Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Progranulin (PGRN) and semaphorins (sema) are known to be involved in immune responses as well as bone remodeling process. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical significance of serum levels of PGRN, sema3A, and sema4D in patients with RA.
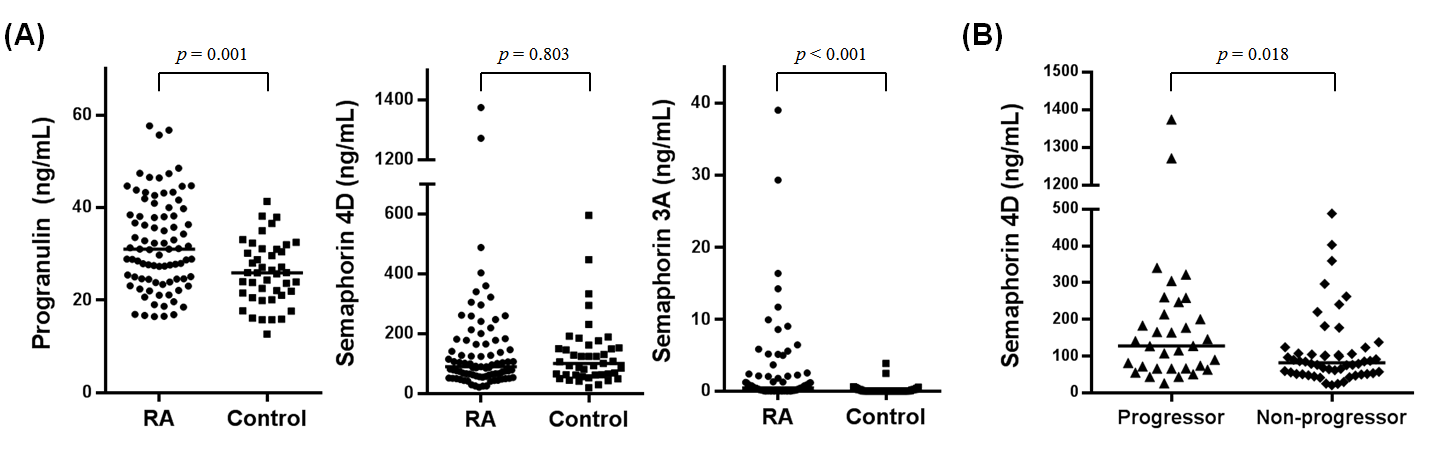
Methods: Blood samples were collected from 85 RA patients who satisfied 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA and 43 age- and gender-matched healthy controls. The serum levels of PGRN and sema3A/4D were determined using ELISA. Additionally, TNF-¥á, IL-6, IL-23, RANK ligand, osteoprotegerin, and osteopontin were measured using magnetic bead-based multiplex assays. RA disease activity was assessed by DAS28 and structural joint damage was assessed by plain radiographs using the modified Sharp/van der Heijder score (SHS) at baseline and after an average 2-year follow-up period. D SHS ¡Ã 1 unit/year was defined as having radiographic progression.
Results: Serum levels of PRGN were significantly increased in patients with RA, compared with healthy controls (31.0 [24.5-39.1] vs 25.9 [21.1-31.0] ng/mL, p=0.001), while those of sema4D did not differ between two groups. Although the serum levels of sema3A were below the detection range in most samples, the serum sema3A level in RA patients was significantly elevated in comparison with the level in the controls (0.44 [0-1.90] vs 0 [0-0.19] ng/mL, p<0.001). In RA patients, serum concentrations of sema4D were found to be correlated with those of IL-6 (¥ã=0.514, p<0.001) and IL-23 (¥ã=0.234, p=0.031) and PGRN was negatively correlated with osteopontin. Serum sema4D levels showed positive correlations with ESR (¥ã=0.336, p=0.002), CRP (¥ã=0.337, p=0.002), DAS28 (¥ã=0.240, p=0.029) and D SHS/year (¥ã=0.244, p=0.025). However, the levels of PGRN and sema3A were not associated with disease activity or joint damage. RA patients with radiographic progression had significantly higher serum sema4D levels than those without progression (127.5 [66.4-230.2] vs 81.9 [52.1-106.9] ng/mL, p=0.018).
Conclusion: Serum sema4D levels were associated with disease activity as well as radiographic progression in RA patients, although its levels were comparable between RA patients and controls. These findings suggest that sema4D might play a role in RA-related joint damage and is a possible biomarker reflecting inflammatory burden and radiographic progression in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim JH, Ha YJ, Chung SW, Kang EH, Song YW, Lee YJ. The Serum Levels of Semaphorin 4D Are Associated with Disease Activity As Well As Radiographic Progression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-serum-levels-of-semaphorin-4d-are-associated-with-disease-activity-as-well-as-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-serum-levels-of-semaphorin-4d-are-associated-with-disease-activity-as-well-as-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/