Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: 4M096: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical III: Miscellaneous (1818–1823)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tildrakizumab (TIL), a high-affinity anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody, is approved to treat moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. A randomized, double-blind, multidose, placebo (PBO)-controlled, phase 2b study (NCT02980692) is evaluating the efficacy and safety of TIL for PsA. This analysis evaluated the efficacy of TIL on 66 swollen and 68 tender joint counts (SJC and TJC) and pain in patients with active PsA at week 24.
Methods: Patients with active PsA (Classification of Psoriatic Arthritis criteria),1 stratified by prior anti-TNF use and baseline body weight (≤90 kg and ≥90 kg), were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to receive TIL (200 mg once every 4 weeks [Q4W], 200 mg every 12 weeks [Q12W], 100 mg Q12W, 20 mg Q12W to week 24) or PBO Q4W to week 24. SJC and TJC were performed by an independent blinded assessor at baseline and Q4W through week 24. Patients rated pain using a visual analog scale (0–100 mm). Safety was assessed by monitoring treatment-emergent adverse events.
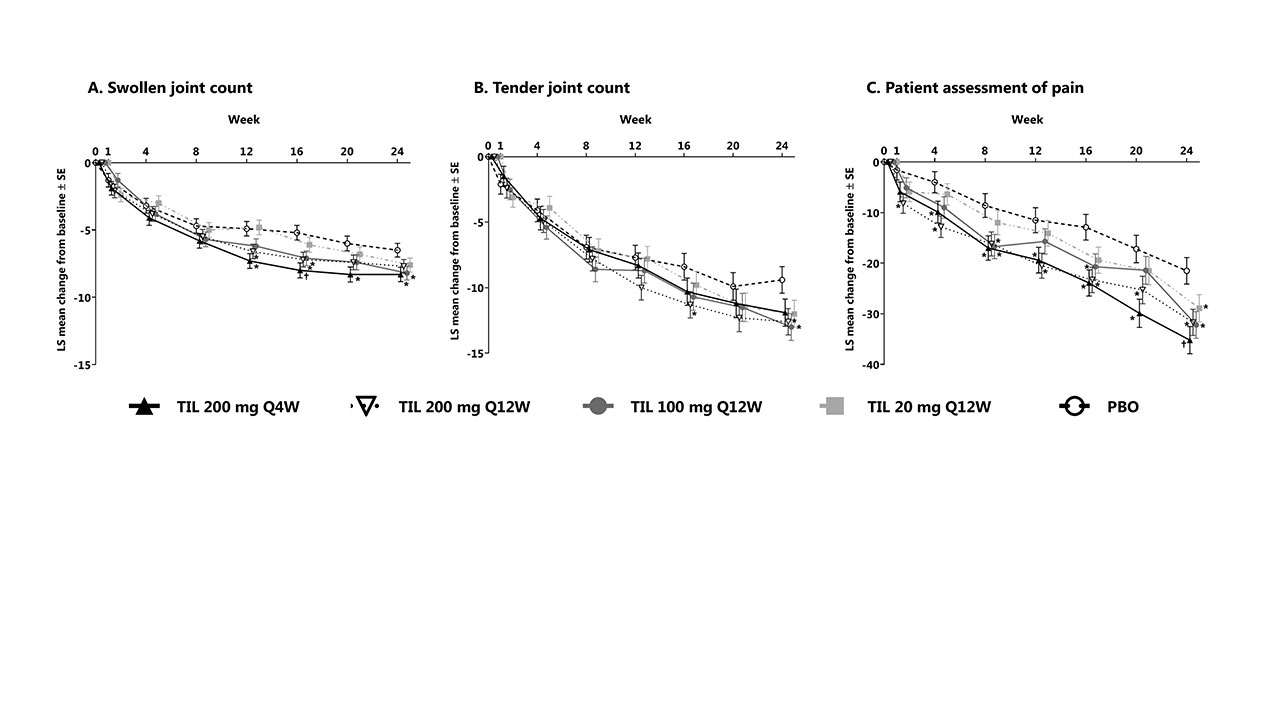
Results: Of 500 patients screened, 391 met the inclusion criteria with 77–79/treatment arm. Mean (SD) age was 48.8 (12.6) years, disease duration 6.8 (7.1) years, body mass index 29.7 (6.2), and 91 were TNF-α experienced (Table 1). At week 24, the least squares (LS) mean (standard error [SE]) reduction from baseline in SJC was 8.3 (0.5)/7.7 (0.5)/8.2 (0.5)/7.6 (0.5) in TIL arms vs 6.5 (0.5) in the PBO arm and statistically significant in TIL 100 mg Q12W and 200 mg Q4W vs PBO (P = 0.0189 and 0.0111, respectively, Figure 1). LS mean (SE) reduction in TJC was 11.9 (1.0)/12.6 (1.0)/13.0 (1.0)/12.0 (1.0) in TIL arms vs 9.4 (1.0) in the PBO arm; statistically significant for TIL 100 and 200 mg Q12W vs PBO (P = 0.0140 and 0.0234). LS mean (SE) reduction in patient pain was 35.2 (2.7)/31.7 (2.6)/32.2 (2.6)/28.9 (2.7) in TIL arms vs 21.5 (2.6) in the PBO arm; statistically significant for TIL 100, 200 mg Q12W, and 200 mg Q4W vs PBO (P = 0.0039, 0.0056, and 0.0003). Percent change from baseline for SJC (73.0%–79.8% TIL vs 59.3% PBO), TJC (62.1%–67.5% TIL vs 48.7% PBO), and pain (47.5%–63.5% TIL vs 33.5% PBO) at week 24 are shown in Figure 2. No malignancies, major adverse cardiac events, or deaths were reported.
Conclusion: At week 24, TIL 100 mg Q12W and 200 mg Q4W significantly reduced SJC vs PBO; TIL 100 and 200 mg Q12W significantly reduced TJC vs PBO. All TIL treatment arms had significant improvement in pain vs PBO in patients with PsA who were anti–TNF-naïve or experienced.
Editorial and writing support was provided by Marie-Louise Ricketts, PhD, of AlphaBioCom, LLC.
References:
- Taylor W, et al. Arth Rheum, 2006; 54: 2665-2673
*For prior anti–TNF-α therapy, total patients analyzed -N- = 79, 78, 80, 78, and 76 for TIL 200 mg Q4W, TIL 200 mg Q12W, TIL 100 mg, TIL 20 mg, and PBO, respectively.
BMI, body mass index; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; SD, standard deviation; TIL, tildrakizumab.
Shown for randomized patients who received ≥1 dose of study drug; values at week 0 represent baseline.
*P <0.05; †P <0.001 vs PBO.
LS, least squares; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; SE, standard error; TIL, tildrakizumab.
Shown for randomized patients who received ≥1 dose of study drug. Swollen and tender joint count graphs were generated based on mean change from baseline; pain assessment graph is based on LS mean change in baseline.
LS, least squares; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q12W, every 12 weeks; TIL, tildrakizumab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Orbai A, Ballerini R, Chou R, Rozzo S, Mendelsohn A, Espinoza L. Tildrakizumab Efficacy for Psoriatic Arthritis: 24-week Analysis of Swollen and Tender Joint Counts and Pain [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tildrakizumab-efficacy-for-psoriatic-arthritis-24-week-analysis-of-swollen-and-tender-joint-counts-and-pain/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tildrakizumab-efficacy-for-psoriatic-arthritis-24-week-analysis-of-swollen-and-tender-joint-counts-and-pain/