Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 8, 2017
Title: Health Services Research II: Methods and Technology in Care and Research
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The Veterans Affairs (VA) Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (VARA) registry is an observational cohort study at 12 VA medical centers that prospectively collects clinical and laboratory outcome measures, which are recorded in the VARA database. To replace manual entry and reduce missing data, a Natural Language Processing (NLP) system was developed to extract outcome measures recorded in standardized text templates embedded in the electronic health record (EHR) notes for US Veterans enrolled in the registry. This study compared pre- and post-implementation experiences with this system.
Methods: VARA database entries for follow-up observations between January 1, 2016 and April 30, 2016 (pre-implementation) were compared to similar entries after NLP implementation January 1, 2017 to April 30, 2017 (post-implementation) with the number of notes containing outcome measures reported. Laboratory measure were automatically collected from EHR reports. At six VARA sites, missing data reports were provided to VARA investigators and clinic notes were reviewed to determine if outcome measures could be retrieved from documentation outside the standardized template. Note addendums were then entered to provide additional data when available.
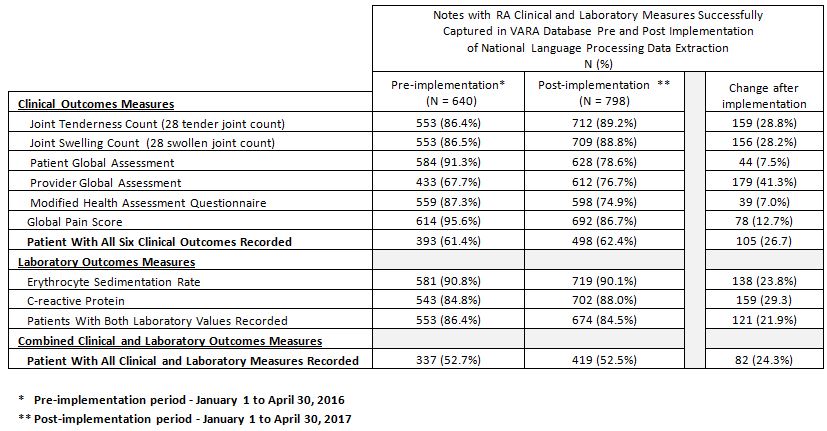
Results: In comparison to 640 notes on 540 patients from 8 VARA sites in the pre-implementation period, 798 notes on 671 unique patients were recorded in the VARA database from 11 VARA sites during the post-implementation period. This represents an increase of 24.7%, 24.3%, and 37.5% in the number of notes, unique patients captured, and sites engaged, respectively. This increase in data capture was much larger than the 8.3% increase in VARA patient enrollment during the same period. The successful capture of specific outcome measures is listed in the Table, which shows an absolute increase in all elements between observation periods. In a pilot effort to do data corrections at six VARA test sites, missing data on 31 notes were evaluated to see if corrections were possible. Investigators were able to retrieve additional information for 10 (32%) notes from data outside the standard template and use note addendums to report these data. An automated NLP extraction was then employed to add this additional information to the database. Permanently missing data were universally due to the failure to document information at the point-of-care, as opposed to failure of the algorithm.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that NLP can be leveraged in conjunction with standardized EHR templates to successfully retrieve patient data from across a national health care system, eliminate the need for manual data entry, and substantially increase the rate of data capture. By facilitating the collection of clinical and laboratory measures in RA patients, these efforts will further enhance the feasibility of conducting epidemiologic and outcomes studies of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cannon G, Rojas J, Bell N, Reimold A, Mikuls TR, Singh N, Kerr GS, Schwab P, Barton J, Caplan L, Baker J, Gaffo AL, Richards JS, Lazaro D, Majithia V, Sauer B. The Use of Natural Language Processing to Identify, Retrieve, Report, and Correct Observational Data on US Veterans Enrolled in the Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-use-of-natural-language-processing-to-identify-retrieve-report-and-correct-observational-data-on-us-veterans-enrolled-in-the-veterans-affairs-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-use-of-natural-language-processing-to-identify-retrieve-report-and-correct-observational-data-on-us-veterans-enrolled-in-the-veterans-affairs-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/