Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis (SpA) involves activation of the innate immune system, inflammation and new bone formation. The innate immune system is activated through pattern recognition receptors including Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4). Inflammation is a result of increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). New bone formation by osteoblasts is determined by a balance between the inhibitory effect of Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) and the stimulatory effect of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). The two cytokines IL-20 and IL-24 have been shown to link innate immune activation and tissue homeostasis.(1) Previously, we have found increased plasma levels of IL-20 and IL-24 in SpA patients. We hypothesized that IL-20 and IL-24 are secreted as part of activation of the innate immune system and affect bone homeostasis. The aim was to describe associations of IL-20 and IL-24 and disease activity and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scores and to identify the sources and targets of the two cytokines in SpA.
Methods: Patients with axial SpA (n=83) were included in the study of associations between cytokine levels and disease activity and MRI scores. Patients with peripheral SpA (n=16) were included for studying sources and targets of IL-20 and IL-24 among synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) using lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and TNFα as positive controls. Healthy human osteoblasts were used for studying the effect of the two cytokines on mineralization using BMP2 as a positive control. The secretion of IL-20, IL-24, MCP-1 and DKK1 were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbant assays and flow cytometry, and mineralization was measured by hydroxyapatite deposition.
Results: The plasma IL-20 and IL-24 levels were increased in SpA patients compared with healthy controls (HCs) by 57% and 83%, respectively (both p<0.0001) and there was a trend towards associations with both future switch to biologic therapy (p=0.031 and p=0.11, respectively), and spine MRI chronicity score (p=0.10 and p=0.15, respectively). The production of IL-20 and IL-24 was increased by LPS, and this TLR4 induced secretion was greater in SpA PBMCs compared with HC PBMCs. IL-20 and IL-24 increased the production of MCP-1 by SpA SFMCs (but not by SpA FLSs), decreased the production of DKK1 by SpA FLSs (but not by SpA SFMCs) and increased mineralization by human osteoblasts (see Figure). The IL-20 and IL-24 induced production of MCP-1 among the SFMCs was found in activated synovial monocytes only.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings indicate that IL-20 and IL-24 could be novel links between activation of the innate immune system and new bone formation in SpA. References: 1. Rutz S et al. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines – from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. 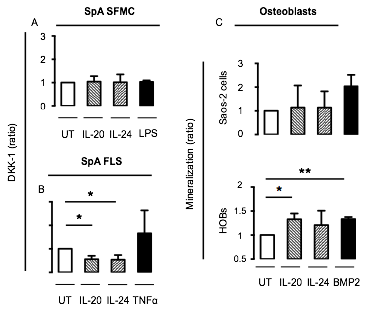
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kragstrup TW, Andersen MN, Schiøttz-Christensen B, Jurik AG, Hvid M, Deleuran B. Toll-like Receptor 4 Induced IL-20 and IL-24 Stimulate Osteoblast Mineralization and Are Increased in Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/toll-like-receptor-4-induced-il-20-and-il-24-stimulate-osteoblast-mineralization-and-are-increased-in-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/toll-like-receptor-4-induced-il-20-and-il-24-stimulate-osteoblast-mineralization-and-are-increased-in-spondyloarthritis/
