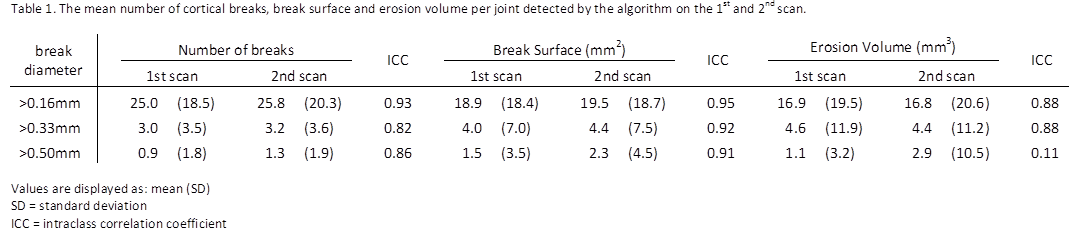Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In RA bone erosions are defined as cortical breaks with adjacent trabecular bone loss. High resolution peripheral quantitative CT (HR-pQCT) is more sensitive than conventional radiography in the detection of erosions in finger joints, but the scoring of erosions on acquired images was performed manually. We thus developed and validated a semi-automatic algorithm for HR-pQCT to detect cortical breaks and adjacent trabecular bone loss. The reproducibility of our algorithm on scan/re-scan (repositioning) data is presented in this study.
Methods: Twenty one subjects (mean (SD); age 49 (11) years) with 17 early RA (n=17, diagnosis <1 year) and undifferentiated arthritis (n=4) were studied. The 2nd and 3rd MCP joints were imaged by HR-pQCT (82µm nominal isotropic voxel size) twice on the same day with repositioning in between the scans. The semi-automatic algorithm was applied to the HR-pQCT images for the detection of cortical breaks. This included automatic detection of the outer contour of the bone, which was verified manually. A cortical mask of 0.33mm from this contour was selected and the remaining inner volume was considered trabecular bone. Cortical breaks with a diameter of >0.16mm, >0.33mm and >0.50mm and trabecular cavities >0.3mm in diameter were extracted, of which only those that were connected to a cortical break remained. Reproducibility for the number of breaks detected, break surface and erosion volumes was calculated per break diameter using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
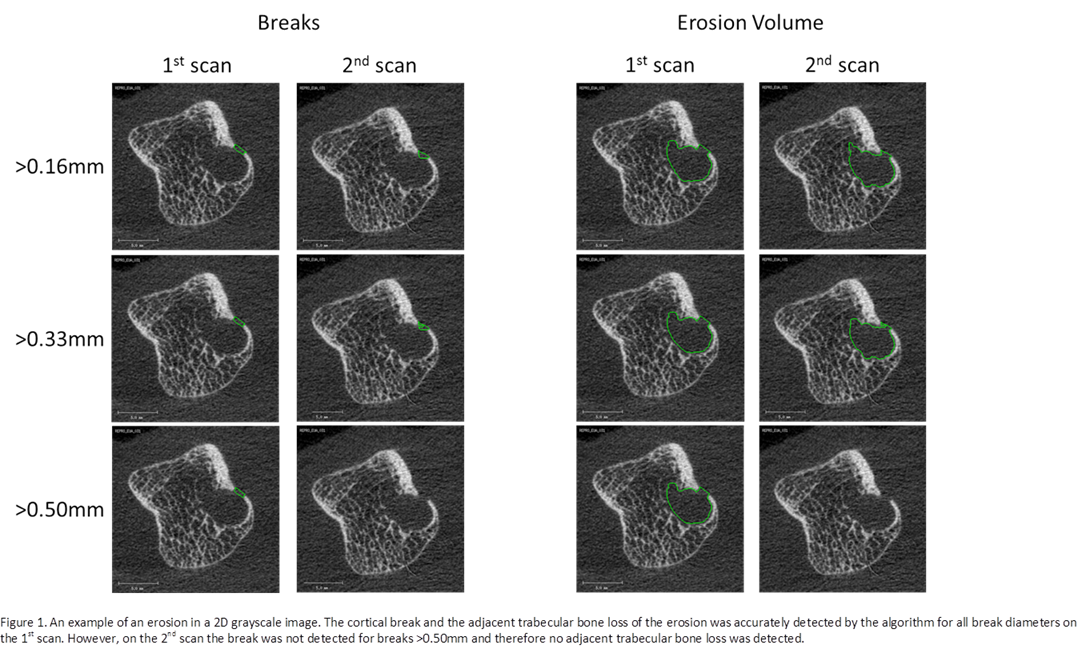
Results: The algorithm enabled detection of cortical breaks and adjacent trabecular bone loss (Fig. 1). The number of breaks, break surface and erosion volume per joint detected was dependent on the minimal break diameter (Table 1). Excellent reproducibility (ICC ≥0.82) was observed for all outcomes and all break diameters, with the exception of erosion volume for breaks >0.50mm (ICC=0.11). This is explained in figure 1 where an erosion was accurately detected on the 1st scan by all break diameters. However, on the 2nd scan the erosion was not detected for breaks >0.50mm. This subsequently leads to a high discrepancy in the erosion volume.
Conclusion: Our semi-automatic algorithm is highly reproducible in the detection of cortical breaks, break surface and erosion volume in repositioning data on HR-pQCT.The use of HR-pQCT in combination with our algorithm is therefore a promising tool for early detection and monitoring of erosions in finger joints.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peters M, de Jong J, Scharmga A, van Tubergen A, Loeffen D, Weijers R, van Rietbergen B, Boyd SK, Barnabe C, Stok KS, Geusens P, van den Bergh J. The Reproducibility of a Semi-Automatic Algorithm in the Detection of Cortical Breaks and Adjacent Trabecular Bone Loss in Scan-Rescan Data from Patients with Early Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-reproducibility-of-a-semi-automatic-algorithm-in-the-detection-of-cortical-breaks-and-adjacent-trabecular-bone-loss-in-scan-rescan-data-from-patients-with-early-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-reproducibility-of-a-semi-automatic-algorithm-in-the-detection-of-cortical-breaks-and-adjacent-trabecular-bone-loss-in-scan-rescan-data-from-patients-with-early-arthritis/