Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Treatment with abatacept and tocilizumab has been shown to be efficacious in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients refractory to tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi). However, reports on long term effectiveness in clinical practice are scarce. In this extension of previously published 48-week data1, we aimed to describe three-year drug survival and clinical response in RA patients treated with abatacept or tocilizumab in routine care, based on data from the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry
Methods:
In the DANBIO registry we identified 341 RA patients treated with abatacept and 790 RA patients treated with tocilizumab. The clinical effectiveness was assessed by drug survival and by changes since baseline in DAS28 and EULAR response rates after 48, 96 and 144 weeks. No imputation of missing values was done. No direct comparison of the 2 drugs was made.
Results:
Of the patients receiving abatacept or tocilizumab, respectively, 20%/25% (abatacept/tocilizumab) were male, median (interquartile range, IQR) age 55(47-64)/58(47-66) years, disease duration 4(1-11)/4(1-12) years and number of previous biological drugs 3(2-4)/2(2-3), >90%/>90% of patients, had previously received ≥1 TNFi.
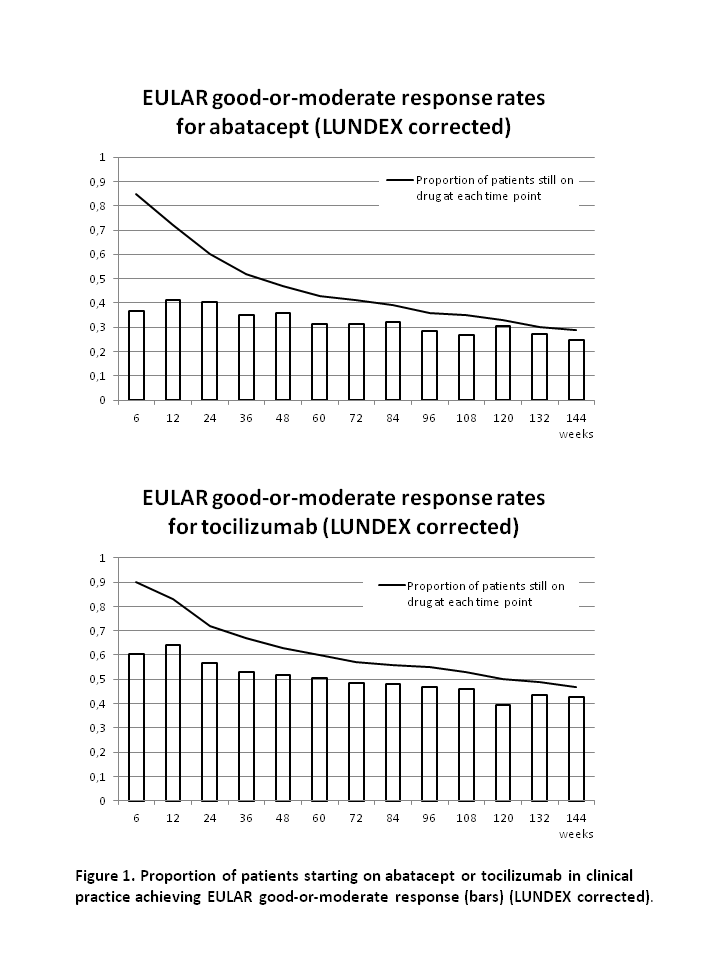
After 48, 96 and 144 weeks, the drug adherence to abatacept was 47%, 35% and 28% and to tocilizumab it was 61%, 54% and 47% (figure).
Median DAS28 at baseline, week 48, week 96 and week 144 in the abatacept group was 5.1, 3.3, 2.8 and 2.7 respectively, and 5.1, 2.6, 2.6 and 2.2 in the tocilizumab group.
At week 48, 96 and 144, the remission rates were 26%, 41% and 48% for abatacept and 47%, 45% and 63% for tocilizumab. Rates of good-or-moderate EULAR response at week 48, 96 and 144 was 76%, 79% and 85% for abatacept and 82%, 85% and 91% for tocilizumab. Response rates after correction for proportion of patients still on drug (LUNDEX values2) are presented in figure 1.
Conclusion:
In this study of RA patients whereof >90% were previous TNFi failures, 28% of patients who started abatacept and 47% who started tocilizumab still received the drug after 144 weeks. Good-or-moderate EULAR response was seen in the majority (85%-91%) of patients who still received the drugs after 144 weeks, reflecting that almost all patients with poor response was withdrawn from therapy. Due to the non-randomised study design, no direct comparison of the drugs was made.
Reference List
1. Leffers HC, Ostergaard M, Glintborg B et al. Efficacy of abatacept and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: results from the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70(7):1216-1222.
2. Kristensen LE, Saxne T, Geborek P. The LUNDEX, a new index of drug efficacy in clinical practice: results of a five-year observational study of treatment with infliximab and etanercept among rheumatoid arthritis patients in southern Sweden. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54(2):600-606.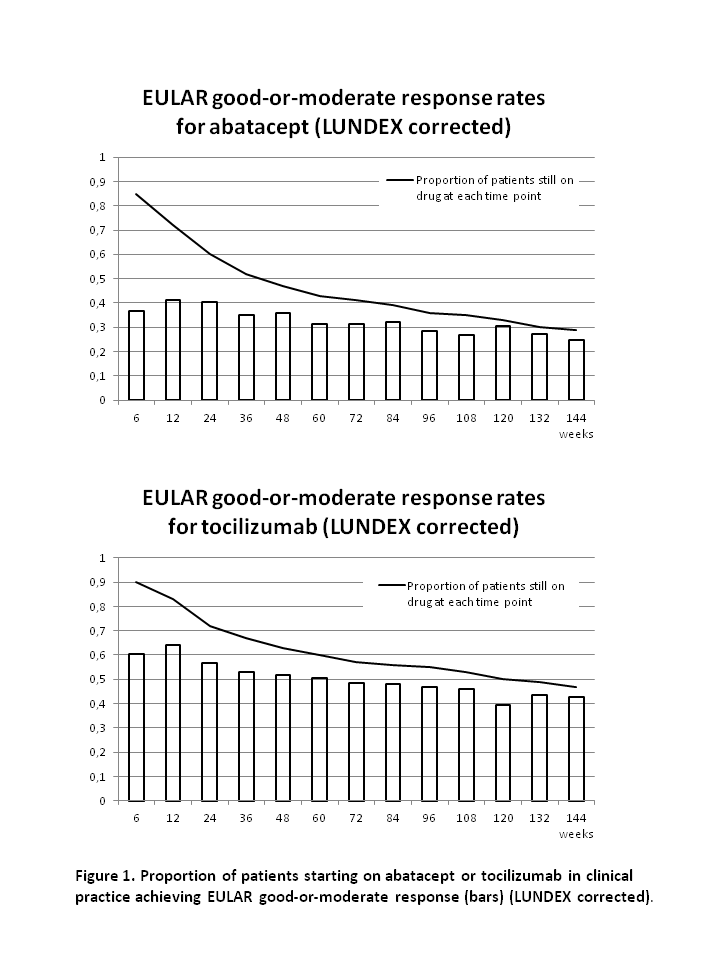
Disclosure:
H. Leffers,
None;
M. Østergaard,
Abbott, Pfizer, Centocor,
2,
Abbott Pfizer, Merck, Roche, UCB,
5,
Abbott, Pfizer, Merck, BMS, UCB, Mundipharma,
8;
B. Glintborg,
None;
N. S. Krogh,
None;
U. Tarp,
None;
T. Lorenzen,
Phizer, Roche,
6;
A. Hansen,
UCB, ABBVIE and MSD,
5;
L. Dreyer,
None;
M. L. Hetland,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Abbott, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, UCB,
8.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/three-year-drug-survival-and-effectiveness-of-abatacept-and-tocilizumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-in-routine-care-results-from-the-nationwide-danish-danbio-registry/
