Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient (pt) support programs (PSPs) are offered to Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pts to help manage treatment of this chronic disease. Little information is available regarding the impact of these PSPs on disease management and factors affecting their use. The purpose of this study was to assess characteristics and predictors that influence pt participation in the PSP among adalimumab (ADA)-treated RA pts.
Methods: In this multinational, ex-US study, RA pts with an insufficient response to ≥1 disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) newly initiating ADA (1 prior biologic DMARD was allowed) were enrolled. Pts were offered a panel of “Core elements” (starter pack, call center/hotline, nursing services, educational material, and injection guide; offered in all participating countries) and “Other elements” (e.g, refill reminders, email, newsletters, support groups, home delivery, and financial assistance; vary by country) of PSP. PSP participation was captured via a PSP utilization questionnaire at each study visit. Pts were classified based on PSP participation: ever (PSP users) vs never (PSP non-users) which served as a dependent variable in a multivariate logistic regression model examining the following parameters: baseline (BL) age, sex, race, RA disease duration, prior use of biologic DMARD, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Patient Activation Measure-13 (PAM-13), BL Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), and BL 28-joint DAS based on CRP (DAS28(CRP)).
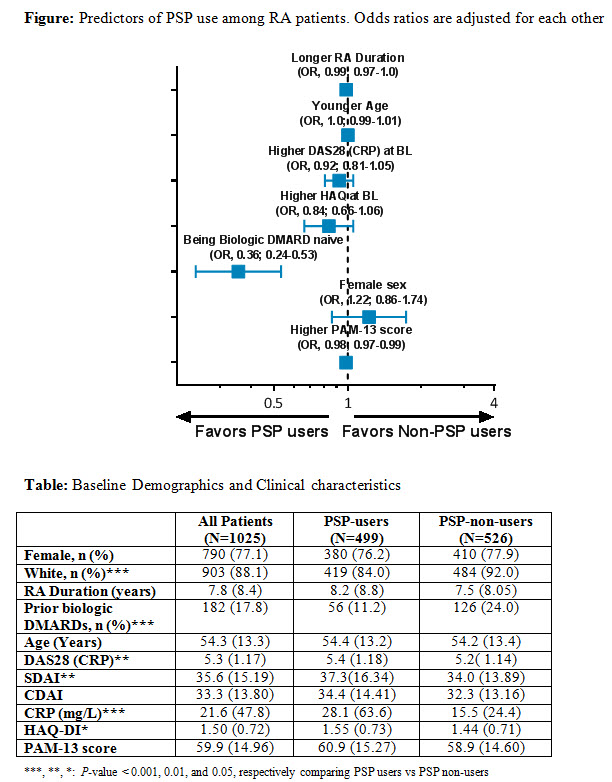
Results: Of the 1,025 pts included in the Intent-to-treat population, 48.7% were PSP users. The BL demographics and clinical characteristics are enlisted (Table). After adjusting for BL demographics and clinical characteristics, the odds ratio of using a PSP was significantly lower in pts who previously used a biologic DMARD. Several factors, including female sex, and higher HAQ-DI, and DAS28(CRP) at BL, had statistically non-significant lower likelihood of PSP utilization (Figure). Study discontinuation rates were significantly (P<0.001) lower among PSP users vs PSP non-users (25.5% vs 41.6%).
Conclusion: In pts with moderate to severe RA newly initiating ADA, PSP users were found to have differences in baseline demographics and clinical characteristics. After accounting for these baseline differences, being naïve to prior biologic DMARD treatment was significantly associated with PSP participation. Pt participation in the PSP was associated with better retention in the study, underscoring a potential link between PSP participation and treatment adherence that should be further explored in prospective studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Den Bosch F, Wassenberg S, Östör A, Wang C, Kalabic J, Garg V. Treatment Outcomes and Predictors of Patient Support Program Use Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Post-Marketing Observational Study (PMOS) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-outcomes-and-predictors-of-patient-support-program-use-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-a-post-marketing-observational-study-pmos/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-outcomes-and-predictors-of-patient-support-program-use-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-a-post-marketing-observational-study-pmos/