Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a combination of specific risk factors for cardiovascular disease.1 The prevalence of MetS in patients (pts) with PsA has been reported to range from 40%–60%; it has been associated with reduced efficacy of PsA treatment.2,3 This study assessed whether MetS status affected efficacy and safety of tildrakizumab—a monoclonal IgG1-κ antibody targeting interleukin-23p19—in pts with PsA.4
Methods: This post-hoc subgroup analysis of a recently completed Phase 2b study (NCT02980692)4 includes data from all pts who received any dose of tildrakizumab (200 mg every 4 weeks [Q4W], 200 mg Q12W, 100 mg Q12W, 20→200 mg Q12W) from baseline through W52, stratified by baseline MetS status.4 Per modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria, MetS was defined by the presence of at least 3 of the following criteria: BMI >30 kg/m2, blood pressure ≥130 mmHg (systolic) and/or 85 mmHg (diastolic), fasting triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL, fasting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol < 40 mg/dL (men) or < 50 mg/dL (women), and fasting glucose >110 mg/dL.1 Efficacy endpoints included proportions of pts achieving 20%/50%/70% improvement from baseline by ACR criteria (ACR20/50/70 response) and change from baseline in swollen joint count, tender joint count, CRP, Patient Global Assessment (PtGA; 0–100 mm visual analog scale [VAS]), patient-reported pain VAS, and Physician Global Assessment (PGA; 0–100 mm VAS) at W24 and W52. Missing data were imputed as nonresponse. Incidence of adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), and AEs of interest were evaluated at W24 and W52. Data are presented descriptively.
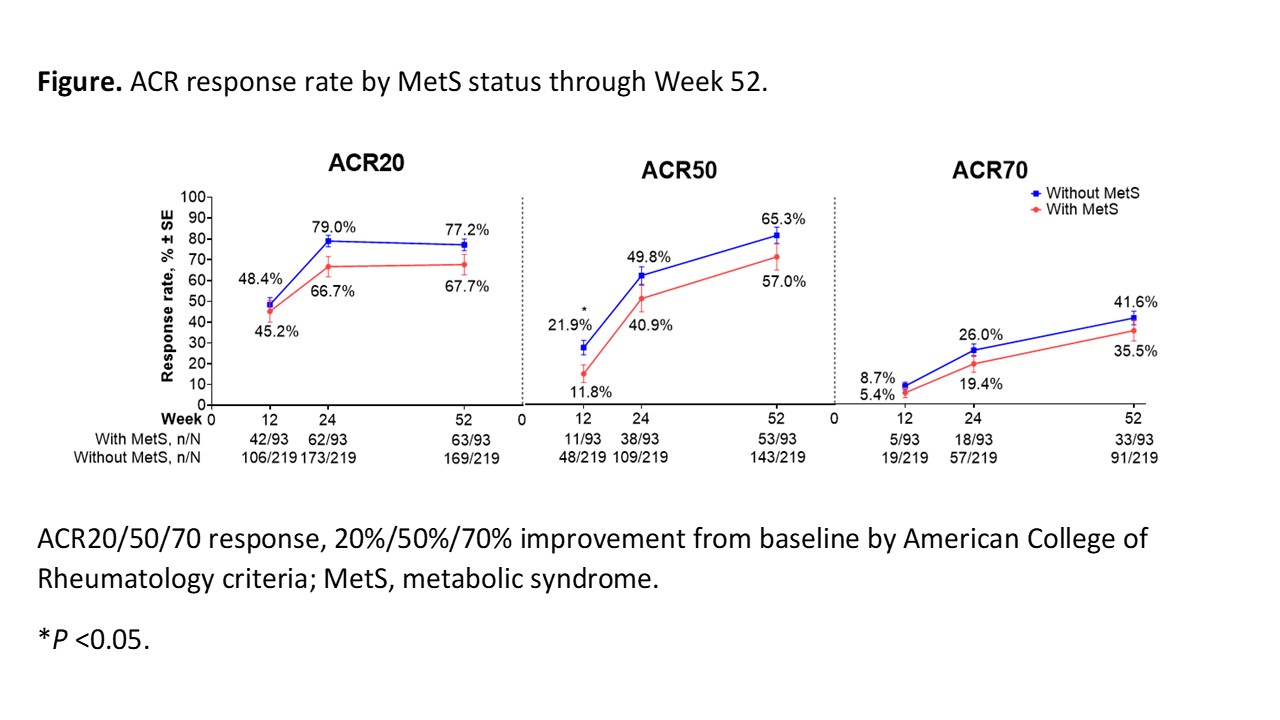
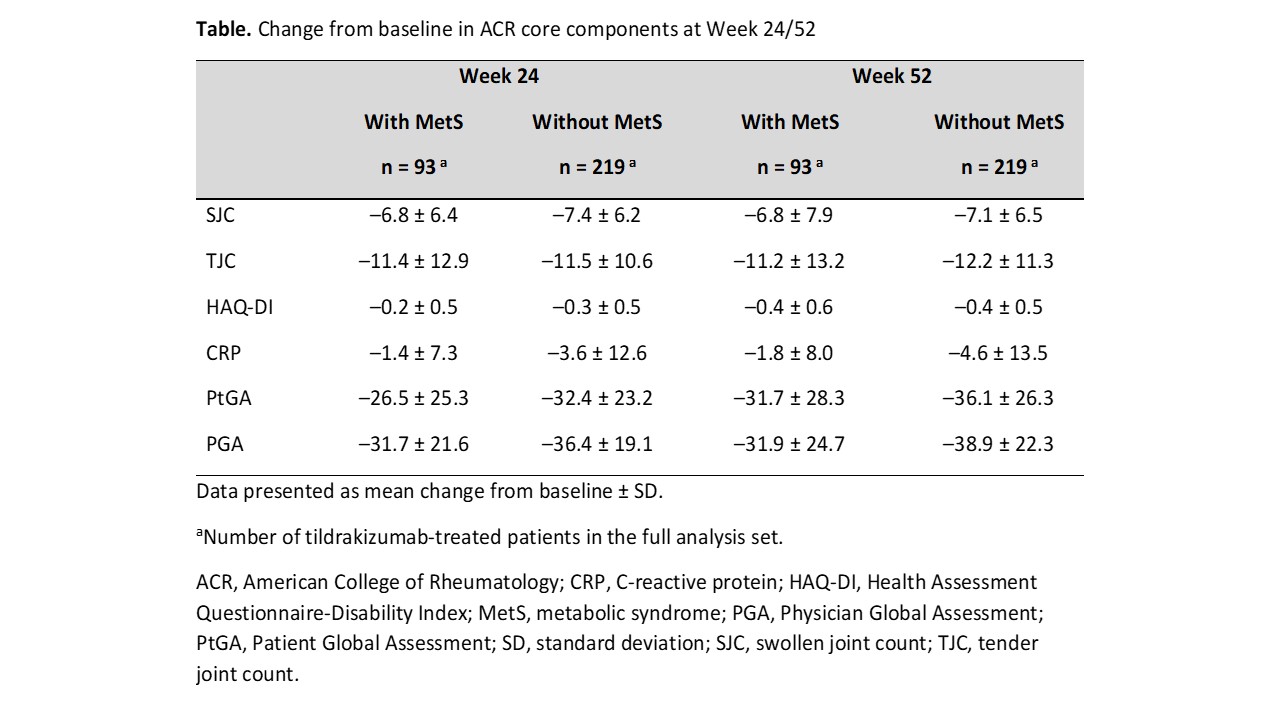
Results: Median baseline weight and BMI were substantially greater in pts with MetS (n = 93) vs those without MetS (n = 219). Tildrakizumab efficacy was generally lower for pts with vs without MetS but was well maintained through W52 in both subgroups (W52 ACR20 response rate [standard error], 67.7% [4.9%] vs 77.2% [2.8%] in pts with vs without MetS; Figure). The ACR50 and ACR70 response rates increased from W24 to W52 regardless of MetS status. Improvements from baseline in ACR response components were observed in both subgroups and maintained through W52. Improvements from baseline in CRP, PtGA, and PGA were numerically greater in pts without vs those with MetS (CRP, −4.6 ± 13.5 vs −1.8 ± 8.0; PtGA, −36.1 ± 26.3 vs −31.7 ± 28.3; PGA, −38.9 ± 22.3 vs −31.9 ± 24.7; Table). The incidence rate of SAEs in pts with vs without MetS was generally low (W0–W24, 4/93 [4.3%] vs 3/219 [1.4%]; W24–W52, 0/93 [0%] vs 3/219 [1.4%]).
Conclusion: In this Phase 2 trial, the efficacy of tildrakizumab in pts with active PsA tended to be lower among pts with comorbid MetS, with improvements from baseline across efficacy measures generally larger in pts without MetS vs those with MetS. Larger studies are necessary to investigate the long-term effects of MetS on tildrakizumab efficacy, safety, and drug survival in PsA.
1. National Institutes of Health. 2001; https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/atp3xsum.pdf 2. Haroon M et al. J Rheumatol. 2014;41:1357–65. 3. Costa L et al. Immunol Res. 2015;61:147–53. 4. Mease PJ et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021. In press.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kavanaugh A, Raychaudhuri S, Ritchlin C, Asahina A, Rahman P, Murphy F, Rozzo S, Yao S, Chou R, Husni E. Tildrakizumab Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis by Metabolic Syndrome Status [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tildrakizumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-by-metabolic-syndrome-status/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tildrakizumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-by-metabolic-syndrome-status/