Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Active tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most devastating side effects of biologic agents use. Several guidelines for the prevention of biologic agents-related infections have been published and recommended screening tests for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). However, the evidence for the repeated screening tests for LTBI in areas that have a high incidence of active TB and the incidence rate of positive conversion after starting biologic agents in patients with rheumatic diseases is lacking. The value of LTBI screening in non-TNF biologics and switching biologics use are also unknown. Herein, we repot the result of follow-up interferon-gamma-release assays (IGRAs) in patients with rheumatic disease receiving biologic agents.
Methods: We studied retrospectively all patients who had received biologic agents (TNF and non-TNF agents) for the treatment of rheumatic diseases in our department from April 2007 to March 2016. To evaluate the results of follow-up IGRAs for detection of latent and newly developing tuberculosis, 406 patients with various rheumatic diseases were screened prior to biologic therapy initiation for LTBI with T-SPOT.TB and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In Tube assays.
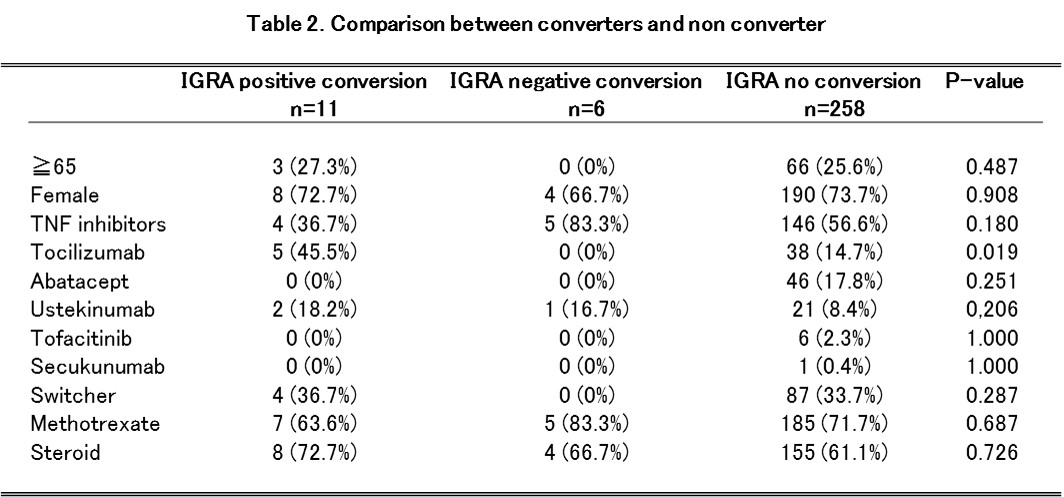
Results : We assessed 275 patients with follow-up IGRA tests. The analysis of the data showed 2.2% (n=6) of IGRA negative conversion and 4.0% (n=11) of IGRA positive conversion (Table 1). There was no difference in patientfs characteristics between converters and non-converter (Table 2). The incidence of active TB after starting biologic agents was 0 % in this study.
Conclusion : Although the evidence for the repeated IGRA and the positive conversion after starting biologic agents in patients with rheumatic diseases is lacking, follow-up IGRA test may be useful to prevent the activation of LTBI in areas that have a high incidence of active TB such as Japan. 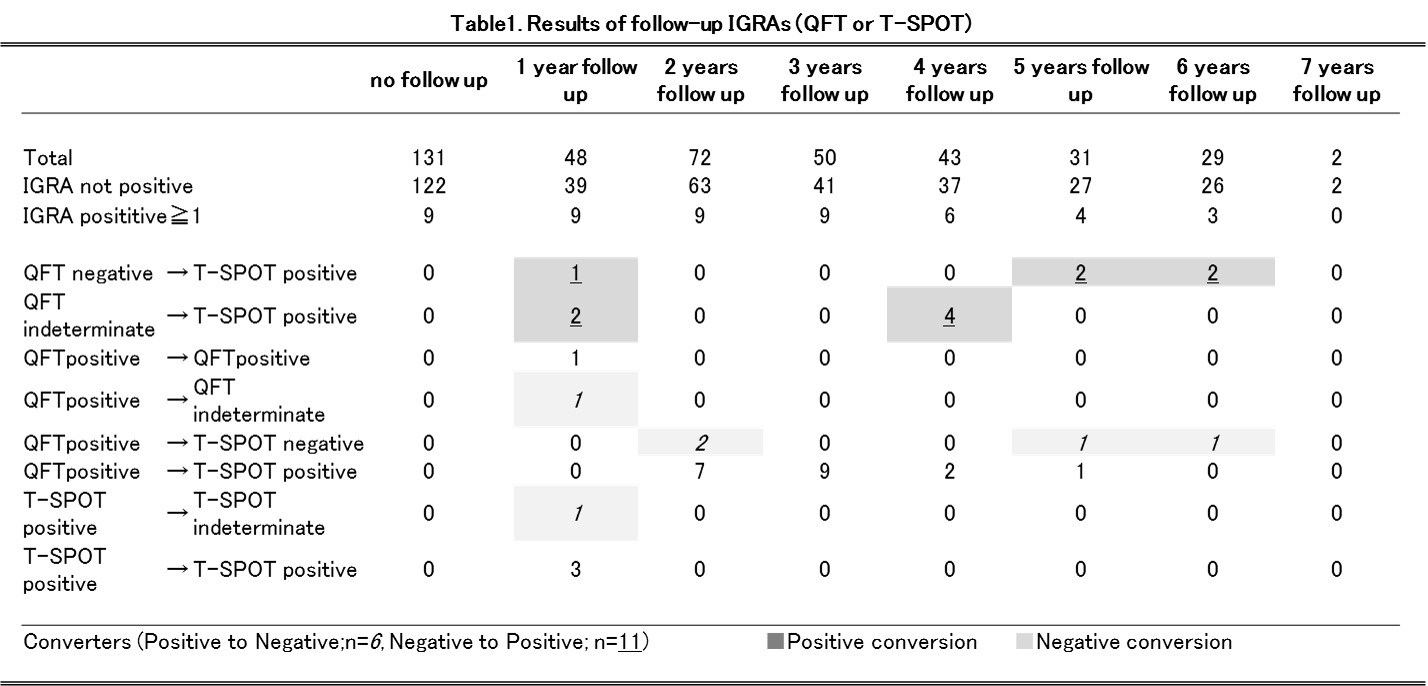
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Suyama Y, Sawada H, Ikeda Y, Kawato R, Tamaki S, Kishimoto M, Okada M. The Result of Follow-up Interferon-Gamma-Release Assays in Patients with Rheumatic Disease Receiving Biologic Agents in a Japanese Hospital [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-result-of-follow-up-interferon-gamma-release-assays-in-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-receiving-biologic-agents-in-a-japanese-hospital/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-result-of-follow-up-interferon-gamma-release-assays-in-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-receiving-biologic-agents-in-a-japanese-hospital/