Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Smart-phone Spondyloarthritis Management System (SpAMS) is a mobile health tool, specifically designed to conduct prospective clinical studies on SpA/AS in China, using real-world clinical workflows. The aim of this study was to explore the effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) in controlling disease activity in a real-world setting.
Methods: The Chinese Ankylosing Spondylitis Prospective Imaging Cohort (CASPIC) is a nation-wide, ongoing, prospective, and state-funded cohort study, launched in conjunction with SpAMS. All patients fulfilled the 1984 modified NY criteria. Patients on medication and with full medication records were enrolled in this study. Generalized additive mixed models were used to study the relationship between TNF inhibitor (TNFi) treatment (users or non-users) and AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) during the follow-up period. The model adjusted for gender, symptom duration, HLA-B27, BMI, smoking status, peripheral arthritis, and treatment with NSAIDs and DMARDs.
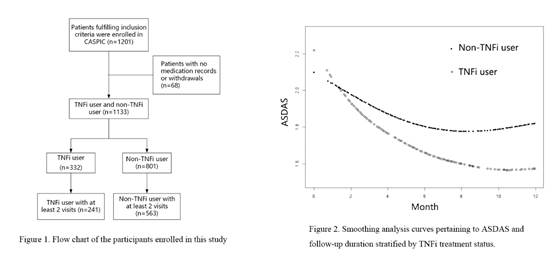
Results: A total of 1201 AS patients were recruited in CASPIC from April 2016 to April 2018. Sixty-eight patients (5.7%) with no medication records or withdrawals were removed (Figure 1). The characteristics of 332 TNFi user and 801 nonuser were summarized in Table 1. Mean (SD) followed-up duration were 12.3 (5.9) months. Mean (SD) duration of TNFi use were 9.3 (5.9) months. TNFi user were slightly younger, more likely to present with peripheral arthritis, had higher baseline disease activity scores, higher baseline inflammation marker levels, and were less likely to be prescribed NSAIDs and DMARDs. TNFi user had a higher ASDAS at baseline which subsequently declined rapidly, and then remained at a consistently lower level throughout the first 12 months than did nonuser (Figure 2). ASDAS decline were significantly more in TNFi user than they were in those of nonuser in the first 3 months (0.62 units, 95%CI 0.13 to 1.10, P=0.017).
Conclusion: The use of TNFi in AS patients may reduce disease activity in a faster and more stable fashion.
Table
|
Characteristic |
Non-TNFi user N=801 |
TNFi user N=332 |
P value |
|
Male sex, % |
84.0 |
81.3 |
0.269 |
|
Age, year, mean(SD) |
31.1 (8.9) |
29.2 (7.9) |
<0.001* |
|
Symptom duration, year, mean(SD) |
8.4 (6.3) |
8.7 (5.7) |
0.533 |
|
BMI, kg/m2, mean(SD) |
23.6 (4.1) |
23.3 (4.4) |
0.250 |
|
HLA-B27 positive, % |
88.6 |
90.7 |
0.326 |
|
PhGA, mean(SD) |
2.1 (1.3) |
2.5 (1.4) |
<0.001* |
|
BASFI, mean(SD) |
1.5 (1.6) |
1.9 (1.8) |
<0.001* |
|
ESR, mean(SD)mm/hour |
14.3 (15.5) |
23.5 (23.4) |
<0.001* |
|
CRP, mean(SD) mg/L |
11.7 (22.9) |
21.6 (32.0) |
<0.001* |
|
ASDAS, mean(SD) |
2.0 (0.9) |
2.4 (1.1) |
<0.001* |
|
Enthesitis, % |
21.8 |
32.5 |
<0.001* |
|
Peripheral arthritis, % |
9.3 |
22.2 |
<0.001* |
|
NSAIDs, % |
99.0 |
94.0 |
<0.001* |
|
DMARDs, % |
71.2 |
54.5 |
<0.001* |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ji X, Zhu J, Zhang J, Huang F. TNF Inhibitor Reduces ASDAS Faster and More Stable in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients: Results from a Real World Prospective Cohort Managed By Smart Phone System [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-inhibitor-reduces-asdas-faster-and-more-stable-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-results-from-a-real-world-prospective-cohort-managed-by-smart-phone-system/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-inhibitor-reduces-asdas-faster-and-more-stable-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-results-from-a-real-world-prospective-cohort-managed-by-smart-phone-system/