Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose . Treating disease to target is emerging as the recommended strategy also in the management of axial-SpA (axSpA) (1). Reaching remission, defined as inactive disease (ID), constitutes the ideal target in clinical practice. Using the new composite disease activity index“Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score” (ASDAS) (2) we assessed the prevalence of ID in a cohort of patients with axSpA treated with anti-TNFα agents. Potential patient- and disease-related factors influencing the status of ID were analyzed.
Methods . The study population was selected from outpatients with axSpA treated with anti-TNFα attending our Rheumatology Department. Disease activity was evaluated in terms of BASDI and ASDAS-CRP during the latest follow up visit. ID was defined as ASDAS-CRP< 1.3 (2).Statistical analysis was performed with STATA.
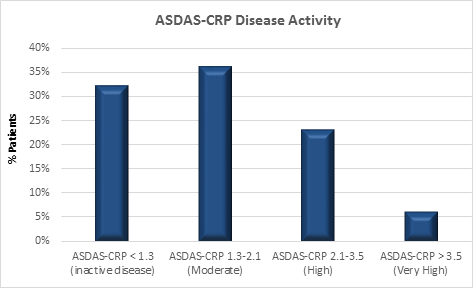
Results . General characteristics of the 53 enrolled patients are presented in Table 1. A BASDAI < 4 was recorded for 70% of the study population, while only 31% showed ID according to ASDAS-CRP (Figure 1). As expected, a strict correlation between the two disease activity indices was confirmed (Spearman's r = 0.76; p < 0.0001). Multivariate logistic regression demonstrated an inverse correlation of ID status with NSAIDs intake (OR 0.15; CI95% 0.45-0.54). ID achievement resulted independent from sex, disease duration, BASMI,DMARDs, type of anti-TNFα agent.
Conclusion . In our cohort of axSpA treated with biological agents, only one third achieved ID according to ASDAS-CRP. Even with the limitations of the small sample size, ID does not correlate with the principle patient- and disease-related features but is inversely associated with NSAIDs intake. Further studies are needed to optimize the targeted treatment of axSpA and to identify potential predictive factors of ID.
References
1. Smolen JS, et al. Treating spondyloarthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis, to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73:6–16.
2. Machado P, et al. Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS): defining cut-off values for disease activity states and improvement scores. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70:47–53.
Table 1. General characteristics of the study population
|
Variable |
Number / Mean± SD |
Percentage (%) |
|
Total number of patients |
53 |
|
|
Male |
30 |
57 % |
|
Female |
23 |
43 % |
|
Diagnosis: axSpA: |
|
|
|
AS |
41 |
76% |
|
non-radiographic axSpA |
12 |
23% |
|
Peripheralinvolvement |
34 |
64% |
|
Age atsymptomsonset |
35 (±12) |
|
|
Age atdiagnosis |
39 (±13) |
|
|
Diseaseduration (years) |
10 (±9) |
|
|
Patients on second line anti-TNFα |
10 |
19% |
|
ConcomitantNSAIDsintake |
34 (15/19) |
64% (28/36) |
|
DMARD combinationtherapy |
21 |
40% |
|
Type of anti-TNFα agent |
|
|
|
Infliximab |
14 |
26% |
|
Adalimumab |
15 |
28% |
|
Golimumab |
14 |
26% |
|
Etanercept |
10 |
19% |
|
Time from anti-TNFα treatment initiation (months) |
33 (±31) |
|
Figure 1. Proportion of patients according to ASDAS-CRP disease activity cutoffs
Disclosure:
S. Monti,
None;
S. Breda,
None;
F. De Nard,
None;
V. Grosso,
None;
M. Todoerti,
None;
C. Montecucco,
None;
R. Caporali,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treating-axial-spa-to-target-prevalence-of-ankylosing-spondylitis-disease-activity-score-asdas-inactive-disease-in-a-cohort-of-patients-treated-with-anti-tnf%ce%b1-agents/