Tocilizumab in refractory Takayasu arteritis: a case series and updated literature review.
Background/Purpose:
The aim of this study is to analyze the efficacy and tolerance of tocilizumab in patients with Takayasu arteritis (TA).
Methods:
We retrospectively studied patients with TA (ACR and/or Ishikawa’s criteria): 5 French multicenter cases and 39 from the literature. Clinical, biological, radiological disease activity and treatment were analyzed before tocilizumab, during the follow-up and at the last available visit.
Results:
Forty four patients (median age 26 years [3-65]) were included in the present study: 5 patients from the 3 French university hospitals and 39 cases from the literature review. Median follow-up after initiation of tocilizumab was 15 months [8-33]. Clinical and biological activities significantly decreased within 3 months, similarly to steroid amount (from 15 mg/day [5-75] at baseline to 10 mg/day [2-30] at 6 months; p<0.05) and steroid-dependence rate. Even radiological activity did not significantly decreased at 6 months, significant decrease of arterial FDG uptake was noted at 6 months. Median duration of tocilizumab treatment was 9 months [3-180]. At the last visit, tocilizumab was continued in 17/32 patients (53%), and was discontinued in the 15 remaining cases because of the remission (n=5), relapse (n=3), persistent radiological activity (n=3), cutaneous rash (n=2), severe infections (n=1) and the absence of tocilizumab financial support (n=1). No death related to tocilizumab treatment was noted.
Conclusion:
This study show the efficacy of tocilizumab in terms of clinical, biological and radiological response, as well as steroid-sparing agent. Only well-designed studies could definitely address the efficacy of tocilizumab in TA.
Table 1. Characteristics of patients with TA from personal data (n=5) and literature review (n=39).
|
Number of evaluable patients |
Baseline assessment (N=44) |
3 months after beginning tocilizumab (N=30) |
6 months after beginning of tocilizumab
|
Last visit N=44 |
|
Tocilizumab treatment |
44 |
28 (93%) |
12/15 (80%) |
17/32 (53%) |
|
Delay from baseline (months) |
– |
3 [2-3] |
6 [4.5-6] |
15 [8-33] |
|
Clinical response |
|
|
|
|
|
Tocilizumab efficacy (by physician) |
– |
13/14 (93%) |
14/18 (78%) |
33/44 (75%) |
|
Disease clinical activity |
41/42(98%) |
1/14 (7%)* |
3/18* (17%)* |
7/34 (26%)* |
|
Laboratory data |
|
|
|
|
|
Biological activity |
28/29 (97%) |
2/15* (13%) |
2/19*(11%) |
7/34 (26%) |
|
ESR (mm/hour) |
42 [8-88] |
4 [0-63] |
5 [0-41]* |
4 [0-41]* |
|
C-reactive protein (mg/l) |
21 [8-126]* |
0 [0-13] |
0.5 [0-124]* |
0 [0.5-17]* |
|
Radiological data |
|
|
|
|
|
Radiological activity |
15/22 (68%) |
3/9* (33%) |
5/15** (33%) |
– |
|
PET FDG vascular uptake |
9/9 |
– |
3/7* (43%) |
– |
|
SUV max |
3.8 [1,3-5,3] |
– |
– |
– |
|
Tocilizumab associated steroids |
27/30 (90%) |
27/30 (90%) |
8/13 (62%) |
18/22 (82%) |
|
Steroids (prednisone; mg/day) |
15 [5-75] |
10 [7-30]* |
10 [2-30]* |
5 [0-30]* |
Values are medians with ranges or frequencies with percentages. ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; Steroid-dependence: prednisone ≥20 mg/day; PET FDG: positron emissions tomography with fluorodesoxyglucose.
* p<0.05 versus baseline
**p=0.05
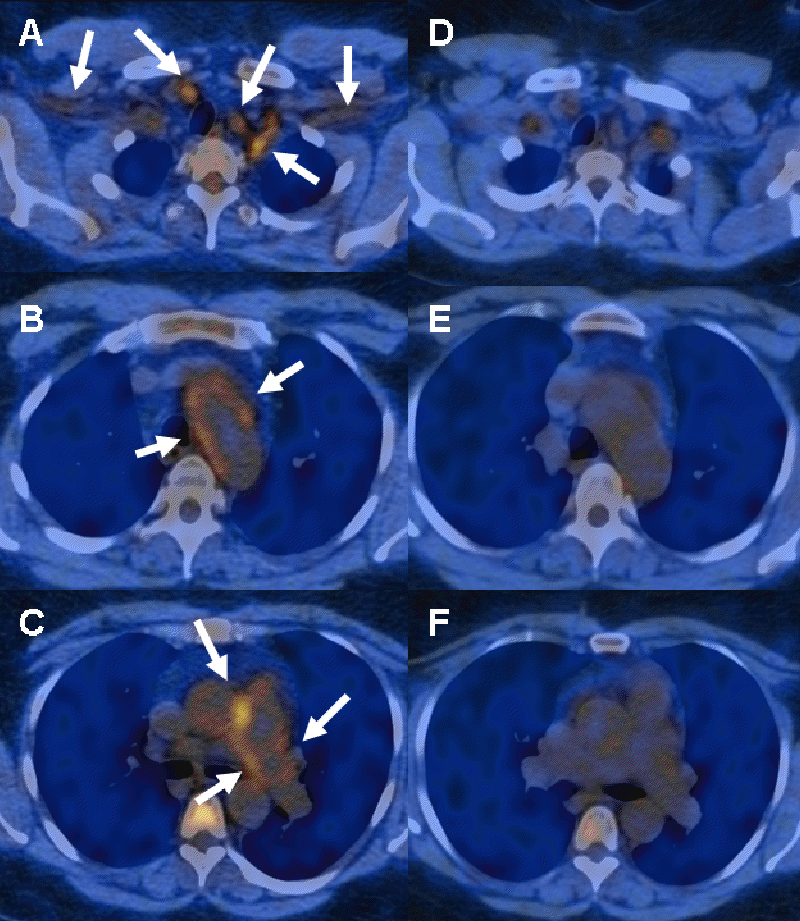
Figure 2. PET-FDG uptake before tocilizumab treatment (A, B, C) and after 6-month tocilizumab (D, E, F) in patient with Takayasu arteritis. A and D: FDG uptake in cervical and subclavians arteries; B and E: FDG uptake in aortic arch; C and F: FDG uptake in pulmonary arteries.
Disclosure:
N. Abisror,
None;
A. Mekinian,
None;
C. Lavigne,
None;
M. A. Vandenhende,
None;
M. Soussan,
None;
O. Fain,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-in-refractory-takayasu-arteritis-a-case-series-and-updated-literature-review-%c2%b2/