Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic immune-mediated rheumatic disease with high comorbidity burden. Biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) are increasingly utilized for disease management. However, there is a need for real-world evidence on PRO collection practices and the impact of bDMARDs on axSpA symptom control. The current study evaluated real-world characteristics, treatment patterns, clinical outcomes, and PRO collection in patients with axSpA using electronic health records (EHR) from a large US rheumatology care network, United Rheumatology (UR).
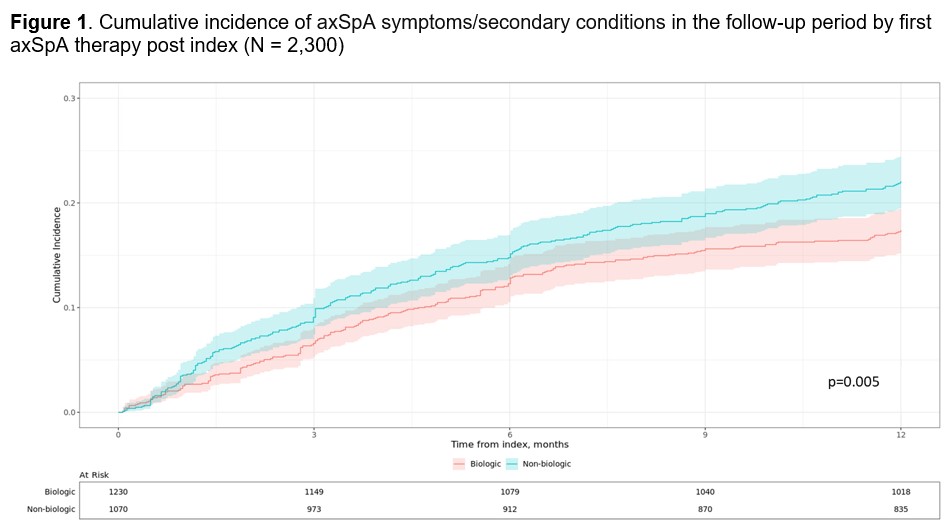
Methods: Adults newly diagnosed with axSpA from 01/2016 to 11/2022 were identified in the UR EHR database. Patients were required to have EHR records in UR for ≥12 months before and after (i.e., baseline and follow up period) first axSpA diagnosis (index date). Patient characteristics were assessed at index or at baseline. Treatment patterns at class level (bDMARDs, conventional synthetic DMARDs, targeted synthetic DMARDs, non-steroidal anti-rheumatic treatment, glucocorticoids) and PROs (BASDAI and RAPID3) were assessed in the follow-up period. Kaplan-Meier methodology was used to compare the cumulative clinical incidence of axSpA symptoms/secondary conditions between patients initiated vs not initiated on bDMARDs, including diagnoses in sacroiliac/peripheral joints or axial skeleton as well as fatigue, stiffness, or back/hip/neck pain diagnoses not recorded during baseline period.
Results: The sample included 2,641 patients (mean age at diagnosis: 53 years [SD: 15]; male: 60%; commercially insured: 74%). The most common diagnoses observed at the baseline period were osteoarthritis (21%), fibromyalgia (7%), and neurological disorder (6%); the most common symptom category was back/hip/neck pain (22%). During follow up, 13% received no axSpA treatment, 24% received non-bDMARDs only, and 63% received bDMARDs and other classes. Among the 1,664 bDMARD users, 28% used bDMARDs only, 72% used bDMARDs and other classes, 74% used bDMARDs as initial treatment, and mean (SD) time from diagnosis to first bDMARD was 1.6 (22.6) months. Among the 636 non-bDMARD users, 57% and 43% were treated with a single vs multiple treatment classes, respectively. bMARD users had a significantly lower cumulative incidence of axSpA symptoms/secondary conditions (17% vs 22%; p< 0.01; Fig 1), suggesting improved symptom control. BASDAI and RAPID3 data were not consistently assessed over time, with only 41% and 43% of patients following recommendations for PRO collection at 0-6 and 6-12 months following axSpA diagnosis, respectively.
Conclusion: This study highlights extensive use of bDMARDs in real-world management of axSpA, which contributes to significantly better symptom management compared to non-bDMARDs. However, findings also indicate that less than half of patients follow recommendations for PRO collection in real-world settings, which could contribute to patients not receiving appropriate treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concoff A, Taiji R, Grennell-Merrick L, Rodrigues J, McDermot C, Niak U, Ionescuittu R, Faucher A, Vekeman F, Nguyen T. Treatment Patterns, Clinical Characteristics, and Patient-Reported Outcomes Among Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Treated in Real-World Rheumatology Practices in the US [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-patterns-clinical-characteristics-and-patient-reported-outcomes-among-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-treated-in-real-world-rheumatology-practices-in-the-us/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-patterns-clinical-characteristics-and-patient-reported-outcomes-among-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-treated-in-real-world-rheumatology-practices-in-the-us/