Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
The Role of Celastrol on Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Erosion in Collagen-Induced Arthritis
Background/Purpose: Celastrus and its extract have been proven effective for treatment Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Celastrol is one of bioactive component of Celastrus with a potent anti-inflammatory effect in RA therapy. However, the direct role of Celastrol on osteoclast remain unknown.
Objectives: To examine the effects of Celastrol on osteoclastogenesis in vitro and bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis(CIA).
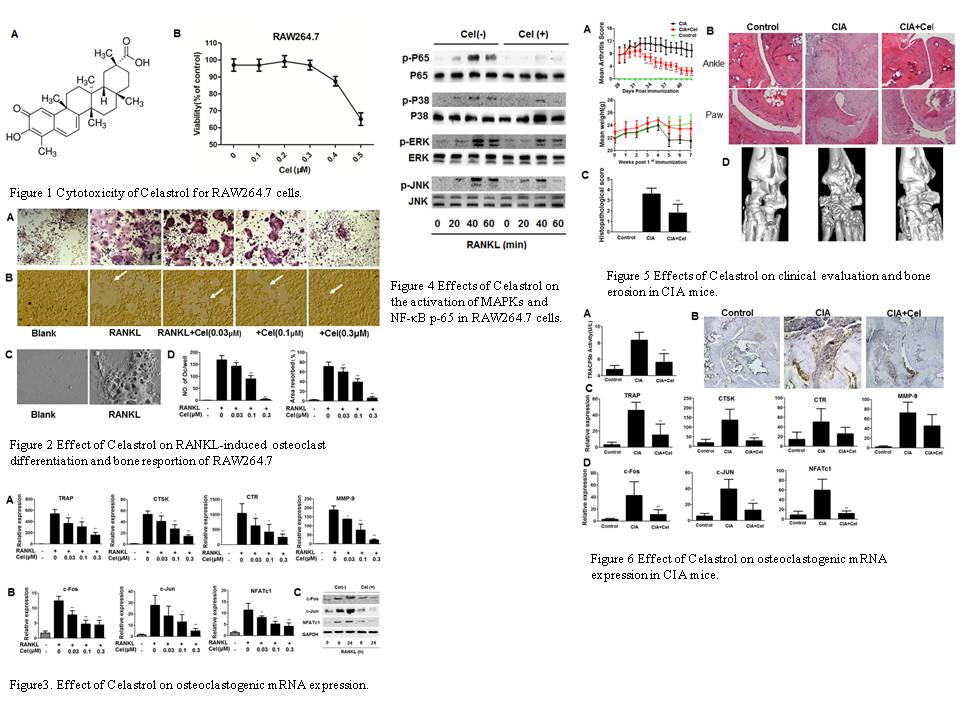
Methods: The roles of Celastrol on osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 was evaluatedby tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining, Real-Time PCR and Western-blot Activity of bone resorption was tested by pit formation assay in the presence or absence of Celastrol.CIA mice were by intraperitoneal injections(IP). The effects of Celastrol bone erosion was analyzed using ELISA, Real-Time PCR, histological analysis and Micro-CT.
Results: Celastrol inhibited RANKL-induced formation of TRAP+ multinucleated cells and bone-resorbing activity in a dose-dependent manner. The osteoclast formation was completely blocked with 0.3 µM of Celastrol. Celastrol reduced the RANKL-induced expression of NFATc1, c-Jun and c-Fos and phosphorylation of NF- ¦Ê B and MAPK signals in RAW264.7. In CIA mice, administration of Celastrol markedly supressed the arthritis score and reduced bone damage in the joints as demonstrated by histology and bone Micro-CT. Osteoclastic markers in the serum and joint tissues were significantly downregulated by Celastrol.
Conclusion: These findings suggests that Celastrol is a potent inhibitor of RANKL- induced bone resorption and has a potential therapeutic benefit in treating bone loss of rheumatoid arthritis or other bone diseases.
Disclosure:
K. Gan,
None;
W. Tan,
None;
M. Zhang,
None;
X. Feng,
None;
L. Xu,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-celastrol-on-osteoclastogenesis-and-bone-erosion-in-collagen-induced-arthritis/