Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: TNF-α is a
key regulator of inflammation, which induces signal transduction by binding to
two structurally and functionally distinct receptors on target cells: TNF
receptor 1 (TNFR1) and TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2). The development of TNF inhibitors has revolutionized the management of rheumatoid
arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Psoriatic
arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. However, previous studies have suggested
a positive role for TNFR2 signaling in maintaining the numbers and function of
regulatory T cells (Tregs). The aim of this study was
to further investigate the role of TNFR1/2 signaling in Tregs.
Methods: To study the influence of TNF signaling on Tregs, we first
isolated splenic cells, thymus and lymph node cells from na•ve TNFR1-/-, TNFR2-/-
and wild-type mice. The
number of Tregs was measured by
flow cytometry. The gene expression profiles of Treg related
markers in spleen and thymus were then compared by real-time qPCR.
Results: Flow cytometry analysis showed that neither TNFR1
nor TNFR2 altered the number of regulatory T cells. However, there was a
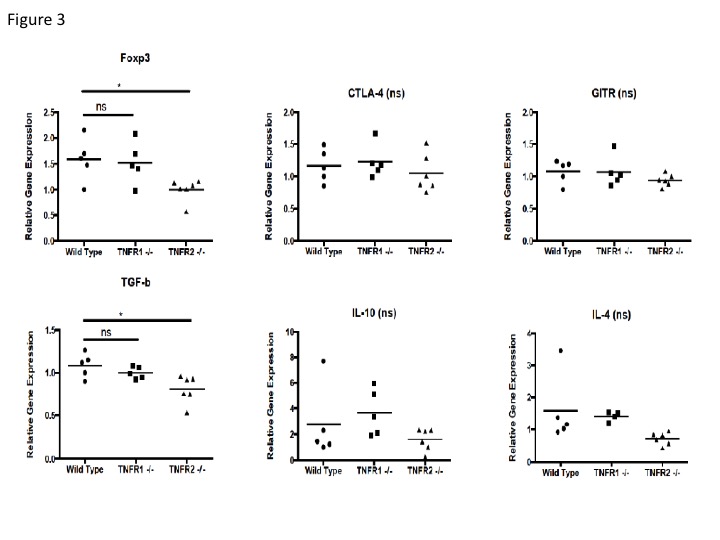
significant decrease in Foxp3 expression intensity in Tregs
from TNFR2-/- mice (Figure 1), which was confirmed in the gene expression
study of Treg related markers
from spleen (Figure 2) and thymus (Figure 3). The gene expression study
of spleen and thymus showed no significant difference of CTLA-4, GITR, IL-10
and IL-4, but a marked decrease of TGF-β in TNFR2-/- mice
compared to wild type mice.
Conclusion: Our data reveal that TNFR2 signaling is
critical in maintaining the expression of Foxp3 in Tregs
in healthy mice, and we are currently exploring its role in arthritis. We
hypothesize that TNF signaling affect the expression of Foxp3 through decreased
production of TGF-β. Our data suggest that the use TNF inhibitors may affect the phenotype
and function of Tregs in which may influence
treatment response in some patients.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tseng WY, McNamee K, Cribbs A, Vyas A, Williams RO. TNF-Alpha Receptor II Signaling Plays an Important Role in Maintaining the Expression of Forkhead Box P3 in Murine Regulatory T Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-alpha-receptor-ii-signaling-plays-an-important-role-in-maintaining-the-expression-of-forkhead-box-p3-in-murine-regulatory-t-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-alpha-receptor-ii-signaling-plays-an-important-role-in-maintaining-the-expression-of-forkhead-box-p3-in-murine-regulatory-t-cells/