Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2257–2325) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), a mainstay SLE therapy, improves survival and reduces flares. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) may be useful in 1) identifying and improving adherence issues, 2) titrating daily dose to achieve therapeutic benefits associated with whole blood HCQ >1000 ng/mL while 3) minimizing cumulative exposure by keeping levels < 2000 ng/mL.1,2Whole blood (WB) is the correct specimen because WB HCQ levels are higher than serum or plasma levels, more stable and reflective of the last month of HCQ ingestion, and are better correlated to efficacy and retinopathy risk.2 Here, we report WB HCQ of 10,463 clinical patient samples and their distribution according to therapeutic targets.
Methods: HCQ in whole blood is quantitated by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Recommended sample collection is ~ 3 – 6 months into regular stable dosing to reach steady state and correlate with clinical efficacy.
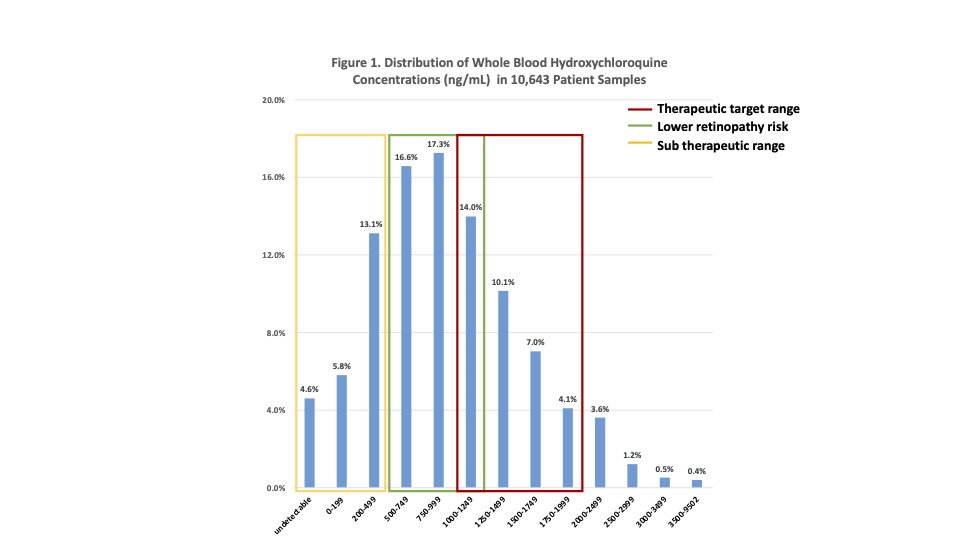
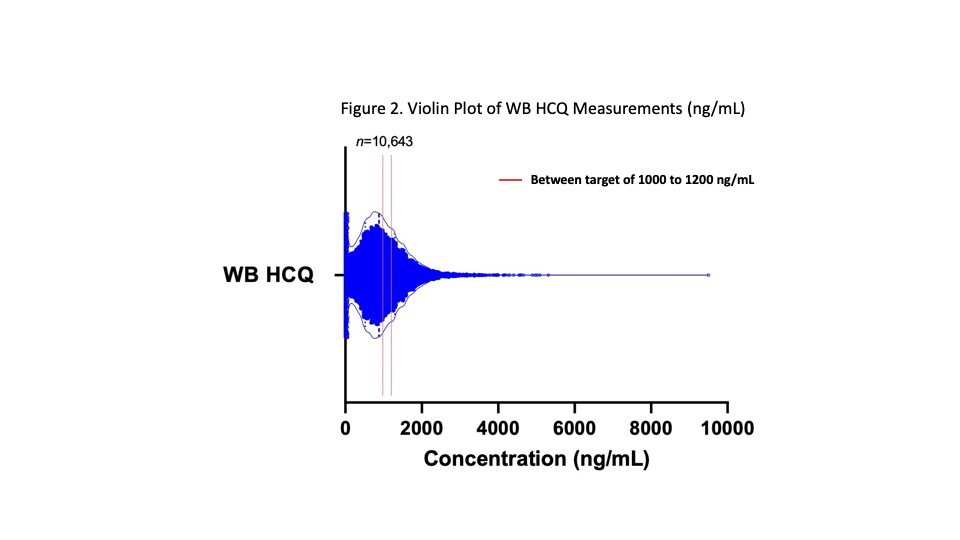
Results: Distribution of WB HCQ in 10,463 patient samples showed more than one-third (3752, 35.9%) were within the target range of > 1000 and < 2000 ng/mL (Figure 1); About one-quarter (2568, 24.5%) were within a tighter therapeutic target window of 1000 to 1500 ng/mL. The vast majority (9852, 94.2%,) of all WB HCQ were < 2000 ng/mL with a small percentage >2000 ng/mL (611, 5.8% between 2000 – 9502 ng/mL). About one-third (31.3%) were higher than 1177 ng/mL which corresponds to the upper tertile with higher retinopathy risk described by Petri et al.1 Adherence issues were evident in 10.5% (1102) with undetectable (483, 4.6%) and very low (< 200 ng/mL) drug (619, 5.9%) . Depending upon the target threshold, levels < 500 ng/mL or < 1000 ng/mL may be considered subtherapeutic as seen in 2498 (23.9%) and 4263 (40.7%) samples, respectively.
Conclusion: Due to wide pharmacokinetic variability and adherence issues, a given prescribed dose of HCQ does not correspond to WB HCQ, e.g. following 4, 5 or 6 mg/kg/day, levels are known to vary widely from subtherapeutic < 500 to >2000 ng/mL.2 Here, our clinical database reiterates this wide range in WB HCQ levels from undetectable (< 25) to 9502 ng/mL in 10,463 patient samples. One-quarter or one-third were within the therapeutic target range of 1000-1500 or 1000-200 ng/mL where >1000 has been associated with better disease control and survival. At the same time, levels less than 1177 avoid higher retinopathy risk (seen in green on Figure 1).1 A small percentage of samples, 5.8%, were higher than 2000 ng/mL, suggesting usefulness of TDM to fine tune daily dose. In 10%, there was evidence of poor adherence, with very low or nil drug, and one-quarter to 40% were subtherapeutic (< 500 or < 1000). The potential benefits of HCQ are many and include reduced flares and improved lupus nephritis, thrombosis risk, and long-term survival. At the same time, prescribed dose does not predict therapeutic levels. TDM-based counseling and dose adjustment may be instrumental in optimizing HCQ benefits while minimizing retinopathy risk.1,2 In conclusion, our analysis demonstrates the growing use of HCQ TDM to facilitate dose titration to safe and most effective target levels.
References 1)Durcan L, et al. J Rheumatol 2015, 42:2092–2097. 2)Petri M, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020, 72:448–453.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang J, Holmquist B, Punzalan R, Chun K. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM) of Hydroxychloroquine in Whole Blood: Analysis of over 10,000 Patient Results Using Lab Developed Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-drug-monitoring-tdm-of-hydroxychloroquine-in-whole-blood-analysis-of-over-10000-patient-results-using-lab-developed-liquid-chromatography-tandem-mass-spectrometry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-drug-monitoring-tdm-of-hydroxychloroquine-in-whole-blood-analysis-of-over-10000-patient-results-using-lab-developed-liquid-chromatography-tandem-mass-spectrometry/