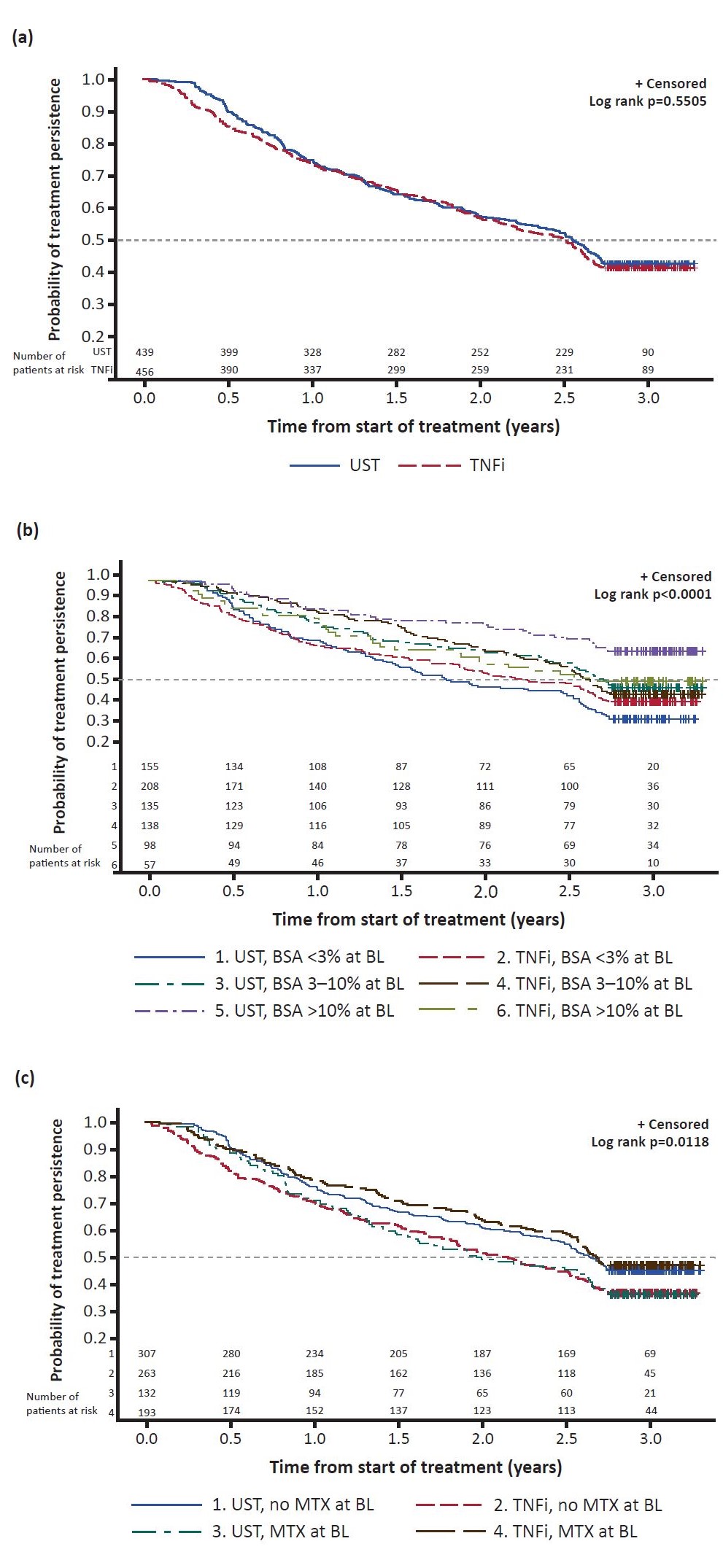 Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier graphs showing treatment persistence by (a) UST vs TNFi; (b) bDMARD and extent of skin involvement at baseline; (c) bDMARD and presence/absence of MTX at baseline. Dotted line indicates median survival. The curves becoming flat after 2.5 years is due to some patients prematurely stopping the study. bDMARD, biologic DMARD; BL, baseline; BSA, body surface area; TNFi, TNF inhibitor; UST, ustekinumab
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier graphs showing treatment persistence by (a) UST vs TNFi; (b) bDMARD and extent of skin involvement at baseline; (c) bDMARD and presence/absence of MTX at baseline. Dotted line indicates median survival. The curves becoming flat after 2.5 years is due to some patients prematurely stopping the study. bDMARD, biologic DMARD; BL, baseline; BSA, body surface area; TNFi, TNF inhibitor; UST, ustekinumab
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Siebert S, Bergmans P, de Vlam K, Gremese E, Joven-Ibáñez B, Korotaeva T, Noël W, Nurmohamed M, Sfikakis P, Theander E, Smolen J. Treatment Persistence Was Similar at 3 Years in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Ustekinumab (STELARA®) or a Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor in a Prospective Real-World Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-persistence-was-similar-at-3-years-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ustekinumab-stelara-or-a-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-in-a-prospective-real-world-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-persistence-was-similar-at-3-years-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ustekinumab-stelara-or-a-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-in-a-prospective-real-world-study/
