Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here, we report tofacitinib safety and tolerability up to 114 months (Mos) and clinical efficacy up to 96 Mos in long-term extension (LTE) studies.
Methods: Data were pooled from 2 open-label studies (NCT00413699 [ongoing; database not locked at March 2017 data cut]; and NCT00661661) of patients (pts) with RA who had participated in Phase 1/2/3 studies of tofacitinib. Pts received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) as monotherapy or with background DMARDs. As pts in the LTE studies were allowed to switch doses, they were assigned to the 5 mg BID group if the total daily dose was <15 mg/day, and to the 10 mg BID group if it was ≥15 mg/day. Primary endpoints were adverse events (AEs) and confirmed laboratory safety data. Secondary endpoints included clinical efficacy measures (ACR20/50/70 response rates, DAS28-4[ESR], HAQ-DI, and Clinical Disease Activity Index). Safety data were included up to Mo 114 and completer-analyzed efficacy data up to Mo 96 (n≤100 post-Mo 96).
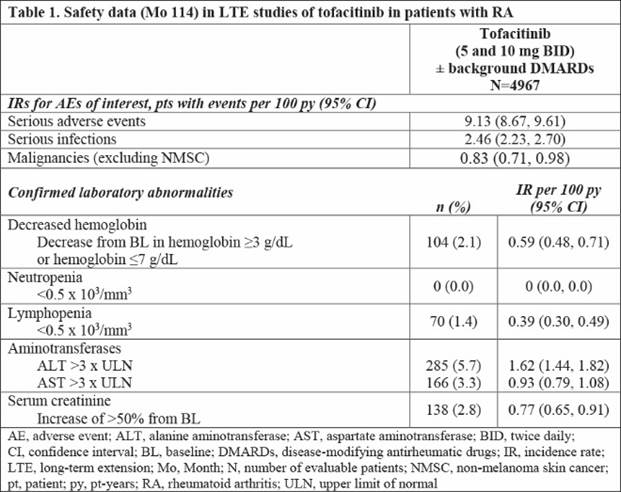
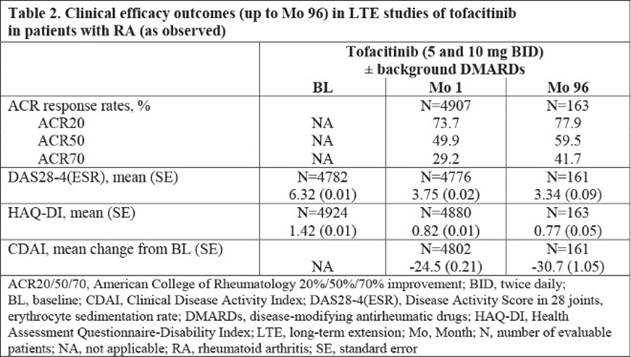
Results: 4967 pts were treated (mean [max] duration: 3.5 [9.4] years). Total tofacitinib exposure was 17,738.5 pt-years (py); 76.4% of pts maintained their initial dose. In total, 2518 pts (50.7%) discontinued (AEs: 1189 [23.9%]; insufficient clinical response: 179 [3.6%]). Most common AE classes with highest AEs: infections and infestations (69.6%; exposure adjusted event rate [EAER; events per 100 py], 19.71) and musculoskeletal/connective tissue disorders (40.3%; EAER, 11.40). Most common AEs: nasopharyngitis (19.1%; EAER, 5.41), upper respiratory tract infection (17.9%; EAER, 5.07), bronchitis (12.6%; EAER, 3.58), and urinary tract infection (12.5%; EAER, 3.55). Serious AEs occurred in 29.4% of pts, and serious infections (SIEs) in 8.9% of pts. Malignancies, excluding non-melanoma skin cancer, were reported in 3.0% of pts. Incidence rates (IR; pts with events per 100 py) for AEs of interest, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), are provided in Table 1. IRs for SAEs, SIEs and malignancies through Mo 114 did not increase vs reported data through Mo 105.1 Confirmed laboratory data are provided in Table 1. No new safety risks were identified. Clinical responses were sustained from Mo 1 to Mo 96 (Table 2).
Conclusion: In patients with RA who remained in the LTE studies, tofacitinib (5 or 10 mg BID), with or without background DMARDs, was associated with consistent safety through Mo 114 and sustained clinical efficacy through Mo 96.
Reference:
- Wollenhaupt J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68 (suppl 10): Abstract 1647.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wollenhaupt J, Silverfield J, Lee EB, Terry K, Kwok K, Strengholt S, DeMasi R, Wang L. Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Safety and Efficacy in Open-Label, Long-Term Extension Studies over 9 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-safety-and-efficacy-in-open-label-long-term-extension-studies-over-9-years/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-safety-and-efficacy-in-open-label-long-term-extension-studies-over-9-years/