Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: In AA amyloidosis patients with RA taking oral medicines such as methotrexate and prednisolone, it is generally accepted that the renal function deteriorates gradually and finally most of the patients will receive hemodialysis in five years, even the disease activity is in good control. However, the effect of biologics therapy on renal insufficiency is not clarified. The main focus of the present study is to compare the effect of tocilizumab and oral medicines on clinical course of the renal function of AA amyloidosis patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Methods: RA patients with amyloidosis who had high disease activity and renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance < 20 ml/min/1.73m2) were enrolled in the present study. The patients were treated with prednisolone and low dose of methotrexate (group 1) or tocilizumab monotherapy (group 2) and we followed up for more than three years prospectively. In those patients who had obtained DAS28 remission, we compared the clinical course of renal function and the disease activity between two groups.
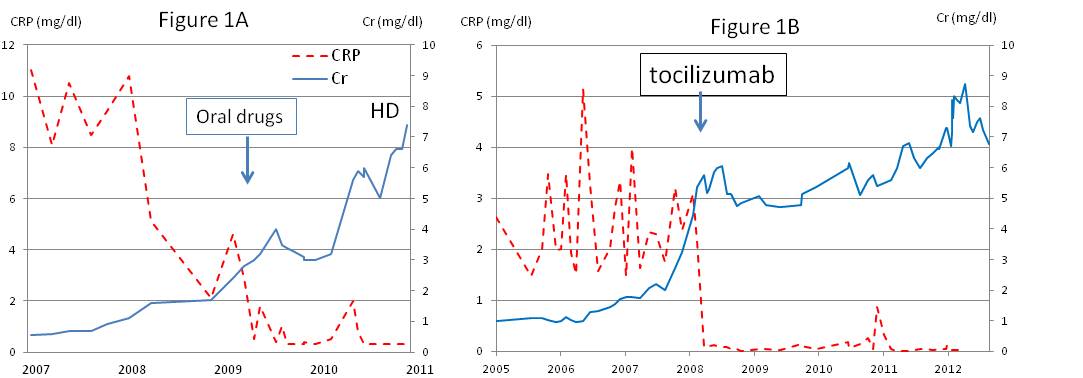
Results: The mean creatinine levels of the group 1 patients and the group 2 patients were 2.2 and 2.4 mg/dl respectively at the entry. The mean CRP levels of the group 1 patients and the group 2 patients were 3.2 and 2.8 mg/dl respectively at the entry. After treated with either oral medicine or tocilizumab, the levels of CRP were decreased to normal levels in less than one year and DAS28 were improved significantly in both groups. The renal functions of group 1 patients were deteriorated rapidly and were introduced hemodialysis in 2.1 years. Typical clinical course was shown in figure 1A. However, the patients of group 2 did not progress renal insufficiency rapidly and were not introduced hemodialysis for more than three years. In a typical case, hemodialysis was not introduced for more than five years (figure 1B).
Conclusion: Both oral medicines and tocilizumab monotherapy introduced clinical remission, however, tocilizumab but not oral medicines survives introducing the hemodialysis for more than three years in AA amyloidosis patients with renal insufficiency. This result shows the different effects on progression of renal insufficiency between tocilizumab and oral medicine, and suggests that we should select tocilizumab rather than oral medicine in these patients.
Figure 1: The typical clinical courses of CRP and Creatinine in amyloidosis patients treated with oral drugs (A) or tocilizumab (B).
Disclosure:
O. Saiki,
None;
H. Uda,
None;
A. Matsumoto,
None;
A. Mizumoto,
None;
T. Harada,
None;
T. Takama,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-survives-introducing-the-hemadialysis-longer-than-oral-medicine-in-aa-amyloidosis-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-of-renal-insufficiency/