Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy II: Trials Therapy
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We compared patient-reported outcomes (PROs) among patients receiving tofacitinib monotherapy, tofacitinib + methotrexate (MTX), and adalimumab (ADA) + MTX, in a head-to-head trial of patients with RA and inadequate responses to MTX (MTX-IR).
Methods: ORAL Strategy (NCT02187055) was a Phase 3b/4, 1-year, triple dummy, active randomized controlled trial (RCT). Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID; tofa mono), tofacitinib 5 mg BID + MTX (tofa+MTX) or subcutaneous ADA 40 mg every other week + MTX (ADA+MTX); MTX doses were
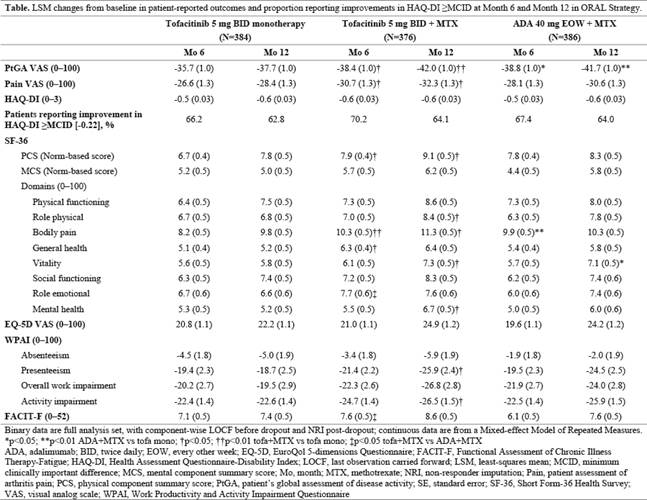
15–25 mg/wk. PROs (secondary endpoints in this RCT) assessed at Months (Mos) 6 and 12 included mean changes from baseline in: patient global assessment of disease activity (visual analog scale [VAS]); arthritis pain (VAS); Health Assessment Questionnaire‑Disability Index (HAQ-DI); Short Form-36 Health Survey; EuroQol 5-dimensions Questionnaire; Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire; Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue; and the proportion of patients reporting improvements in HAQ-DI ≥minimum clinically important difference (MCID; -0.22). Nominal p values were calculated with no adjustment for multiple comparisons.
Results: Among 1146 patients treated (tofa mono: n=384; tofa+MTX: n=376; ADA+MTX: n=386), baseline demographics and disease characteristics were comparable. At Mos 6 and 12, improvements in all PROs were similar for tofa+MTX and ADA+MTX (there were essentially no differences based on nominal p values) and numerically greater than with tofacitinib monotherapy (Table). Mean changes from baseline in HAQ-DI scores were similar in each treatment group at Mos 6 and 12; similar proportions reported improvements ≥MCID.
Conclusion: MTX-IR patients with RA reported PRO improvements with all 3 treatment regimens that were clinically meaningful, comparable for tofacitinib + MTX and adalimumab + MTX, and numerically higher with combination therapy than with tofacitinib monotherapy. Nominal p values should be interpreted with caution as they were not controlled for Type 1 error.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Mysler E, Moots RJ, Wallenstein G, DeMasi R, Luo Z, Soma K, Iikuni N, Fleischmann R. Tofacitinib with and without Methotrexate Versus Adalimumab with Methotrexate for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Phase 3b/4 Randomized Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-with-and-without-methotrexate-versus-adalimumab-with-methotrexate-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-phase-3b4-randomized-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-with-and-without-methotrexate-versus-adalimumab-with-methotrexate-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-phase-3b4-randomized-trial/